Closest Node to Path in Tree
Problem
You are given a positive integer n representing the number of nodes in a tree, numbered from 0 to n - 1 (inclusive). You are also given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [node1i, node2i] denotes that there is a bidirectional edge connecting node1i and node2i in the tree.
You are given a 0-indexed integer array query of length m where query[i] = [starti, endi, nodei] means that for the ith query, you are tasked with finding the node on the path from starti to endi that is closest to nodei.
Return an integer arrayanswer of lengthm , whereanswer[i]is the answer to theith query.
Examples
Example 1:
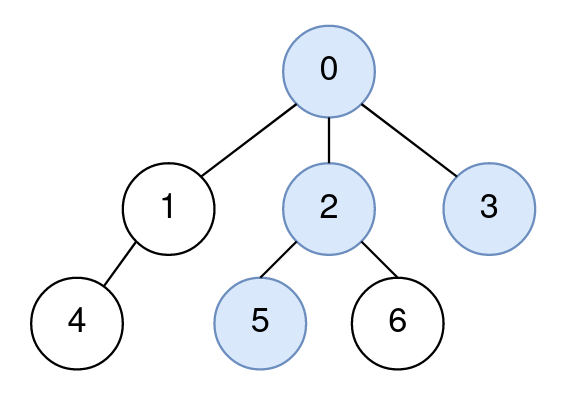
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]], query = [[5,3,4],[5,3,6]]
Output: [0,2]
Explanation:
The path from node 5 to node 3 consists of the nodes 5, 2, 0, and 3.
The distance between node 4 and node 0 is 2.
Node 0 is the node on the path closest to node 4, so the answer to the first query is 0.
The distance between node 6 and node 2 is 1.
Node 2 is the node on the path closest to node 6, so the answer to the second query is 2.
Example 2:
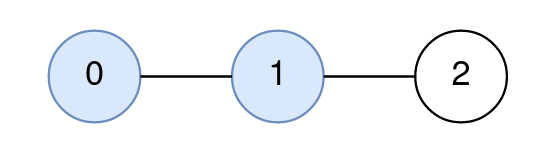
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2]], query = [[0,1,2]]
Output: [1]
Explanation:
The path from node 0 to node 1 consists of the nodes 0, 1.
The distance between node 2 and node 1 is 1.
Node 1 is the node on the path closest to node 2, so the answer to the first query is 1.
Example 3:
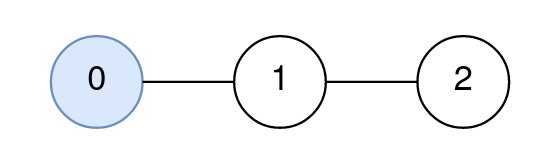
Input: n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2]], query = [[0,0,0]]
Output: [0]
Explanation:
The path from node 0 to node 0 consists of the node 0.
Since 0 is the only node on the path, the answer to the first query is 0.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 1000edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= node1i, node2i <= n - 1node1i != node2i1 <= query.length <= 1000query[i].length == 30 <= starti, endi, nodei <= n - 1- The graph is a tree.
Solution
Method 1 – BFS Preprocessing + Path Extraction
Intuition
To efficiently answer multiple queries, we precompute the shortest distances from every node to every other node using BFS. For each query, extract the path from start to end, then for each node on the path, find the one closest to the target node.
Approach
- Build the tree as an adjacency list.
- For each node, run BFS to compute the shortest distance to all other nodes (O(n^2) preprocessing).
- For each query
[start, end, node]:- Extract the path from start to end using parent pointers from BFS.
- For each node on the path, compute its distance to node.
- Return the node on the path with the smallest distance to node (if tie, return the smallest index).
