Add Two Numbers represented as Linked List in Forward order
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
What if the digits are stored in regular order instead of reversed order?
Examples
Example 1:
Input:
l1: 1 -> 0 -> 0 -> 7
l2: 9 -> 3
Output: 1 -> 1 -> 0 -> 0
Explanation: Here are 2 numbers: 1007 and 93. On addition we get 1100.
Solution
Method 1 - Reverse the Lists
We can simple reverse the list, and then the problem becomes: [Add Two Numbers represented as Linked List in Reversed Order](add-two-numbers-represented-as-linked-list-in-reversed-order)
Code
Java
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
l1 = reverseIterative(l1);
l2 = reverseIterative(l2);
ListNode l3 = addTwoReversedNumbers(l1, l2);
l3 = reverseIterative(l3);
return l3;
}
Method 2 - Adding 0s to Shorter List
What if we don’t want to reverse the number?
The method involves the following steps:
- Measure the length of each list.
- If they differ, equalise their lengths by prepending nodes with value 0 to the shorter list.
- Initialize a new list with
newHead = null. - Utilize recursion to traverse both lists to the end, sum corresponding nodes, handle carry-over, and append nodes to the new list until the recursion completes.
Code
Java
public class AddLinkedListForwardOrder {
public int carry=0;
public Node newHead = null;
public Node add(Node h1, Node h2){
//first we will make sure that both the Linked list has same no of nodes
// to ensure that we will append 0 in front of shorter list
int h1Len = getLength(h1);
int h2Len = getLength(h2);
if(h1Len>h2Len){
int diff = h1Len-h2Len;
while(diff>0){
Node n = new Node(0);
n.next = h2;
h2=n;
diff--;
}
}
if(h1Len<h2Len){
int diff = h2Len-h1Len;
while(diff>0){
Node n = new Node(0);
n.next = h1;
h1=n;
diff--;
}
}
Node newHead = addBackRecursion(h1, h2);
//check for the carry forward, if not 0 then we need to create another node for the end
//example adding 1->1 and 9->9 then recursive function will return 0->0 and carry =1
if(carry!=0){
Node n = new Node(carry);
n.next = newHead;
newHead = n;
}
return newHead;
}
public Node addBackRecursion(Node h1, Node h2){
if(h1==null && h2==null){
return null;
}
addBackRecursion(h1.next, h2.next);
int a = h1.data + h2.data + carry;
carry=0;
//System.out.println(a);
if(a>=10){
carry =1;
a = a%10;
}
Node n = new Node(a);
if(newHead==null){
newHead =n;
}else{
n.next = newHead;
newHead = n;
}
//carry=0;
return newHead;
}
public int getLength(Node head){
int len=0;
while(head!=null){
len++;
head = head.next;
}
return len;
}
}
Method 3 - Add Two Lists and Normalize
- Input lists might have different sizes, so it's necessary to determine their lengths. Although one could normalise the lists by adding leading zeros to the shorter one, this would consume additional memory, so this step will be skipped.
- Iterate over the lists, calculate the sum of nodes, and place the result in a new list. The resulting list will be built in reverse order without tracking the carry value. See step 1 below in the diagram.
