Binary Tree Path Sum - Maximum between any two leaves
MediumUpdated: Sep 28, 2025
Problem
Given a binary tree, find the maximum path sum from one leaf node to another.
Examples
Example 1
graph TD A(10) A --- B(2) A --- C(10) B(2) --- D(20) B(2) --- E(1) linkStyle 0 stroke:#FF0000,stroke-width:2px; linkStyle 1 stroke:#FF0000,stroke-width:2px; linkStyle 2 stroke:#FF0000,stroke-width:2px;
root = [10, 2, 10, 20, 1]
Output: 42
Explanation: The maximum path sum is obtained for the path 20 → 2 → 10 → 10. The sum of these values is 20 + 2 + 10 + 10 = 42.
Example 2
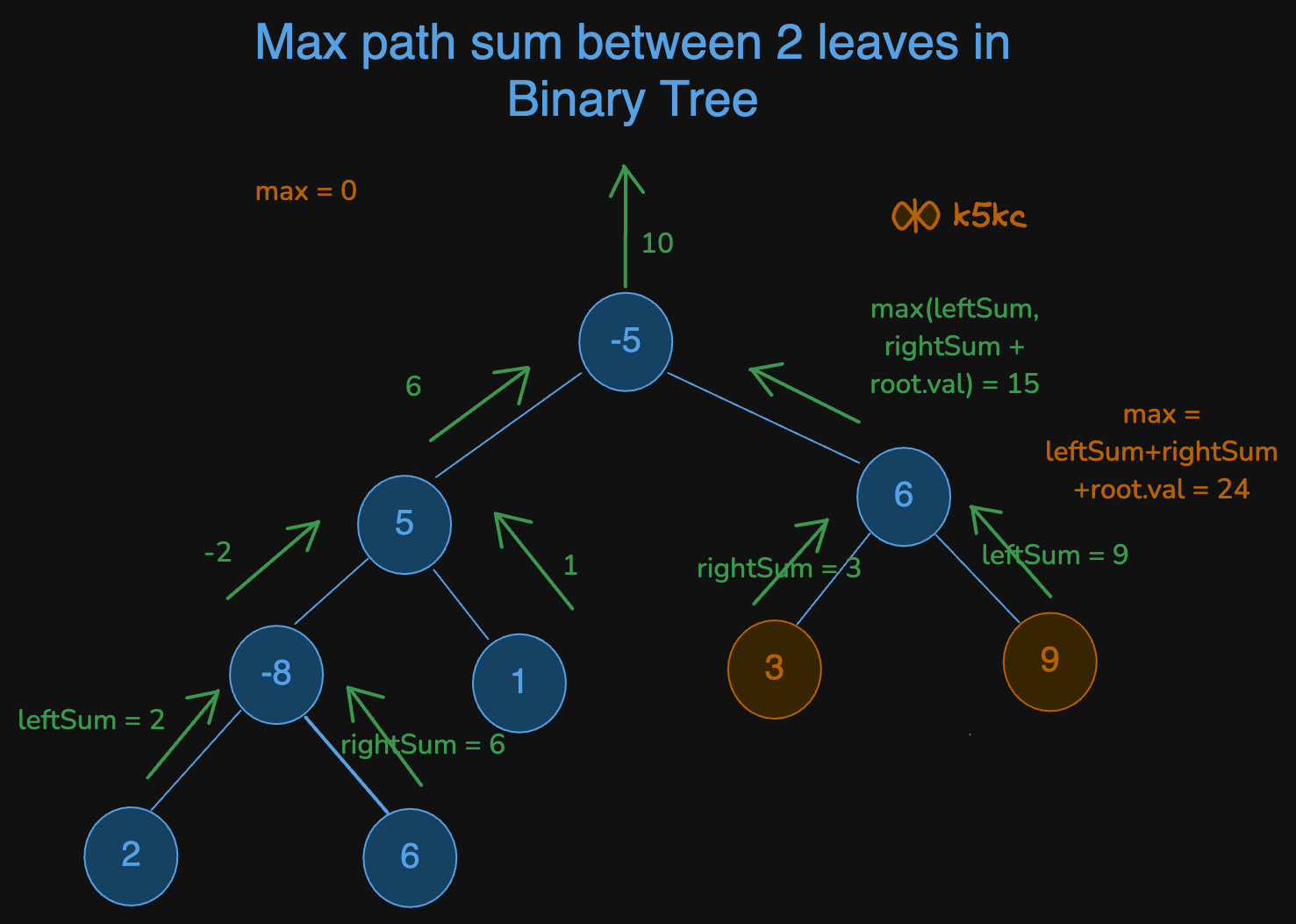
graph TD A("5") --- B(5) & C(6) B --- D("-8") & E(1) C --- F(3) & G(9) D --- H(2) & I(6) linkStyle 4 stroke:#FF0000,stroke-width:2px; linkStyle 5 stroke:#FF0000,stroke-width:2px;
root = [-15, 5, 6, -8, 1, 3, 9, 2, 6]
Output: 18
Explanation: The maximum path sum is obtained for the path 3 → 6 → 9. The sum of these values is 2 + (-8) + 5 + 6 + 9 = 27.
