Allocate Mailboxes
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given the array houses where houses[i] is the location of the ith house along a street and an integer k, allocate k mailboxes in the street.
Return the minimum total distance between each house and its nearest mailbox.
The test cases are generated so that the answer fits in a 32-bit integer.
Examples
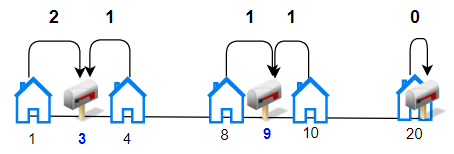
Example 1
Input: houses = [1,4,8,10,20], k = 3
Output: 5
Explanation: Allocate mailboxes in position 3, 9 and 20.
Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is |3-1| + |4-3| + |9-8| + |10-9| + |20-20| = 5
Example 2
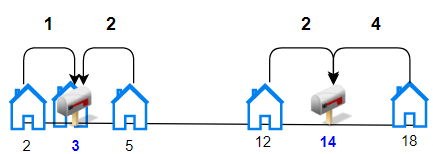
Input: houses = [2,3,5,12,18], k = 2
Output: 9
Explanation: Allocate mailboxes in position 3 and 14.
Minimum total distance from each houses to nearest mailboxes is |2-3| + |3-3| + |5-3| + |12-14| + |18-14| = 9.
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming with Median Preprocessing
Intuition
The key idea is that for any group of houses, placing a mailbox at the median minimizes the sum of distances. We use dynamic programming to partition the houses into k groups, each covered by a mailbox, and minimize the total distance.
Approach
- Sort the Houses: Sorting ensures we can efficiently compute medians and groupings.
- Precompute Costs: For every subarray
[i, j], compute the minimum distance to cover housesitojwith one mailbox (at the median). - DP Definition: Let
dp[i][k]be the minimum total distance to allocatekmailboxes among the firstihouses. - DP Transition: For each
iandk, try placing the last mailbox covering housesjtoi-1and combine with the best solution fork-1mailboxes among the firstjhouses. - Initialization:
dp[0][0] = 0(zero houses, zero mailboxes). - Result: The answer is
dp[n][k], wherenis the number of houses.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int minDistance(vector<int>& h, int k) {
int n = h.size();
sort(h.begin(), h.end());
vector<vector<int>> cost(n, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2, c = 0;
for (int x = i; x <= j; ++x)
c += abs(h[x] - h[m]);
cost[i][j] = c;
}
vector<vector<int>> dp(n + 1, vector<int>(k + 1, 1e9));
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int m = 1; m <= k; ++m)
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
dp[i][m] = min(dp[i][m], dp[j][m - 1] + cost[j][i - 1]);
return dp[n][k];
}
};
Go
func minDistance(h []int, k int) int {
n := len(h)
sort.Ints(h)
cost := make([][]int, n)
for i := range cost {
cost[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := i; j < n; j++ {
m := (i + j) / 2
c := 0
for x := i; x <= j; x++ {
c += abs(h[x] - h[m])
}
cost[i][j] = c
}
}
dp := make([][]int, n+1)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([]int, k+1)
for j := range dp[i] {
dp[i][j] = 1e9
}
}
dp[0][0] = 0
for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {
for m := 1; m <= k; m++ {
for j := 0; j < i; j++ {
if dp[j][m-1]+cost[j][i-1] < dp[i][m] {
dp[i][m] = dp[j][m-1] + cost[j][i-1]
}
}
}
}
return dp[n][k]
}
func abs(a int) int {
if a < 0 {
return -a
}
return a
}
Java
class Solution {
public int minDistance(int[] h, int k) {
int n = h.length;
Arrays.sort(h);
int[][] cost = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
for (int j = i; j < n; ++j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2, c = 0;
for (int x = i; x <= j; ++x)
c += Math.abs(h[x] - h[m]);
cost[i][j] = c;
}
int[][] dp = new int[n + 1][k + 1];
for (int[] row : dp)
Arrays.fill(row, 1000000000);
dp[0][0] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
for (int m = 1; m <= k; ++m)
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j)
dp[i][m] = Math.min(dp[i][m], dp[j][m - 1] + cost[j][i - 1]);
return dp[n][k];
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun minDistance(h: IntArray, k: Int): Int {
val n = h.size
h.sort()
val cost = Array(n) { IntArray(n) }
for (i in 0 until n)
for (j in i until n) {
val m = (i + j) / 2
var c = 0
for (x in i..j)
c += kotlin.math.abs(h[x] - h[m])
cost[i][j] = c
}
val dp = Array(n + 1) { IntArray(k + 1) { 1_000_000_000 } }
dp[0][0] = 0
for (i in 1..n)
for (m in 1..k)
for (j in 0 until i)
dp[i][m] = minOf(dp[i][m], dp[j][m - 1] + cost[j][i - 1])
return dp[n][k]
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def minDistance(self, h: list[int], k: int) -> int:
n = len(h)
h.sort()
cost = [[0] * n for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i, n):
m = (i + j) // 2
cost[i][j] = sum(abs(h[x] - h[m]) for x in range(i, j + 1))
dp = [[float('inf')] * (k + 1) for _ in range(n + 1)]
dp[0][0] = 0
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for m in range(1, k + 1):
for j in range(i):
dp[i][m] = min(dp[i][m], dp[j][m - 1] + cost[j][i - 1])
return dp[n][k]
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn min_distance(mut h: Vec<i32>, k: i32) -> i32 {
let n = h.len();
h.sort();
let mut cost = vec![vec![0; n]; n];
for i in 0..n {
for j in i..n {
let m = (i + j) / 2;
let mut c = 0;
for x in i..=j {
c += (h[x] - h[m]).abs();
}
cost[i][j] = c;
}
}
let mut dp = vec![vec![1_000_000_000; (k + 1) as usize]; n + 1];
dp[0][0] = 0;
for i in 1..=n {
for m in 1..=k as usize {
for j in 0..i {
dp[i][m] = dp[i][m].min(dp[j][m - 1] + cost[j][i - 1]);
}
}
}
dp[n][k as usize]
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^3)(due to three nested loops for DP and cost preprocessing) - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n^2)(for cost and DP tables)