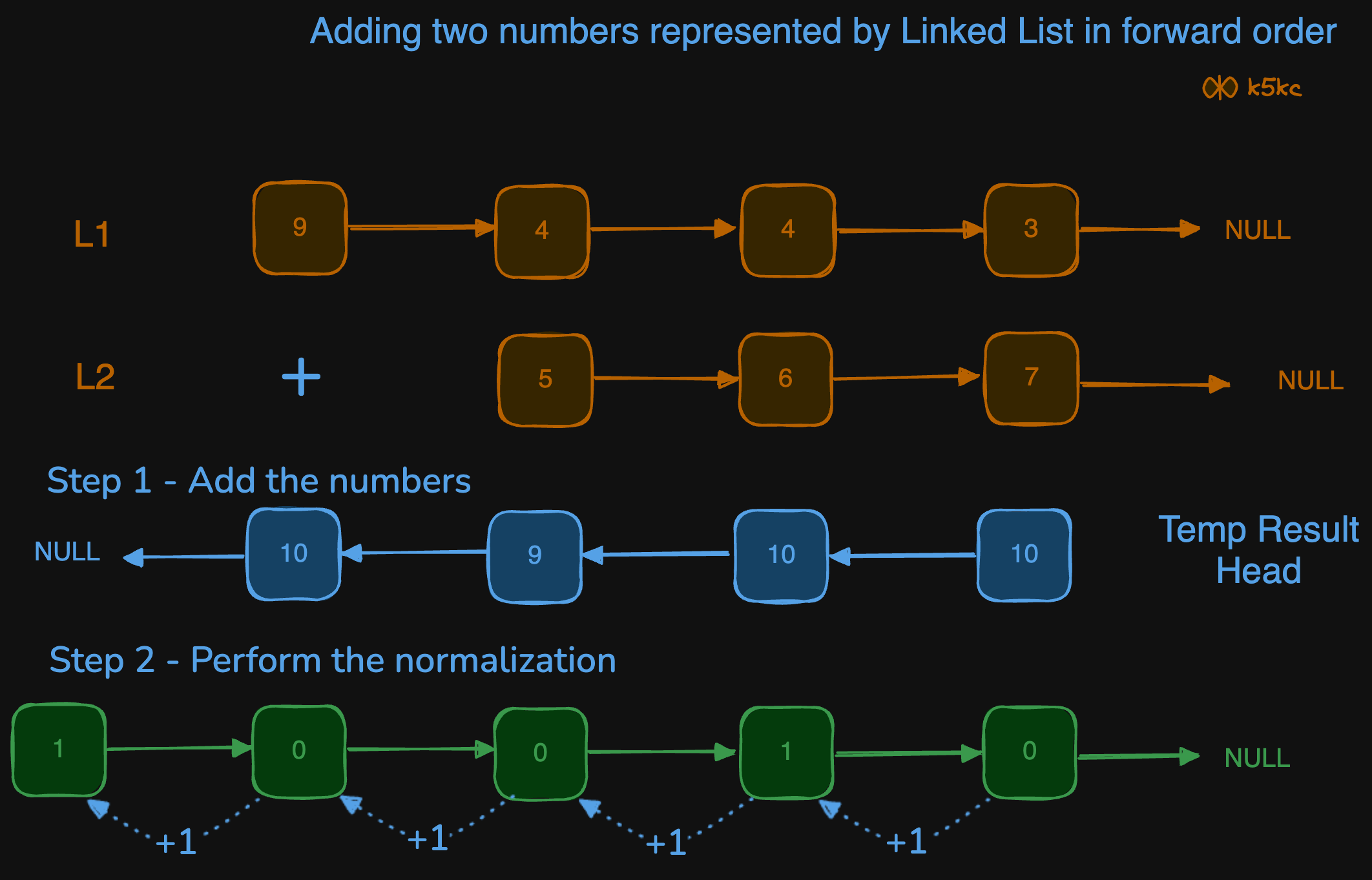
- Normalize the resulting list by traversing from the head (lowest order node), adjusting node values (
val % 10), storing the carry value, and reversing the list again. See step 2 in above diagram. - If the carry value is greater than zero after normalisation, create a new node and set it as the new head of the result list.
Code
Java
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
// We will use sizes to understand which list's nodes should be frozen for a while.
int s1 = size(l1);
int s2 = size(l2);
ListNode resHead = null;
ListNode n = null;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null) {
int v1 = 0;
int v2 = 0;
if (s1 >= s2) {
v1 = l1 != null ? l1.val : 0;
l1 = l1.next;
s1--;
}
// Comparing with s1 + 1 since s1 might be decremented previously
if (s2 >= s1 + 1) {
v2 = l2 != null ? l2.val : 0;
l2 = l2.next;
s2--;
}
// Creating the resulting list in the reversed order.
n = new ListNode(v1 + v2);
n.next = resHead;
resHead = n;
}
int carry = 0;
resHead = null;
// Now, let's perform the normalization.
while (n != null) {
n.val += carry;
if (n.val >= 10) {
n.val = n.val % 10;
carry = 1;
} else {
carry = 0;
}
ListNode buf = n.next;
n.next = resHead;
resHead = n;
n = buf;
}
if (carry > 0) {
n = new ListNode(1);
n.next = resHead;
resHead = n;
}
return resHead;
}
private int size(ListNode l) {
int s = 0;
while (l != null) {
l = l.next;
s++;
}
return s;
}