Choose Edges to Maximize Score in a Tree
Problem
You are given a weighted tree consisting of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1.
The tree is rooted at node 0 and represented with a 2D array edges of size n where edges[i] = [pari, weighti] indicates that node pari is the parent of node i, and the edge between them has a weight equal to weighti. Since the root does not have a parent, you have edges[0] = [-1, -1].
Choose some edges from the tree such that no two chosen edges are adjacent and the sum of the weights of the chosen edges is maximized.
Return themaximum sum of the chosen edges.
Note :
- You are allowed to not choose any edges in the tree, the sum of weights in this case will be
0. - Two edges
Edge1andEdge2in the tree are adjacent if they have a common node.- In other words, they are adjacent if
Edge1connects nodesaandbandEdge2connects nodesbandc.
- In other words, they are adjacent if
Examples
Example 1:
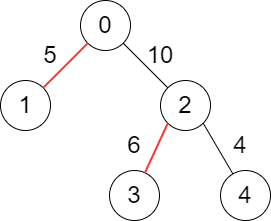
Input: edges = [[-1,-1],[0,5],[0,10],[2,6],[2,4]]
Output: 11
Explanation: The above diagram shows the edges that we have to choose colored in red.
The total score is 5 + 6 = 11.
It can be shown that no better score can be obtained.
Example 2:
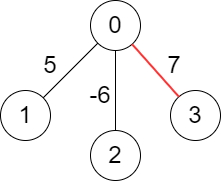
Input: edges = [[-1,-1],[0,5],[0,-6],[0,7]]
Output: 7
Explanation: We choose the edge with weight 7.
Note that we cannot choose more than one edge because all edges are adjacent to each other.
Constraints:
n == edges.length1 <= n <= 10^5edges[i].length == 2par0 == weight0 == -10 <= pari <= n - 1for alli >= 1.pari != i-10^6 <= weighti <= 10^6for alli >= 1.edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
Method 1 – Tree DP (Maximum Weight Independent Set on Edges)
Intuition
We need to select a subset of edges in a tree such that no two selected edges are adjacent and the sum of their weights is maximized. This is a classic tree DP problem, similar to the "maximum weight independent set" but on edges instead of nodes.
Reasoning
For each node, we can decide for each child edge whether to include it or not. If we include an edge, we cannot include any edge adjacent to it (i.e., edges connected to its endpoints). We use DP to keep track of two states for each node: the maximum sum if the edge to its parent is not chosen, and the maximum sum if it is chosen.
Approach
- Build the tree as an adjacency list from the edges array.
- For each node, define a DP function that returns two values:
not_chosen: the maximum sum if the edge to its parent is not chosen.chosen: the maximum sum if the edge to its parent is chosen (cannot choose any child edge).
- For each child, recursively compute its DP values.
- If the edge to the child is chosen, add its weight and the
not_chosenvalue from the child. - If not chosen, take the maximum of
chosenandnot_chosenfrom the child.
- If the edge to the child is chosen, add its weight and the
- The answer is the
not_chosenvalue at the root (since the root has no parent edge).
Edge cases:
- Tree with only one node: answer is 0.
- All edge weights negative: answer is 0 (choose no edge).
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
long long maximumScore(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = edges.size();
vector<vector<pair<int,int>>> g(n);
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
int p = edges[i][0], w = edges[i][1];
g[p].emplace_back(i, w);
}
function<pair<long long, long long>(int)> dfs = [&](int u) {
long long not_chosen = 0, chosen = 0;
for (auto& [v, w] : g[u]) {
auto [nc, c] = dfs(v);
not_chosen += max(nc, c);
chosen += nc + w;
}
return make_pair(not_chosen, chosen);
};
return dfs(0).first;
}
};
Go
func maximumScore(edges [][]int) int64 {
n := len(edges)
g := make([][]struct{v, w int}, n)
for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
p, w := edges[i][0], edges[i][1]
g[p] = append(g[p], struct{v, w int}{i, w})
}
var dfs func(int) (int64, int64)
dfs = func(u int) (int64, int64) {
var notChosen, chosen int64
for _, e := range g[u] {
nc, c := dfs(e.v)
notChosen += max64(nc, c)
chosen += nc + int64(e.w)
}
return notChosen, chosen
}
res, _ := dfs(0)
return res
}
func max64(a, b int64) int64 { if a > b { return a }; return b }
Java
class Solution {
public long maximumScore(int[][] edges) {
int n = edges.length;
List<int[]>[] g = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) g[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int p = edges[i][0], w = edges[i][1];
g[p].add(new int[]{i, w});
}
long[] dfs(int u) {
long notChosen = 0, chosen = 0;
for (int[] e : g[u]) {
long[] res = dfs(e[0]);
notChosen += Math.max(res[0], res[1]);
chosen += res[0] + e[1];
}
return new long[]{notChosen, chosen};
}
return dfs(0)[0];
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun maximumScore(edges: Array<IntArray>): Long {
val n = edges.size
val g = Array(n) { mutableListOf<Pair<Int, Int>>() }
for (i in 1 until n) {
val (p, w) = edges[i]
g[p].add(i to w)
}
fun dfs(u: Int): Pair<Long, Long> {
var notChosen = 0L; var chosen = 0L
for ((v, w) in g[u]) {
val (nc, c) = dfs(v)
notChosen += maxOf(nc, c)
chosen += nc + w
}
return notChosen to chosen
}
return dfs(0).first
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def maximum_score(self, edges: list[list[int]]) -> int:
n = len(edges)
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(1, n):
p, w = edges[i]
g[p].append((i, w))
def dfs(u: int) -> tuple[int, int]:
not_chosen, chosen = 0, 0
for v, w in g[u]:
nc, c = dfs(v)
not_chosen += max(nc, c)
chosen += nc + w
return not_chosen, chosen
return dfs(0)[0]
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn maximum_score(edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i64 {
let n = edges.len();
let mut g = vec![vec![]; n];
for i in 1..n {
let p = edges[i][0] as usize;
let w = edges[i][1];
g[p].push((i, w));
}
fn dfs(u: usize, g: &Vec<Vec<(usize, i32)>>) -> (i64, i64) {
let mut not_chosen = 0i64;
let mut chosen = 0i64;
for &(v, w) in &g[u] {
let (nc, c) = dfs(v, g);
not_chosen += nc.max(c);
chosen += nc + w as i64;
}
(not_chosen, chosen)
}
dfs(0, &g).0
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), as each node and edge is visited once in the DFS. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), as we store the tree and recursion stack.