Check If a String Is a Valid Sequence from Root to Leaves Path in a Binary Tree
MediumUpdated: Jul 3, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a binary tree where each path going from the root to any leaf form a valid sequence , check if a given string is a valid sequence in such binary tree.
We get the given string from the concatenation of an array of integers arr and the concatenation of all values of the nodes along a path results in a sequence in the given binary tree.
Examples
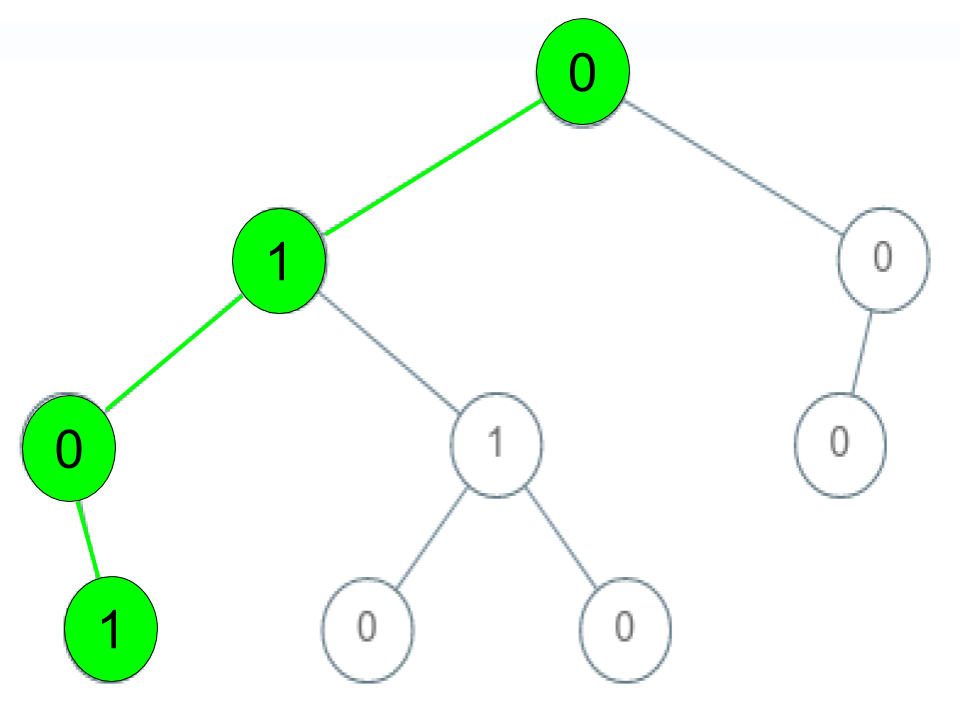 Example 1:
Example 1:
Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,0,1]
Output: true
Explanation: The path 0 -> 1 -> 0 -> 1 is a valid sequence (green color in the figure).
Other valid sequences are:
0 -> 1 -> 1 -> 0
0 -> 0 -> 0
Example 2:
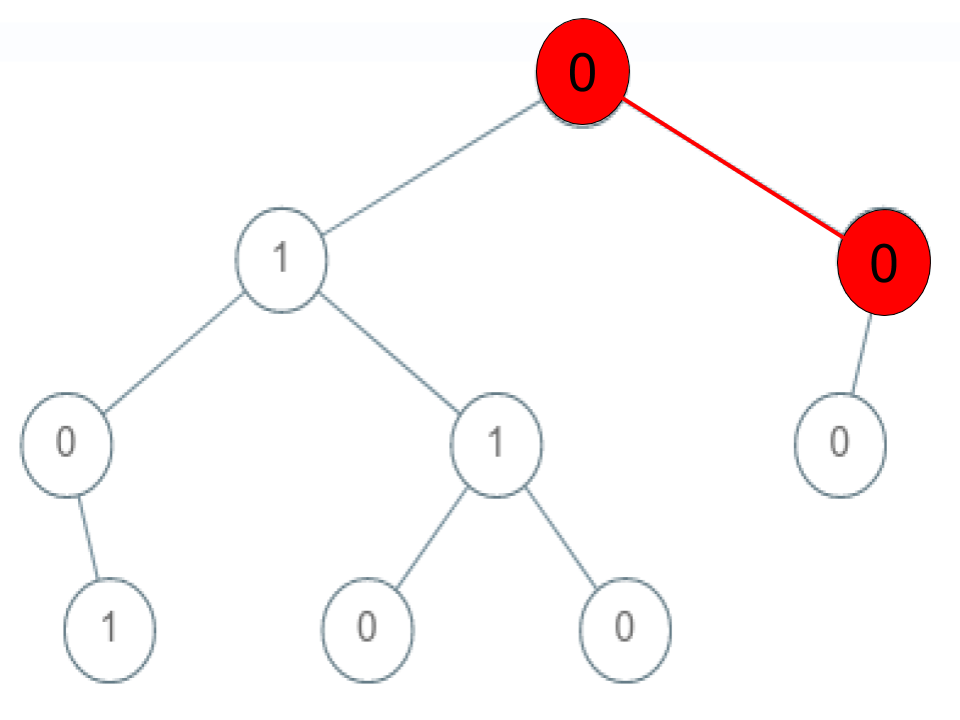
Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,0,1]
Output: false
Explanation: The path 0 -> 0 -> 1 does not exist, therefore it is not even a sequence.
