Check if Grid Satisfies Conditions
EasyUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given a 2D matrix grid of size m x n. You need to check if each cell grid[i][j] is:
- Equal to the cell below it, i.e.
grid[i][j] == grid[i + 1][j](if it exists). - Different from the cell to its right, i.e.
grid[i][j] != grid[i][j + 1](if it exists).
Return true if all the cells satisfy these conditions, otherwise, return false.
Examples
Example 1
Input: grid = [[1,0,2],[1,0,2]]
Output: true
Explanation:
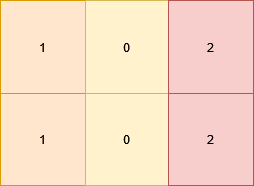
All the cells in the grid satisfy the conditions.
Example 2
Input: grid = [[1,1,1],[0,0,0]]
Output: false
Explanation:
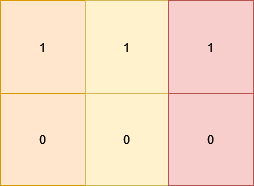
All cells in the first row are equal.
Example 3
Input: grid = [[1],[2],[3]]
Output: false
Explanation:

Cells in the first column have different values.
Constraints
1 <= n, m <= 100 <= grid[i][j] <= 9
Solution
Method 1 – Direct Grid Scan
Intuition
We need to check two conditions for each cell: (1) it is equal to the cell below (if it exists), and (2) it is different from the cell to its right (if it exists). We can scan the grid and check these conditions for every cell.
Approach
- Let m and n be the number of rows and columns in the grid.
- For each cell (i, j):
- If i + 1 < m, check if grid[i][j] == grid[i+1][j]. If not, return false.
- If j + 1 < n, check if grid[i][j] != grid[i][j+1]. If not, return false.
- If all checks pass, return true.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool satisfiesConditions(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i + 1 < m && grid[i][j] != grid[i+1][j]) return false;
if (j + 1 < n && grid[i][j] == grid[i][j+1]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
Go
func satisfiesConditions(grid [][]int) bool {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if i+1 < m && grid[i][j] != grid[i+1][j] {
return false
}
if j+1 < n && grid[i][j] == grid[i][j+1] {
return false
}
}
}
return true
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean satisfiesConditions(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i + 1 < m && grid[i][j] != grid[i+1][j]) return false;
if (j + 1 < n && grid[i][j] == grid[i][j+1]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun satisfiesConditions(grid: Array<IntArray>): Boolean {
val m = grid.size
val n = grid[0].size
for (i in 0 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
if (i + 1 < m && grid[i][j] != grid[i+1][j]) return false
if (j + 1 < n && grid[i][j] == grid[i][j+1]) return false
}
}
return true
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def satisfiesConditions(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> bool:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if i + 1 < m and grid[i][j] != grid[i+1][j]:
return False
if j + 1 < n and grid[i][j] == grid[i][j+1]:
return False
return True
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn satisfies_conditions(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> bool {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if i + 1 < m && grid[i][j] != grid[i+1][j] {
return false;
}
if j + 1 < n && grid[i][j] == grid[i][j+1] {
return false;
}
}
}
true
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(mn), wheremandnare the grid dimensions. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)