Check If It Is a Straight Line
EasyUpdated: Jul 31, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given an array coordinates, coordinates[i] = [x, y], where [x, y] represents the coordinate of a point. Check if these points make a straight line in the XY plane.
Examples
Example 1:
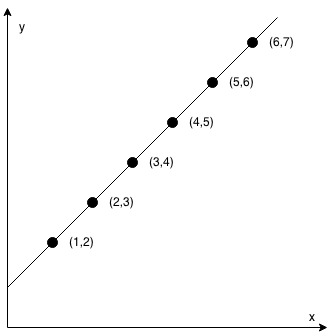
Input:
coordinates = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[6,7]]
Output:
true
Example 2:
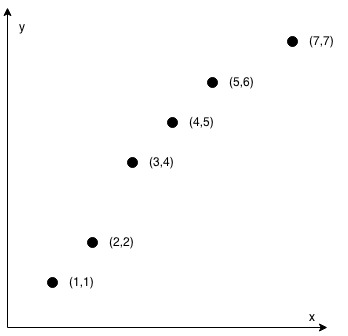
Input:
coordinates = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,4],[4,5],[5,6],[7,7]]
Output:
false
Solution
Method 1 – Cross Product Consistency
Intuition
All points are in a straight line if the slope between every pair of consecutive points is the same. To avoid division and floating point issues, we use the cross product: for points (x0, y0), (x1, y1), (xi, yi), the vectors (x1-x0, y1-y0) and (xi-x0, yi-y0) should be collinear, i.e., (x1-x0)(yi-y0) == (y1-y0)(xi-x0).
Approach
- Compute the direction vector (dx, dy) from the first two points.
- For each subsequent point, check if the cross product with the direction vector is zero.
- If all checks pass, the points are collinear.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool checkStraightLine(vector<vector<int>>& c) {
int dx = c[1][0] - c[0][0], dy = c[1][1] - c[0][1];
for (int i = 2; i < c.size(); ++i) {
if (dx * (c[i][1] - c[0][1]) != dy * (c[i][0] - c[0][0]))
return false;
}
return true;
}
};
Go
func checkStraightLine(c [][]int) bool {
dx, dy := c[1][0]-c[0][0], c[1][1]-c[0][1]
for i := 2; i < len(c); i++ {
if dx*(c[i][1]-c[0][1]) != dy*(c[i][0]-c[0][0]) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean checkStraightLine(int[][] c) {
int dx = c[1][0] - c[0][0], dy = c[1][1] - c[0][1];
for (int i = 2; i < c.length; i++) {
if (dx * (c[i][1] - c[0][1]) != dy * (c[i][0] - c[0][0]))
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun checkStraightLine(c: Array<IntArray>): Boolean {
val dx = c[1][0] - c[0][0]
val dy = c[1][1] - c[0][1]
for (i in 2 until c.size) {
if (dx * (c[i][1] - c[0][1]) != dy * (c[i][0] - c[0][0]))
return false
}
return true
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def checkStraightLine(self, c: list[list[int]]) -> bool:
dx, dy = c[1][0] - c[0][0], c[1][1] - c[0][1]
for i in range(2, len(c)):
if dx * (c[i][1] - c[0][1]) != dy * (c[i][0] - c[0][0]):
return False
return True
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn check_straight_line(c: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> bool {
let dx = c[1][0] - c[0][0];
let dy = c[1][1] - c[0][1];
for i in 2..c.len() {
if dx * (c[i][1] - c[0][1]) != dy * (c[i][0] - c[0][0]) {
return false;
}
}
true
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
checkStraightLine(c: number[][]): boolean {
const dx = c[1][0] - c[0][0], dy = c[1][1] - c[0][1];
for (let i = 2; i < c.length; i++) {
if (dx * (c[i][1] - c[0][1]) !== dy * (c[i][0] - c[0][0]))
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is the number of points. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1), only constant extra space is used.