Check if Matrix Is X-Matrix
EasyUpdated: Jul 4, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
A square matrix is said to be an X-Matrix if both of the following conditions hold:
- All the elements in the diagonals of the matrix are non-zero.
- All other elements are 0.
Given a 2D integer array grid of size n x n representing a square matrix, return true ifgrid is an X-Matrix. Otherwise, return false.
Examples
Example 1
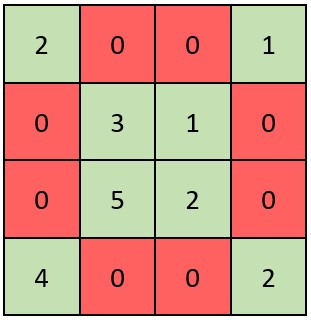
Input: grid = [[2,0,0,1],[0,3,1,0],[0,5,2,0],[4,0,0,2]]
Output: true
Explanation: Refer to the diagram above.
An X-Matrix should have the green elements (diagonals) be non-zero and the red elements be 0.
Thus, grid is an X-Matrix.
Example 2
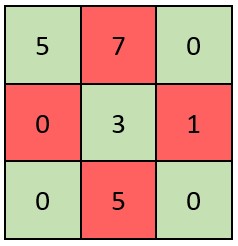
Input: grid = [[5,7,0],[0,3,1],[0,5,0]]
Output: false
Explanation: Refer to the diagram above.
An X-Matrix should have the green elements (diagonals) be non-zero and the red elements be 0.
Thus, grid is not an X-Matrix.
Constraints
n == grid.length == grid[i].length3 <= n <= 1000 <= grid[i][j] <= 10^5
Solution
Method 1 – Direct Diagonal and Off-Diagonal Check
Intuition
For a matrix to be an X-Matrix, all diagonal elements (main and anti-diagonal) must be non-zero, and all other elements must be zero. We can check each cell and verify these conditions directly.
Approach
- Let n be the size of the matrix.
- For each cell (i, j):
- If i == j or i + j == n - 1 (diagonal positions): check grid[i][j] != 0.
- Else (off-diagonal): check grid[i][j] == 0.
- If all checks pass, return true; otherwise, return false.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool checkXMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == j || i + j == n - 1) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) return false;
} else {
if (grid[i][j] != 0) return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
};
Go
func checkXMatrix(grid [][]int) bool {
n := len(grid)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if i == j || i+j == n-1 {
if grid[i][j] == 0 {
return false
}
} else {
if grid[i][j] != 0 {
return false
}
}
}
}
return true
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean checkXMatrix(int[][] grid) {
int n = grid.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == j || i + j == n - 1) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) return false;
} else {
if (grid[i][j] != 0) return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun checkXMatrix(grid: Array<IntArray>): Boolean {
val n = grid.size
for (i in 0 until n) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
if (i == j || i + j == n - 1) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) return false
} else {
if (grid[i][j] != 0) return false
}
}
}
return true
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def checkXMatrix(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> bool:
n = len(grid)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(n):
if i == j or i + j == n - 1:
if grid[i][j] == 0:
return False
else:
if grid[i][j] != 0:
return False
return True
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn check_x_matrix(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> bool {
let n = grid.len();
for i in 0..n {
for j in 0..n {
if i == j || i + j == n - 1 {
if grid[i][j] == 0 {
return false;
}
} else {
if grid[i][j] != 0 {
return false;
}
}
}
}
true
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^2), wherenis the size of the matrix. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1)