All Paths from Source to Target
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a directed acyclic graph (DAG) of n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1, find all possible paths from node 0 to node n - 1 and return them in any order.
The graph is given as follows: graph[i] is a list of all nodes you can visit from node i (i.e., there is a directed edge from node i to node graph[i][j]).
Examples
Example 1:
graph LR 0 --> 1 & 2--> 3
Input:
graph = [[1,2],[3],[3],[]]
Output:
[[0,1,3],[0,2,3]]
Explanation: There are two paths: 0 -> 1 -> 3 and 0 -> 2 -> 3.
Example 2:
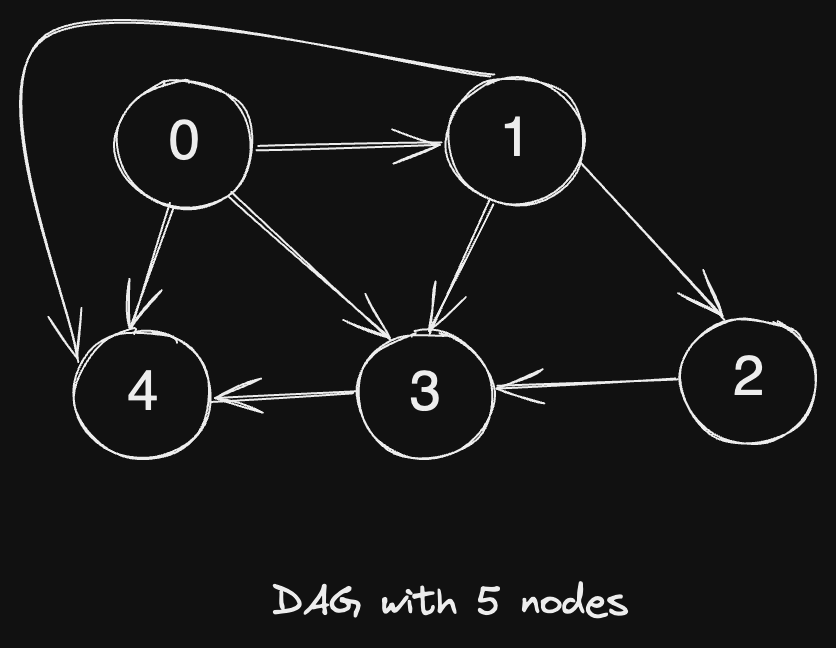
Input:
graph = [[4,3,1],[3,2,4],[3],[4],[]]
Output:
[[0,4],[0,3,4],[0,1,3,4],[0,1,2,3,4],[0,1,4]]
Solution
Method 1 – Backtracking (DFS)
Intuition
The key idea is to use depth-first search (DFS) to explore all possible paths from the source (node 0) to the target (node n-1). At each node, recursively visit all its neighbors, building up the current path. When the target is reached, add the path to the answer.
Approach
- Start DFS from node 0 with an empty path.
- At each node, add it to the current path.
- If the node is the target (n-1), add a copy of the path to the answer.
- Otherwise, recursively visit all neighbors.
- Backtrack by removing the node from the path after visiting neighbors.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> allPathsSourceTarget(vector<vector<int>>& graph) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> path;
function<void(int)> dfs = [&](int u) {
path.push_back(u);
if (u == graph.size() - 1) ans.push_back(path);
else for (int v : graph[u]) dfs(v);
path.pop_back();
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
};
Go
func allPathsSourceTarget(graph [][]int) [][]int {
var ans [][]int
var path []int
var dfs func(int)
dfs = func(u int) {
path = append(path, u)
if u == len(graph)-1 {
tmp := make([]int, len(path))
copy(tmp, path)
ans = append(ans, tmp)
} else {
for _, v := range graph[u] {
dfs(v)
}
}
path = path[:len(path)-1]
}
dfs(0)
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> allPathsSourceTarget(int[][] graph) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
dfs(0, graph, path, ans);
return ans;
}
private void dfs(int u, int[][] graph, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> ans) {
path.add(u);
if (u == graph.length - 1) ans.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
else for (int v : graph[u]) dfs(v, graph, path, ans);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun allPathsSourceTarget(graph: Array<IntArray>): List<List<Int>> {
val ans = mutableListOf<List<Int>>()
val path = mutableListOf<Int>()
fun dfs(u: Int) {
path.add(u)
if (u == graph.size - 1) ans.add(path.toList())
else for (v in graph[u]) dfs(v)
path.removeAt(path.size - 1)
}
dfs(0)
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def allPathsSourceTarget(self, graph: list[list[int]]) -> list[list[int]]:
ans = []
path = []
def dfs(u: int):
path.append(u)
if u == len(graph) - 1:
ans.append(path[:])
else:
for v in graph[u]:
dfs(v)
path.pop()
dfs(0)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn all_paths_source_target(graph: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
fn dfs(u: usize, graph: &Vec<Vec<i32>>, path: &mut Vec<i32>, ans: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) {
path.push(u as i32);
if u == graph.len() - 1 {
ans.push(path.clone());
} else {
for &v in &graph[u] {
dfs(v as usize, graph, path, ans);
}
}
path.pop();
}
let mut ans = vec![];
let mut path = vec![];
dfs(0, &graph, &mut path, &mut ans);
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
allPathsSourceTarget(graph: number[][]): number[][] {
const ans: number[][] = [];
const path: number[] = [];
const dfs = (u: number) => {
path.push(u);
if (u === graph.length - 1) ans.push([...path]);
else for (const v of graph[u]) dfs(v);
path.pop();
};
dfs(0);
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(2^n * n), since in the worst case (complete DAG), there are up to 2^(n-1) paths, each of length up to n. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(2^n * n), for storing all paths and recursion stack.