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> closestNode(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<vector<int>>& query) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
vector<vector<int>> dist(n, vector<int>(n, -1));
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
queue<int> q; q.push(i); dist[i][i] = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
for (int v : g[u]) if (dist[i][v] == -1) {
dist[i][v] = dist[i][u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
vector<int> ans;
for (auto& q : query) {
int s = q[0], e = q[1], t = q[2];
vector<int> parent(n, -1);
queue<int> qu; qu.push(s); parent[s] = s;
while (!qu.empty()) {
int u = qu.front(); qu.pop();
if (u == e) break;
for (int v : g[u]) if (parent[v] == -1) {
parent[v] = u;
qu.push(v);
}
}
vector<int> path;
for (int x = e; x != s; x = parent[x]) path.push_back(x);
path.push_back(s);
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
int res = path[0], minDist = dist[t][res];
for (int x : path) {
if (dist[t][x] < minDist || (dist[t][x] == minDist && x < res)) {
res = x; minDist = dist[t][x];
}
}
ans.push_back(res);
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func closestNode(n int, edges [][]int, query [][]int) []int {
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], e[1])
g[e[1]] = append(g[e[1]], e[0])
}
dist := make([][]int, n)
for i := range dist {
dist[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := range dist[i] {
dist[i][j] = -1
}
}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
q := []int{i}
dist[i][i] = 0
for len(q) > 0 {
u := q[0]; q = q[1:]
for _, v := range g[u] {
if dist[i][v] == -1 {
dist[i][v] = dist[i][u] + 1
q = append(q, v)
}
}
}
}
ans := []int{}
for _, qu := range query {
s, e, t := qu[0], qu[1], qu[2]
parent := make([]int, n)
for i := range parent { parent[i] = -1 }
q := []int{s}; parent[s] = s
for len(q) > 0 {
u := q[0]; q = q[1:]
if u == e { break }
for _, v := range g[u] {
if parent[v] == -1 {
parent[v] = u
q = append(q, v)
}
}
}
path := []int{}
for x := e; x != s; x = parent[x] { path = append(path, x) }
path = append(path, s)
for i, j := 0, len(path)-1; i < j; i, j = i+1, j-1 { path[i], path[j] = path[j], path[i] }
res, minDist := path[0], dist[t][path[0]]
for _, x := range path {
if dist[t][x] < minDist || (dist[t][x] == minDist && x < res) {
res, minDist = x, dist[t][x]
}
}
ans = append(ans, res)
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int[] closestNode(int n, int[][] edges, int[][] query) {
List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) g[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] e : edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1]);
g[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
int[][] dist = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) Arrays.fill(dist[i], -1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(i); dist[i][i] = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int u = q.poll();
for (int v : g[u]) if (dist[i][v] == -1) {
dist[i][v] = dist[i][u] + 1;
q.add(v);
}
}
}
int[] ans = new int[query.length];
for (int idx = 0; idx < query.length; idx++) {
int s = query[idx][0], e = query[idx][1], t = query[idx][2];
int[] parent = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(parent, -1);
Queue<Integer> qu = new LinkedList<>();
qu.add(s); parent[s] = s;
while (!qu.isEmpty()) {
int u = qu.poll();
if (u == e) break;
for (int v : g[u]) if (parent[v] == -1) {
parent[v] = u;
qu.add(v);
}
}
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
for (int x = e; x != s; x = parent[x]) path.add(x);
path.add(s);
Collections.reverse(path);
int res = path.get(0), minDist = dist[t][res];
for (int x : path) {
if (dist[t][x] < minDist || (dist[t][x] == minDist && x < res)) {
res = x; minDist = dist[t][x];
}
}
ans[idx] = res;
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun closestNode(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>, query: Array<IntArray>): IntArray {
val g = Array(n) { mutableListOf<Int>() }
for (e in edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1])
g[e[1]].add(e[0])
}
val dist = Array(n) { IntArray(n) { -1 } }
for (i in 0 until n) {
val q = ArrayDeque<Int>()
q.add(i); dist[i][i] = 0
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val u = q.removeFirst()
