Average Height of Buildings in Each Segment
Problem
A perfectly straight street is represented by a number line. The street has building(s) on it and is represented by a 2D integer array buildings, where buildings[i] = [starti, endi, heighti]. This means that there is a building with heighti in the half-closed segment [starti, endi).
You want to describe the heights of the buildings on the street with the minimum number of non-overlapping segments. The street can be represented by the 2D integer array street where street[j] = [leftj, rightj, averagej] describes a half-closed segment [leftj, rightj) of the road where the average heights of the buildings in thesegment is averagej.
- For example, if
buildings = [[1,5,2],[3,10,4]],the street could be represented bystreet = [[1,3,2],[3,5,3],[5,10,4]]because:- From 1 to 3, there is only the first building with an average height of
2 / 1 = 2. - From 3 to 5, both the first and the second building are there with an average height of
(2+4) / 2 = 3. - From 5 to 10, there is only the second building with an average height of
4 / 1 = 4.
- From 1 to 3, there is only the first building with an average height of
Given buildings, return the 2D integer arraystreet as described above (excluding any areas of the street where there are no buldings). You may return the array in any order.
The average of n elements is the sum of the n elements divided (integer division) by n.
A half-closed segment [a, b) is the section of the number line between points a and b including point a and not including point b.
Examples
Example 1:
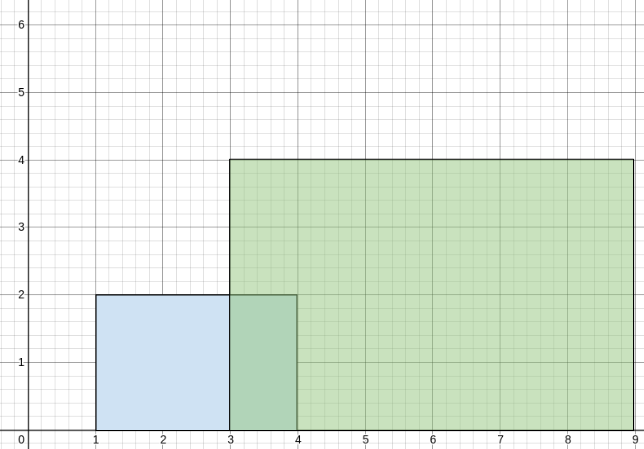
Input: buildings = [[1,4,2],[3,9,4]]
Output: [[1,3,2],[3,4,3],[4,9,4]]
Explanation:
From 1 to 3, there is only the first building with an average height of 2 / 1 = 2.
From 3 to 4, both the first and the second building are there with an average height of (2+4) / 2 = 3.
From 4 to 9, there is only the second building with an average height of 4 / 1 = 4.
Example 2:
Input: buildings = [[1,3,2],[2,5,3],[2,8,3]]
Output: [[1,3,2],[3,8,3]]
Explanation:
From 1 to 2, there is only the first building with an average height of 2 / 1 = 2.
From 2 to 3, all three buildings are there with an average height of (2+3+3) / 3 = 2.
From 3 to 5, both the second and the third building are there with an average height of (3+3) / 2 = 3.
From 5 to 8, there is only the last building with an average height of 3 / 1 = 3.
The average height from 1 to 3 is the same so we can group them into one segment.
The average height from 3 to 8 is the same so we can group them into one segment.
Example 3:
Input: buildings = [[1,2,1],[5,6,1]]
Output: [[1,2,1],[5,6,1]]
Explanation:
From 1 to 2, there is only the first building with an average height of 1 / 1 = 1.
From 2 to 5, there are no buildings, so it is not included in the output.
From 5 to 6, there is only the second building with an average height of 1 / 1 = 1.
We cannot group the segments together because an empty space with no buildings seperates the segments.
Constraints:
1 <= buildings.length <= 10^5buildings[i].length == 30 <= starti < endi <= 10^81 <= heighti <= 10^5
Solution
Method 1 – Sweep Line with Segment Merging
Intuition
We treat each building's start and end as events, and use a sweep line to track the total height and count of active buildings. For each interval between events, we compute the average height. If consecutive intervals have the same average, we merge them.
Approach
- For each building
[start, end, height], add two events:(start, +height, +1)and(end, -height, -1). - Sort all events by position.
- Sweep through the events:
- At each event, update the total height and count.
- For each segment between two events, if count > 0, compute the average height and record the segment.
- Merge consecutive segments with the same average height.
