Add One Row to Tree
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given the root of a binary tree and two integers val and depth, add a row of nodes with value val at the given depth depth.
Note that the root node is at depth 1.
The adding rule is:
- Given the integer
depth, for each not null tree nodecurat the depthdepth - 1, create two tree nodes with valuevalascur's left subtree root and right subtree root. cur's original left subtree should be the left subtree of the new left subtree root.cur's original right subtree should be the right subtree of the new right subtree root.- If
depth == 1that means there is no depthdepth - 1at all, then create a tree node with valuevalas the new root of the whole original tree, and the original tree is the new root's left subtree.
Examples
Example 1:
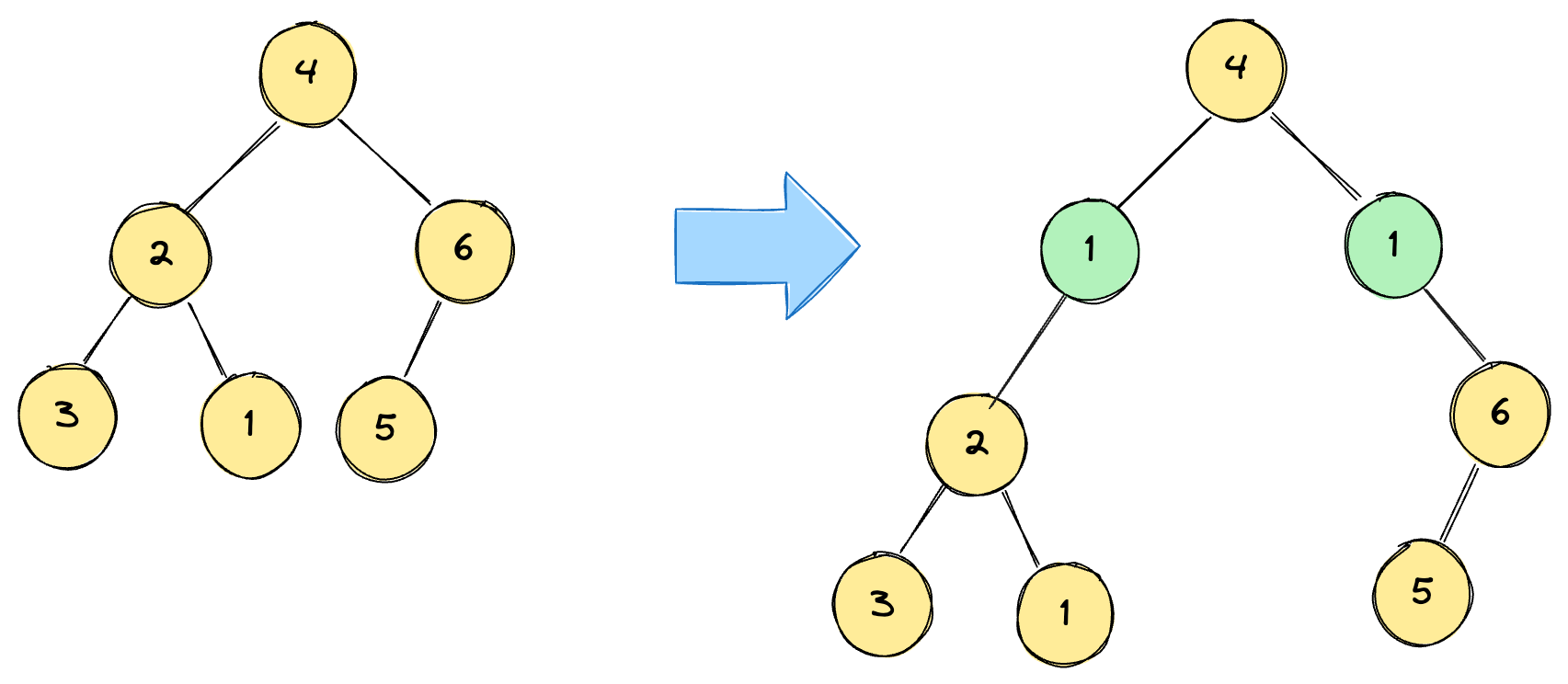
Input:
root = [4,2,6,3,1,5], val = 1, depth = 2
Output:
[4,1,1,2,null,null,6,3,1,5]
Example 2:
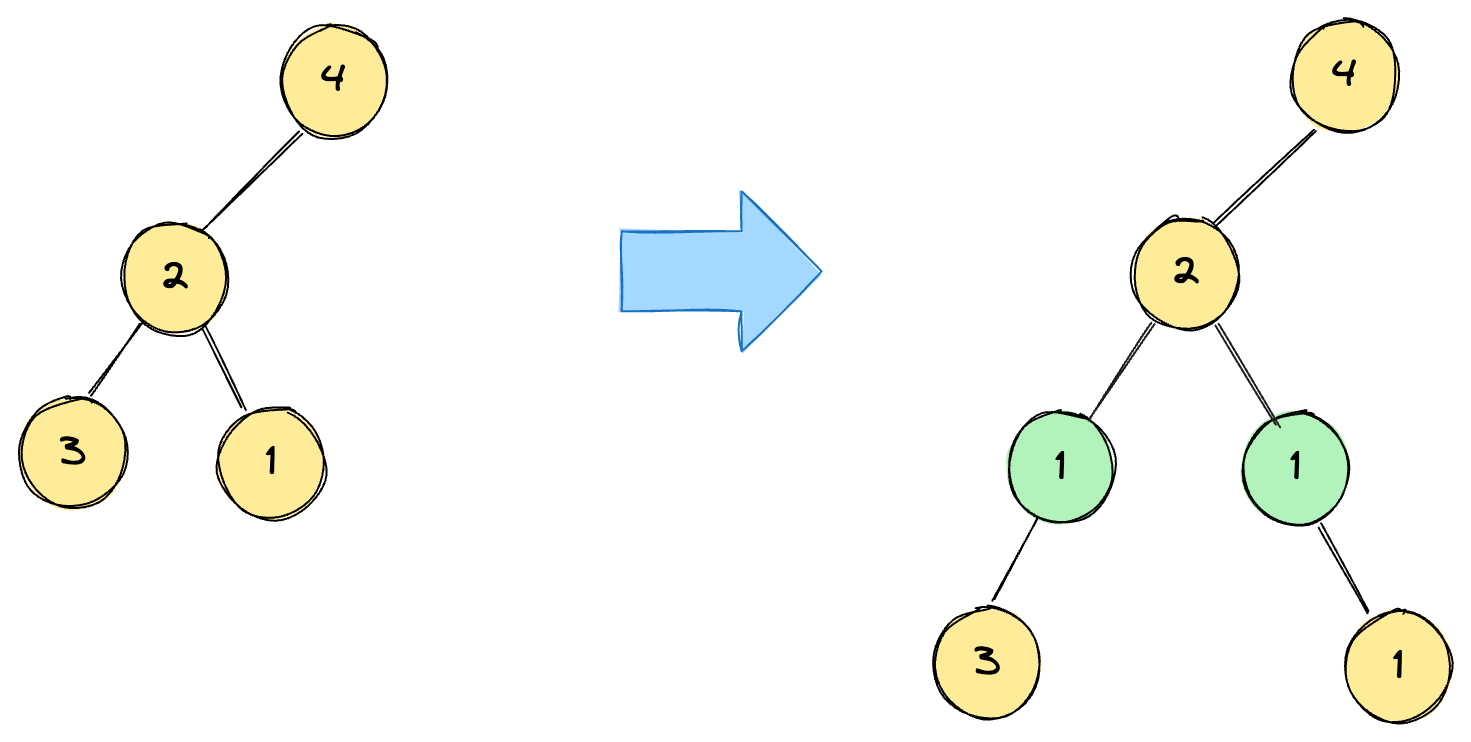
Input:
root = [4,2,null,3,1], val = 1, depth = 3
Output:
[4,2,null,1,1,3,null,null,1]
Solution
Method 1 - DFS
Base case
- If the root is null, we do nothing and simply return the root,
- If depth is 1, in that case we are adding a new node above current root. So, we should handle that
- If depth is 2, we just create 2 tree nodes, with left child being root’s left, and right child being root’s right.
- Then we also update root’s left and right to newly created nodes in respective order
- Otherwise, start traversing towards the depth of tree. As, we traverse 1 level lower, we reduce depth by 1
Code
Java
public TreeNode addOneRow(TreeNode root, int val, int depth) {
if (root == null) {
return root;
}
if (depth == 1) {
return new TreeNode(val, root, null);
} else if (depth == 2) {
root.left = new TreeNode(val, root.left, null);
root.right = new TreeNode(val, null, root.right);
}
addOneRow(root.left, val, depth - 1);
addOneRow(root.right, val, depth - 1);
return root;
}
Complexity
- Time:
O(n)where n is number of nodes in tree. - Space:
O(1)