Binary Tree Left Side View
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Problem
Given the root of a binary tree, imagine yourself standing on the left side of it. Return the values of the nodes you can see ordered from top to bottom.
What is Left View of a Binary Tree?
When just look at the tree from the left side , all the nodes you can see will be the left view of the tree.
Examples
Example 1:
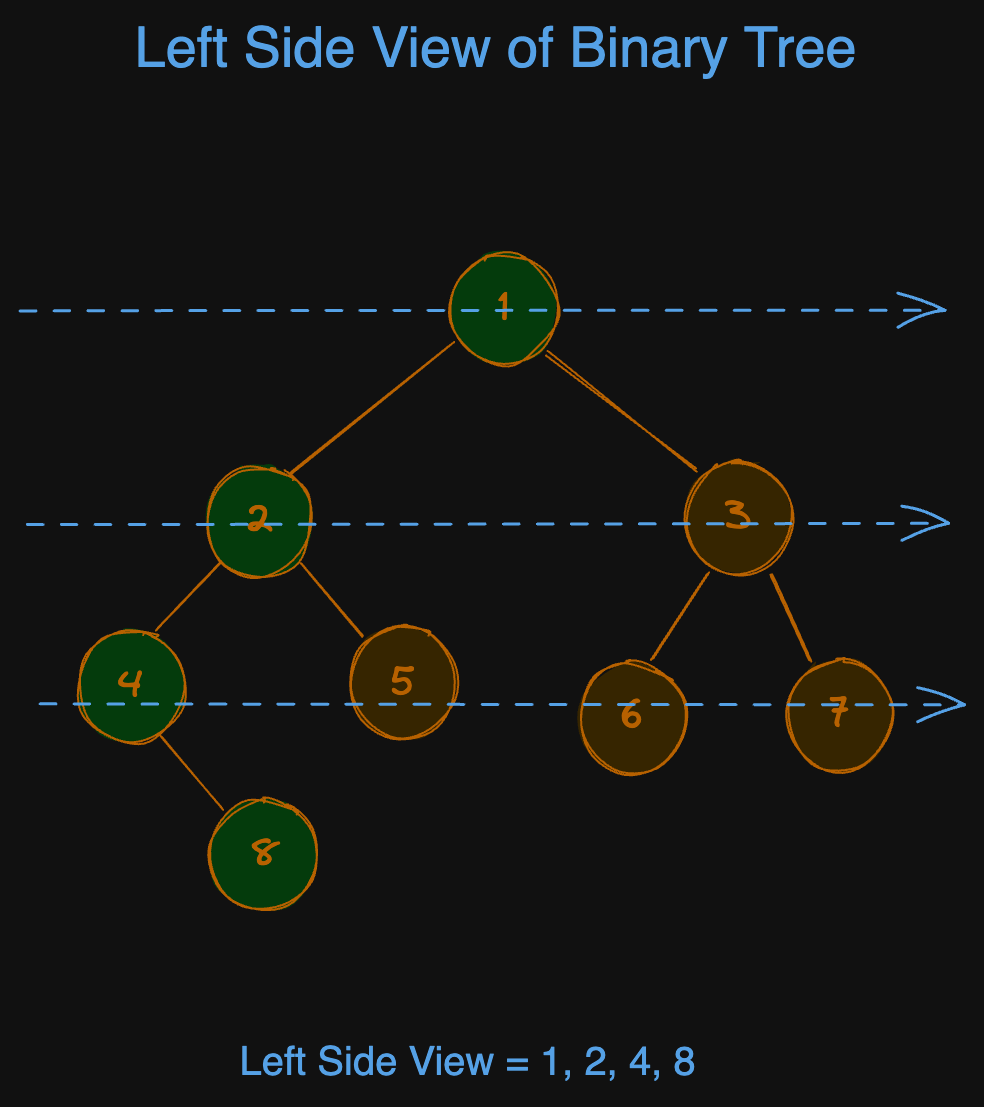
Input:
root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7, null, 8]
Output:
[1, 2, 4, 8]
Solution
This problem is similar to [Binary Tree Right Side View](binary-tree-right-side-view). The left view of a binary tree can be obtained by traversing the tree level-by-level (using a level order traversal) and collecting the first node at each level.
Method 1 - Use the Level Change Indication and Recursing on Left First
- Traverse the tree from left to right
- Print the first node you encounter
- Take two variables , currentLevel=0 and nextLevel=1
- As soon as you change level , change the currentLevel = nextLevel
- Print only when
current level<nextLevelso this way you will print only the first element - For rest of the nodes on the the level currentLevel and nextLevel are equal so it wont print
Code
Java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> leftView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int levelSize = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < levelSize; i++) {
TreeNode currentNode = queue.poll();
if (i == 0) {
result.add(currentNode.val);
}
if (currentNode.left != null) {
queue.add(currentNode.left);
}
if (currentNode.right != null) {
queue.add(currentNode.right);
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def leftView(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
result = []
if not root:
return result
queue = deque([root])
while queue:
level_size = len(queue)
for i in range(level_size):
node = queue.popleft()
if i == 0:
result.append(node.val)
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return result
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n)- wherenis the number of nodes in the binary tree. Each node is visited once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)- due to the storage of nodes in the queue used for level order traversal.