- Return the merged segments.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> averageHeightOfBuildings(vector<vector<int>>& buildings) {
vector<tuple<int,int,int>> events;
for (auto& b : buildings) {
events.emplace_back(b[0], b[2], 1);
events.emplace_back(b[1], -b[2], -1);
}
sort(events.begin(), events.end());
int prev = -1, h = 0, cnt = 0;
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (auto& [pos, dh, dc] : events) {
if (prev != -1 && cnt > 0 && prev < pos) {
int avg = h / cnt;
if (!ans.empty() && ans.back()[2] == avg && ans.back()[1] == prev) {
ans.back()[1] = pos;
} else {
ans.push_back({prev, pos, avg});
}
}
h += dh;
cnt += dc;
prev = pos;
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
type event struct{pos, dh, dc int}
func averageHeightOfBuildings(buildings [][]int) [][]int {
var events []event
for _, b := range buildings {
events = append(events, event{b[0], b[2], 1})
events = append(events, event{b[1], -b[2], -1})
}
sort.Slice(events, func(i, j int) bool { return events[i].pos < events[j].pos })
var ans [][]int
prev, h, cnt := -1, 0, 0
for _, e := range events {
if prev != -1 && cnt > 0 && prev < e.pos {
avg := h / cnt
if len(ans) > 0 && ans[len(ans)-1][2] == avg && ans[len(ans)-1][1] == prev {
ans[len(ans)-1][1] = e.pos
} else {
ans = append(ans, []int{prev, e.pos, avg})
}
}
h += e.dh
cnt += e.dc
prev = e.pos
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> averageHeightOfBuildings(int[][] buildings) {
List<int[]> events = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] b : buildings) {
events.add(new int[]{b[0], b[2], 1});
events.add(new int[]{b[1], -b[2], -1});
}
events.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int prev = -1, h = 0, cnt = 0;
for (int[] e : events) {
int pos = e[0], dh = e[1], dc = e[2];
if (prev != -1 && cnt > 0 && prev < pos) {
int avg = h / cnt;
if (!ans.isEmpty() && ans.get(ans.size()-1).get(2) == avg && ans.get(ans.size()-1).get(1) == prev) {
ans.get(ans.size()-1).set(1, pos);
} else {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(prev, pos, avg));
}
}
h += dh;
cnt += dc;
prev = pos;
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun averageHeightOfBuildings(buildings: Array<IntArray>): List<List<Int>> {
val events = mutableListOf<Triple<Int,Int,Int>>()
for (b in buildings) {
events.add(Triple(b[0], b[2], 1))
events.add(Triple(b[1], -b[2], -1))
}
events.sortBy { it.first }
val ans = mutableListOf<List<Int>>()
var prev = -1; var h = 0; var cnt = 0
for ((pos, dh, dc) in events) {
if (prev != -1 && cnt > 0 && prev < pos) {
val avg = h / cnt
if (ans.isNotEmpty() && ans.last()[2] == avg && ans.last()[1] == prev) {
ans.last()[1] = pos
} else {
ans.add(mutableListOf(prev, pos, avg))
}
}
h += dh
cnt += dc
prev = pos
}
return ans
}
}
Python
from typing import List
class Solution:
def averageHeightOfBuildings(self, buildings: List[List[int]]) -> List[List[int]]:
events = []
for s, e, h in buildings:
events.append((s, h, 1))
events.append((e, -h, -1))
events.sort()
ans: list[list[int]] = []
prev, total, cnt = -1, 0, 0
for pos, dh, dc in events:
if prev != -1 and cnt > 0 and prev < pos:
avg = total // cnt
if ans and ans[-1][2] == avg and ans[-1][1] == prev:
ans[-1][1] = pos
else:
ans.append([prev, pos, avg])
total += dh
cnt += dc
prev = pos
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn average_height_of_buildings(buildings: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut events = vec![];
for b in &buildings {
events.push((b[0], b[2], 1));
events.push((b[1], -b[2], -1));
}
events.sort();
let mut ans = vec![];
let (mut prev, mut h, mut cnt) = (-1, 0, 0);
for (pos, dh, dc) in events {
if prev != -1 && cnt > 0 && prev < pos {
let avg = h / cnt;
if let Some(last) = ans.last_mut() {
if last[2] == avg && last[1] == prev {
last[1] = pos;
prev = pos;
h += dh;
cnt += dc;
continue;
}
}
ans.push(vec![prev, pos, avg]);
}
h += dh;
cnt += dc;
prev = pos;
}
ans
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity: O(N log N), where N is the number of events (2 * buildings.length).
- 🧺 Space complexity: O(N) for storing events and the answer.