for (v in g[u]) if (dist[i][v] == -1) {
dist[i][v] = dist[i][u] + 1
q.add(v)
}
}
}
val ans = IntArray(query.size)
for ((idx, qu) in query.withIndex()) {
val (s, e, t) = qu
val parent = IntArray(n) { -1 }
val q = ArrayDeque<Int>()
q.add(s); parent[s] = s
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val u = q.removeFirst()
if (u == e) break
for (v in g[u]) if (parent[v] == -1) {
parent[v] = u
q.add(v)
}
}
val path = mutableListOf<Int>()
var x = e
while (x != s) { path.add(x); x = parent[x] }
path.add(s)
path.reverse()
var res = path[0]; var minDist = dist[t][res]
for (x in path) {
if (dist[t][x] < minDist || (dist[t][x] == minDist && x < res)) {
res = x; minDist = dist[t][x]
}
}
ans[idx] = res
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def closestNode(self, n: int, edges: list[list[int]], query: list[list[int]]) -> list[int]:
from collections import deque
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v in edges:
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
dist = [[-1]*n for _ in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
q = deque([i]); dist[i][i] = 0
while q:
u = q.popleft()
for v in g[u]:
if dist[i][v] == -1:
dist[i][v] = dist[i][u] + 1
q.append(v)
ans = []
for s, e, t in query:
parent = [-1]*n
q = deque([s]); parent[s] = s
while q:
u = q.popleft()
if u == e: break
for v in g[u]:
if parent[v] == -1:
parent[v] = u
q.append(v)
path = []
x = e
while x != s:
path.append(x)
x = parent[x]
path.append(s)
path = path[::-1]
res, minDist = path[0], dist[t][path[0]]
for x in path:
if dist[t][x] < minDist or (dist[t][x] == minDist and x < res):
res, minDist = x, dist[t][x]
ans.append(res)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn closest_node(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, query: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = n as usize;
let mut g = vec![vec![]; n];
for e in &edges {
g[e[0] as usize].push(e[1] as usize);
g[e[1] as usize].push(e[0] as usize);
}
let mut dist = vec![vec![-1; n]; n];
for i in 0..n {
let mut q = std::collections::VecDeque::new();
q.push_back(i); dist[i][i] = 0;
while let Some(u) = q.pop_front() {
for &v in &g[u] {
if dist[i][v] == -1 {
dist[i][v] = dist[i][u] + 1;
q.push_back(v);
}
}
}
}
let mut ans = vec![];
for qu in query {
let (s, e, t) = (qu[0] as usize, qu[1] as usize, qu[2] as usize);
let mut parent = vec![-1; n];
let mut q = std::collections::VecDeque::new();
q.push_back(s); parent[s] = s as i32;
while let Some(u) = q.pop_front() {
if u == e { break; }
for &v in &g[u] {
if parent[v] == -1 {
parent[v] = u as i32;
q.push_back(v);
}
}
}
let mut path = vec![];
let mut x = e;
while x != s {
path.push(x);
x = parent[x] as usize;
}
path.push(s);
path.reverse();
let mut res = path[0];
let mut min_dist = dist[t][res];
for &x in &path {
if dist[t][x] < min_dist || (dist[t][x] == min_dist && x < res) {
res = x;
min_dist = dist[t][x];
}
}
ans.push(res as i32);
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
closestNode(n: number, edges: number[][], query: number[][]): number[] {
const g: number[][] = Array.from({length: n}, () => []);
for (const [u, v] of edges) {
g[u].push(v);
g[v].push(u);
}
const dist: number[][] = Array.from({length: n}, () => Array(n).fill(-1));
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
const q: number[] = [i];
dist[i][i] = 0;
for (let head = 0; head < q.length; head++) {
const u = q[head];
for (const v of g[u]) {
if (dist[i][v] === -1) {
dist[i][v] = dist[i][u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
const ans: number[] = [];
for (const [s, e, t] of query) {
const parent: number[] = Array(n).fill(-1);
const q: number[] = [s];
parent[s] = s;
for (let head = 0; head < q.length; head++) {
const u = q[head];
if (u === e) break;
for (const v of g[u]) {
if (parent[v] === -1) {
parent[v] = u;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
const path: number[] = [];
let x = e;
while (x !== s) { path.push(x); x = parent[x]; }
path.push(s);
path.reverse();
let res = path[0], minDist = dist[t][res];
for (const x of path) {
if (dist[t][x] < minDist || (dist[t][x] === minDist && x < res)) {
res = x; minDist = dist[t][x];
}
}
ans.push(res);
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity: O(n^2 + m * n), where n is the number of nodes and m is the number of queries.
- 🧺 Space complexity: O(n^2)