Implement stack using deque
Problem
A deque, also known as a double-ended queue, is a special kind of queue where insertions and deletions can be done at both the beginning and the end. A deque can be visualized as a linked list where each node points to the next node as well as the previous node, allowing constant time O(1) insertions and deletions at both ends.
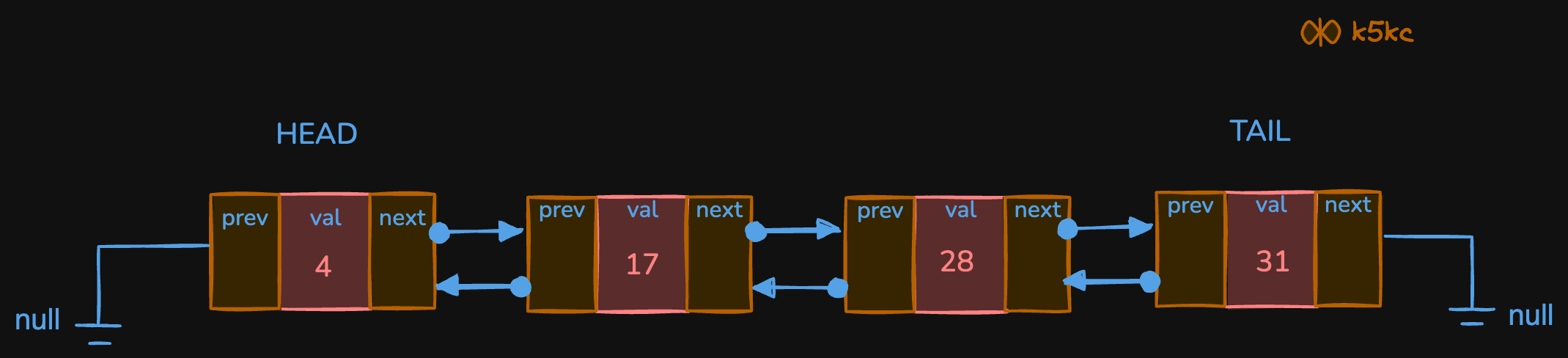
Now, deque can be used to implement a stack and queue. The task is to implement a stack using a deque.
A stack is a linear data structure that follows the Last In First Out (LIFO) principle. The stack operations to implement are:
push(x): Push elementxonto the stack.pop(): Removes the element on top of the stack and returns it.top(): Get the top element.isEmpty(): Return whether the stack is empty.
Examples
Example 1:
Input:
Operations: ["push(1)", "push(2)", "top()", "pop()", "isEmpty()"]
Output:
[null, null, 2, 2, false]
Explanation:
- push(1) adds 1 to the stack.
- push(2) adds 2 to the stack.
- top() returns the current top element, which is 2.
- pop() removes and returns the current top element, which is 2.
- isEmpty() returns false as the stack is not empty.
Solution
Method 1 - Using Deque
Given that a deque (double-ended queue) allows for insertion and deletion at both ends, we can map its operations to those of a stack and a queue appropriately. Here is a more structured explanation:
| Deque | Stack | Queue |
|---|---|---|
| size() | size()) | size() |
| isEmpty() | isEmpty() | isEmpty() |
| insertFirst() | ||
| insertLast() | push() | enqueue() |
| removeFirst() | dequeue() | |
| removeLast() | pop() |
Code
Java
In java we can use Deque implementations like LinkedList, ArrayDeque, etc.
public class Solution {
private Deque<Integer> deque;
public Solution() {
deque = new LinkedList<>();
}
// Push element x onto stack
public void push(int x) {
deque.addLast(x);
}
// Removes the element on top of the stack and returns it
public int pop() {
return deque.removeLast();
}
// Get the top element
public int top() {
return deque.peekLast();
}
// Return whether the stack is empty
public boolean isEmpty() {
return deque.isEmpty();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution stack = new Solution();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
System.out.println(stack.top()); // Outputs: 2
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // Outputs: 2
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty()); // Outputs: false
stack.push(5);
System.out.println(stack.pop()); // Outputs: 5
System.out.println(stack.isEmpty()); // Outputs: true
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.deque: deque[int] = deque()
def push(self, x: int) -> None:
self.deque.append(x)
def pop(self) -> int:
return self.deque.pop()
def top(self) -> int:
return self.deque[-1]
def isEmpty(self) -> bool:
return len(self.deque) == 0
# Example usage
stack = Solution()
stack.push(1)
stack.push(2)
print(stack.top()) # Outputs: 2
print(stack.pop()) # Outputs: 2
print(stack.isEmpty()) # Outputs: False
stack.push(5)
print(stack.pop()) # Outputs: 5
print(stack.isEmpty()) # Outputs: True