Checking Existence of Edge Length Limited Paths
Problem
An undirected graph of n nodes is defined by edgeList, where edgeList[i] = [ui, vi, disi] denotes an edge between nodes ui and vi with distance disi. Note that there may be multiple edges between two nodes.
Given an array queries, where queries[j] = [pj, qj, limitj], your task is to determine for each queries[j] whether there is a path between pj and qj such that each edge on the path has a distance strictly less than limitj .
Return a boolean array answer, where answer.length == queries.length and the jth value of answer is true if there is a path for queries[j] is true, and false otherwise.
Examples
Example 1:
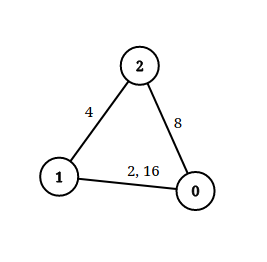
Input:
n = 3, edgeList = [[0,1,2],[1,2,4],[2,0,8],[1,0,16]], queries = [[0,1,2],[0,2,5]]
Output:
[false,true]
Explanation: The above figure shows the given graph. Note that there are two overlapping edges between 0 and 1 with distances 2 and 16.
For the first query, between 0 and 1 there is no path where each distance is less than 2, thus we return false for this query.
For the second query, there is a path (0 -> 1 -> 2) of two edges with distances less than 5, thus we return true for this query.
Example 2:
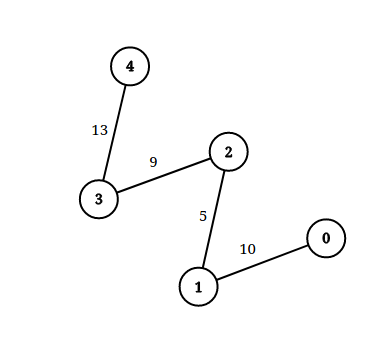
Input:
n = 5, edgeList = [[0,1,10],[1,2,5],[2,3,9],[3,4,13]], queries = [[0,4,14],[1,4,13]]
Output:
[true,false]
Explanation: The above figure shows the given graph.
Similar Problems
[Checking Existence of Edge Length Limited Paths II](checking-existence-of-edge-length-limited-paths-ii)
Solution
Method 1 – Offline Queries with Union-Find
Intuition
The key idea is to process all queries and edges in increasing order of their limits/weights. As we process edges with weights less than the current query's limit, we use Union-Find to connect nodes. For each query, we check if the two nodes are connected in the current Union-Find structure.
Approach
- Sort the queries by their limit, keeping track of their original indices.
- Sort the edge list by edge weight.
- Initialize a Union-Find (Disjoint Set Union) structure for all nodes.
- For each query, add all edges with weight less than the query's limit to the Union-Find.
- For each query, check if the two nodes are connected in the Union-Find and record the result.
- Return the results in the original query order.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<bool> distanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edgeList, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
vector<int> idx(queries.size());
iota(idx.begin(), idx.end(), 0);
sort(idx.begin(), idx.end(), [&](int a, int b) { return queries[a][2] < queries[b][2]; });
sort(edgeList.begin(), edgeList.end(), [](auto& a, auto& b) { return a[2] < b[2]; });
vector<int> par(n);
iota(par.begin(), par.end(), 0);
function<int(int)> find = [&](int x) { return par[x] == x ? x : par[x] = find(par[x]); };
vector<bool> ans(queries.size());
int j = 0;
for (int i : idx) {
while (j < edgeList.size() && edgeList[j][2] < queries[i][2]) {
int u = edgeList[j][0], v = edgeList[j][1];
par[find(u)] = find(v);
++j;
}
ans[i] = find(queries[i][0]) == find(queries[i][1]);
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func distanceLimitedPathsExist(n int, edgeList [][]int, queries [][]int) []bool {
idx := make([]int, len(queries))
for i := range idx { idx[i] = i }
sort.Slice(idx, func(a, b int) bool { return queries[idx[a]][2] < queries[idx[b]][2] })
sort.Slice(edgeList, func(a, b int) bool { return edgeList[a][2] < edgeList[b][2] })
par := make([]int, n)
for i := range par { par[i] = i }
var find func(int) int
find = func(x int) int { if par[x] != x { par[x] = find(par[x]) }; return par[x] }
ans := make([]bool, len(queries))
j := 0
for _, i := range idx {
for j < len(edgeList) && edgeList[j][2] < queries[i][2] {
u, v := edgeList[j][0], edgeList[j][1]
par[find(u)] = find(v)
j++
}
ans[i] = find(queries[i][0]) == find(queries[i][1])
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean[] distanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, int[][] edgeList, int[][] queries) {
