Combination Sum 4 - All permutations
Problem
Given an array of distinct integers nums and a target integer target, return the number of possible combinations that add up to target.
The test cases are generated so that the answer can fit in a 32-bit integer.
Examples
Example 1:
Input: nums = [1,2,3], target = 4
Output: 7
Explanation:
The possible combination ways are:
(1, 1, 1, 1)
(1, 1, 2)
(1, 2, 1)
(1, 3)
(2, 1, 1)
(2, 2)
(3, 1)
Note that different sequences are counted as different combinations.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [9], target = 3
Output: 0
Note
This is not Combination sum problem, but Permutation Sum Problem, because [1,1,2] and [2,1,1] are treated differently.
Solution
Method 1 - Recursion
This is the recursion tree:
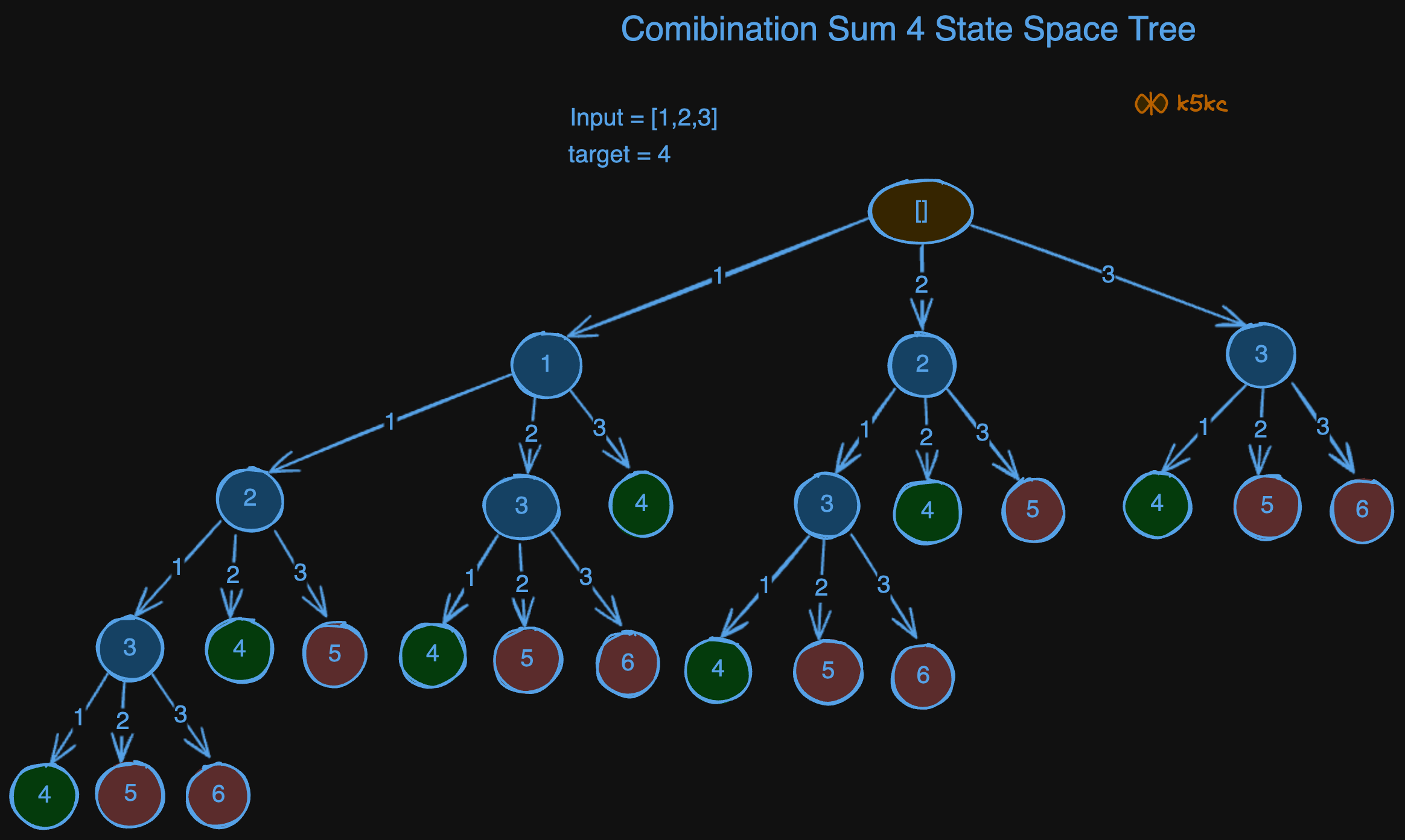
Code
Java
public int combinationSum4(int[] nums, int target) {
if (target == 0) {
return 1;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums [i] <= target)
count += combinationSum4 (nums, target - nums [i]);
}
return count;
}
Method 2 - Top Down DP with Memoization
We can see repeating subproblems - for eg. see the node 3, in recursion tree in method 1.
Code
Java
public int combinationSum4(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] dp = new int[target + 1];
Arrays.fill(dp, -1);
dp[0] = 1;
return backtrack(nums, dp, target);
}
private int backtrack(int[] nums, int[] dp, int sum) {
if (sum < 0) return 0;
if (dp[sum] != -1) return dp[sum];
int total = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
total += backtrack(nums, dp, sum - num);
}
dp[sum] = total;
return dp[sum];
}
Method 3 - Bottom up DP
This problem is similar to [Coin Change with Fewest Number of Coins Given Infinite Supply](coin-change-with-fewest-number-of-coins-given-infinite-supply). It's a typical dynamic programming problem.
Code
Java
public int combinationSum4(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0)
return 0;
int[] dp = new int[target + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i<= target; i++) {
for (int num: nums) {
if (i >= num) {
dp[i] += dp[i - num];
}
}
}
return dp[target];
}
Here is coin change code:
public int change(int amount, int[] coins) {
int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int coin : coins) {
for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
if (i >= coin) {
dp[i] += dp[i - coin];
}
}
}
return dp[amount];
}
You may find the solution to this problem is basically the same with that, except the order of for loop.