Example 3:
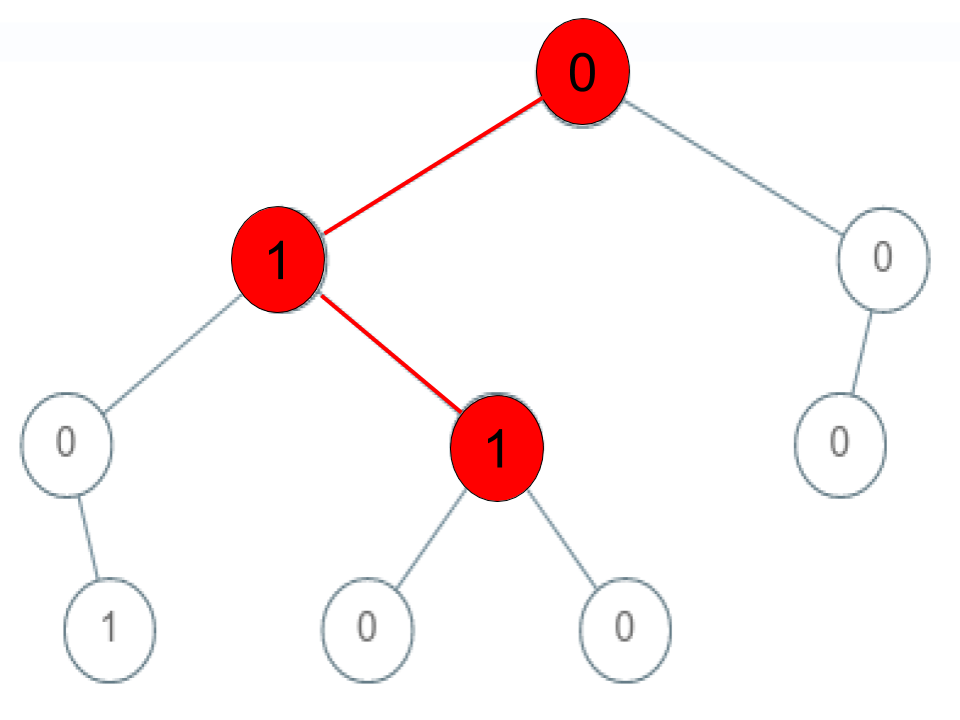
Input: root = [0,1,0,0,1,0,null,null,1,0,0], arr = [0,1,1]
Output: false
Explanation: The path 0 -> 1 -> 1 is a sequence, but it is not a valid sequence.
Constraints:
1 <= arr.length <= 50000 <= arr[i] <= 9- Each node's value is between
[0 - 9].
Solution
Method 1 – Depth-First Search (DFS) Path Matching
Intuition
We need to check if there exists a root-to-leaf path in the binary tree such that the sequence of node values matches the given array. This is a classic DFS problem where we match the current node's value with the current index in the array and recursively check the left and right subtrees.
Approach
- Start DFS from the root node and index 0 of the array.
- At each node:
- If the node is null or the index is out of bounds, return false.
- If the node's value does not match arr[index], return false.
- If at a leaf node and index is at the last element of arr, return true.
- Recursively check left and right children with index + 1.
- Return true if any path matches, else false.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidSequence(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& arr) {
return dfs(root, arr, 0);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* node, vector<int>& arr, int idx) {
if (!node || idx >= arr.size() || node->val != arr[idx]) return false;
if (!node->left && !node->right && idx == arr.size() - 1) return true;
return dfs(node->left, arr, idx + 1) || dfs(node->right, arr, idx + 1);
}
};
Go
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func isValidSequence(root *TreeNode, arr []int) bool {
var dfs func(node *TreeNode, idx int) bool
dfs = func(node *TreeNode, idx int) bool {
if node == nil || idx >= len(arr) || node.Val != arr[idx] {
return false
}
if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil && idx == len(arr)-1 {
return true
}
return dfs(node.Left, idx+1) || dfs(node.Right, idx+1)
}
return dfs(root, 0)
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSequence(TreeNode root, int[] arr) {
return dfs(root, arr, 0);
}
private boolean dfs(TreeNode node, int[] arr, int idx) {
if (node == null || idx >= arr.length || node.val != arr[idx]) return false;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null && idx == arr.length - 1) return true;
return dfs(node.left, arr, idx + 1) || dfs(node.right, arr, idx + 1);
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun isValidSequence(root: TreeNode?, arr: IntArray): Boolean {
fun dfs(node: TreeNode?, idx: Int): Boolean {
if (node == null || idx >= arr.size || node.`val` != arr[idx]) return false
if (node.left == null && node.right == null && idx == arr.size - 1) return true
return dfs(node.left, idx + 1) || dfs(node.right, idx + 1)
}
return dfs(root, 0)
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def isValidSequence(self, root: 'TreeNode', arr: list[int]) -> bool:
def dfs(node: 'TreeNode', idx: int) -> bool:
if not node or idx >= len(arr) or node.val != arr[idx]:
return False
if not node.left and not node.right and idx == len(arr) - 1:
return True
return dfs(node.left, idx + 1) or dfs(node.right, idx + 1)
return dfs(root, 0)
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn is_valid_sequence(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, arr: Vec<i32>) -> bool {
fn dfs(node: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, arr: &Vec<i32>, idx: usize) -> bool {
if node.is_none() || idx >= arr.len() { return false; }
let n = node.as_ref().unwrap().borrow();
if n.val != arr[idx] { return false; }
if n.left.is_none() && n.right.is_none() && idx == arr.len() - 1 { return true; }
dfs(n.left.clone(), arr, idx + 1) || dfs(n.right.clone(), arr, idx + 1)
}
dfs(root, &arr, 0)
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), wherenis the number of nodes in the tree. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(h), wherehis the height of the tree (recursion stack).