int m = queries.length;
int[] idx = new int[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) idx[i] = i;
Arrays.sort(idx, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(queries[a][2], queries[b][2]));
Arrays.sort(edgeList, Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[2]));
int[] par = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) par[i] = i;
java.util.function.IntUnaryOperator find = new java.util.function.IntUnaryOperator() {
public int applyAsInt(int x) { return par[x] == x ? x : (par[x] = applyAsInt(par[x])); }
};
boolean[] ans = new boolean[m];
int j = 0;
for (int i : idx) {
while (j < edgeList.length && edgeList[j][2] < queries[i][2]) {
int u = edgeList[j][0], v = edgeList[j][1];
par[find.applyAsInt(u)] = find.applyAsInt(v);
j++;
}
ans[i] = find.applyAsInt(queries[i][0]) == find.applyAsInt(queries[i][1]);
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun distanceLimitedPathsExist(n: Int, edgeList: Array<IntArray>, queries: Array<IntArray>): BooleanArray {
val idx = queries.indices.sortedBy { queries[it][2] }
edgeList.sortBy { it[2] }
val par = IntArray(n) { it }
fun find(x: Int): Int = if (par[x] == x) x else { par[x] = find(par[x]); par[x] }
val ans = BooleanArray(queries.size)
var j = 0
for (i in idx) {
while (j < edgeList.size && edgeList[j][2] < queries[i][2]) {
val (u, v) = edgeList[j]
par[find(u)] = find(v)
j++
}
ans[i] = find(queries[i][0]) == find(queries[i][1])
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def distanceLimitedPathsExist(self, n: int, edgeList: list[list[int]], queries: list[list[int]]) -> list[bool]:
idx = sorted(range(len(queries)), key=lambda i: queries[i][2])
edgeList.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
par = list(range(n))
def find(x):
if par[x] != x:
par[x] = find(par[x])
return par[x]
ans = [False] * len(queries)
j = 0
for i in idx:
while j < len(edgeList) and edgeList[j][2] < queries[i][2]:
u, v = edgeList[j][0], edgeList[j][1]
par[find(u)] = find(v)
j += 1
ans[i] = find(queries[i][0]) == find(queries[i][1])
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn distance_limited_paths_exist(n: i32, mut edge_list: Vec<Vec<i32>>, mut queries: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<bool> {
let n = n as usize;
let mut idx: Vec<_> = (0..queries.len()).collect();
idx.sort_by_key(|&i| queries[i][2]);
edge_list.sort_by_key(|e| e[2]);
let mut par: Vec<_> = (0..n).collect();
fn find(par: &mut Vec<usize>, x: usize) -> usize {
if par[x] != x { par[x] = find(par, par[x]); }
par[x]
}
let mut ans = vec![false; queries.len()];
let mut j = 0;
for &i in &idx {
while j < edge_list.len() && edge_list[j][2] < queries[i][2] {
let (u, v) = (edge_list[j][0] as usize, edge_list[j][1] as usize);
let pu = find(&mut par, u);
let pv = find(&mut par, v);
par[pu] = pv;
j += 1;
}
let (a, b) = (queries[i][0] as usize, queries[i][1] as usize);
ans[i] = find(&mut par, a) == find(&mut par, b);
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
distanceLimitedPathsExist(n: number, edgeList: number[][], queries: number[][]): boolean[] {
const idx = queries.map((_, i) => i).sort((a, b) => queries[a][2] - queries[b][2]);
edgeList.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]);
const par = Array.from({length: n}, (_, i) => i);
const find = (x: number): number => par[x] === x ? x : (par[x] = find(par[x]));
const ans: boolean[] = Array(queries.length).fill(false);
let j = 0;
for (const i of idx) {
while (j < edgeList.length && edgeList[j][2] < queries[i][2]) {
const [u, v] = edgeList[j];
par[find(u)] = find(v);
j++;
}
ans[i] = find(queries[i][0]) === find(queries[i][1]);
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O((n + m + q) * α(n)), where n is the number of nodes, m is the number of edges, q is the number of queries, and α is the inverse Ackermann function for Union-Find operations. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n + m + q), for the parent array, edge list, and queries.