Solution
Method 1 - Recursive postorder traversal
To solve this problem:
- Key Observations:
- The maximum path will either:
- Lie completely within one subtree (left or right), or
- Pass through the current node, combining contributions from both the left and right subtrees.
- To compute this maximum, perform a post-order traversal, which allows us to evaluate the left and right subtrees first, then compute the combination at the current node.
- The maximum path will either:
- Goal: Maintain a global variable (
max_sumin Python andmaxSumin Java) to store the maximum path sum encountered so far, which may include contributions from both left and right subtrees via the root or stay entirely within one subtree.
Approach
- Variable Setup:
- Create a global variable
max_sum(Python) ormaxSum(Java) and initialise it to the smallest possible integer value (float('-inf')in Python orInteger.MIN_VALUEin Java). This will hold the maximum path sum encountered during traversal.
- Create a global variable
- Post-order Traversal:
- Traverse the tree in post-order: Starting from the root, process the left and right subtrees before evaluating the current node.
- Local Computation at Each Node:
- For each node:
- Compute the maximum path sum for the left and right subtrees recursively.
- If the current node has both left and right children, calculate a candidate path sum passing through the current node:
candidate_sum = left_sum + right_sum + node.val - Update the global
max_sumifcandidate_sumexceeds the currentmax_sum. - Return the maximum path sum that can be extended upwards:
return max(left_sum, right_sum) + node.val
- For each node:
- Final Value:
- At the end of the traversal,
max_sumcontains the maximum path sum from one leaf node to another.
- At the end of the traversal,
Dry Run
Code
Java
class Solution {
private int maxSum = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
// Helper function
int helper(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
// If node is leaf, return its value
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) return node.val;
// Recursive calls for left and right subtrees
int leftSum = node.left != null ? helper(node.left) : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int rightSum = node.right != null ? helper(node.right) : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Update global maxSum for leaf-to-leaf path
if (node.left != null && node.right != null) {
maxSum = Math.max(maxSum, leftSum + rightSum + node.val);
}
// Return max path sum for this subtree
return Math.max(leftSum, rightSum) + node.val;
}
helper(root);
return maxSum != Integer.MIN_VALUE ? maxSum : root.val;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.max_sum = float('-inf')
# Function to calculate the maximum path sum from leaf to leaf
def maxPathSum(self, root):
def helper(node):
if not node:
return 0
# If current node is a leaf node
if not node.left and not node.right:
return node.val
# Recursive calls to left and right subtrees
left_sum = helper(node.left) if node.left else float('-inf')
right_sum = helper(node.right) if node.right else float('-inf')
# Update the global maximum when left and right exist
if node.left and node.right:
self.max_sum = max(self.max_sum, left_sum + right_sum + node.val)
# Return max path sum for the current node's subtree
return max(left_sum, right_sum) + node.val
helper(root)
return self.max_sum if self.max_sum != float('-inf') else root.val
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n)since each node is visited once during traversal. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(h)wherehis the height of the binary tree due to the recursion stack.
Continue Practicing
Binary Tree Path Sum - Maximum between any two nodesHardBinary Tree Path Sum - Find all paths between any two nodesMediumBinary Tree Path Sum - Maximum Sum Leaf to Root pathMediumMinimum Length Root to Leaf Binary Tree Path for Given SumMediumBinary Tree Path Sum - Minimum Sum Root to Leaf pathEasyPath Sum 1 - Check if root to leaf path existsEasyPath Sum 2 - find all root to leaf pathsMediumPath Sum 3 - Count paths from parent to childMediumMinimum Length Root to Leaf BST Path for Given SumMediumPath Sum IVMediumSum Root to Leaf NumbersMedium