Complete Binary Tree Inserter
MediumUpdated: Jul 7, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible.
Design an algorithm to insert a new node to a complete binary tree keeping it complete after the insertion.
Implement the CBTInserter class:
CBTInserter(TreeNode root)Initializes the data structure with therootof the complete binary tree.int insert(int v)Inserts aTreeNodeinto the tree with valueNode.val == valso that the tree remains complete, and returns the value of the parent of the insertedTreeNode.TreeNode get_root()Returns the root node of the tree.
Examples
Example 1
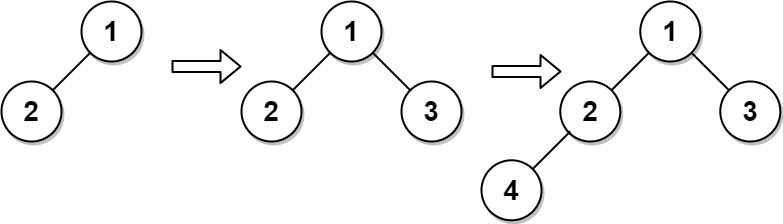
**Input**
["CBTInserter", "insert", "insert", "get_root"]
[[[1, 2]], [3], [4], []]
**Output**
[null, 1, 2, [1, 2, 3, 4]]
**Explanation**
CBTInserter cBTInserter = new CBTInserter([1, 2]);
cBTInserter.insert(3); // return 1
cBTInserter.insert(4); // return 2
cBTInserter.get_root(); // return [1, 2, 3, 4]
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 5000rootis a complete binary tree.0 <= val <= 5000- At most
104calls will be made toinsertandget_root.
Solution
Method 1 – BFS Queue for Insertion Tracking
Intuition
To efficiently insert into a complete binary tree, we can keep track of nodes that are not full (i.e., have less than two children). By using a queue, we always know where the next insertion should happen to maintain completeness.
Approach
- Use a queue to store nodes that are potential parents for new nodes (nodes with less than two children).
- On initialization, perform a BFS traversal to fill the queue with such nodes.
- For
insert(val), take the front node from the queue:- If it has no left child, insert as left child.
- Else, insert as right child and remove the node from the queue (now full).
- Add the new node to the queue (it may receive children in the future).
- For
get_root(), return the root node.
Code
C++
class CBTInserter {
TreeNode* r;
std::queue<TreeNode*> q;
public:
CBTInserter(TreeNode* root) : r(root) {
std::queue<TreeNode*> t;
t.push(root);
while (!t.empty()) {
auto n = t.front(); t.pop();
if (!n->left || !n->right) q.push(n);
if (n->left) t.push(n->left);
if (n->right) t.push(n->right);
}
}
int insert(int v) {
auto n = q.front();
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(v);
if (!n->left) n->left = node;
else { n->right = node; q.pop(); }
q.push(node);
return n->val;
}
TreeNode* get_root() { return r; }
};
Go
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
type CBTInserter struct {
r *TreeNode
q []*TreeNode
}
func Constructor(root *TreeNode) CBTInserter {
t := []*TreeNode{root}
q := []*TreeNode{}
for len(t) > 0 {
n := t[0]
t = t[1:]
if n.Left == nil || n.Right == nil {
q = append(q, n)
}
if n.Left != nil { t = append(t, n.Left) }
if n.Right != nil { t = append(t, n.Right) }
}
return CBTInserter{r: root, q: q}
}
func (this *CBTInserter) Insert(v int) int {
n := this.q[0]
node := &TreeNode{Val: v}
if n.Left == nil {
n.Left = node
} else {
n.Right = node
this.q = this.q[1:]
}
this.q = append(this.q, node)
return n.Val
}
func (this *CBTInserter) Get_root() *TreeNode {
return this.r
}
Java
class CBTInserter {
private TreeNode r;
private Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
public CBTInserter(TreeNode root) {
r = root;
Queue<TreeNode> t = new LinkedList<>();
t.offer(root);
while (!t.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode n = t.poll();
if (n.left == null || n.right == null) q.offer(n);
if (n.left != null) t.offer(n.left);
if (n.right != null) t.offer(n.right);
}
}
public int insert(int v) {
TreeNode n = q.peek();
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(v);
if (n.left == null) n.left = node;
else { n.right = node; q.poll(); }
q.offer(node);
return n.val;
}
public TreeNode get_root() { return r; }
}
Kotlin
class CBTInserter(root: TreeNode) {
private val r = root
private val q: ArrayDeque<TreeNode> = ArrayDeque()
init {
val t = ArrayDeque<TreeNode>()
t.add(root)
while (t.isNotEmpty()) {
val n = t.removeFirst()
if (n.left == null || n.right == null) q.add(n)
n.left?.let { t.add(it) }
n.right?.let { t.add(it) }
}
}
fun insert(v: Int): Int {
val n = q.first()
val node = TreeNode(v)
if (n.left == null) n.left = node
else { n.right = node; q.removeFirst() }
q.add(node)
return n.`val`
}
fun get_root(): TreeNode = r
}
Python
class CBTInserter:
def __init__(self, root: TreeNode):
self.r = root
self.q = []
t = [root]
while t:
n = t.pop(0)
if not n.left or not n.right:
self.q.append(n)
if n.left:
t.append(n.left)
if n.right:
t.append(n.right)
def insert(self, v: int) -> int:
n = self.q[0]
node = TreeNode(v)
if not n.left:
n.left = node
else:
n.right = node
self.q.pop(0)
self.q.append(node)
return n.val
def get_root(self) -> TreeNode:
return self.r
Rust
use std::collections::VecDeque;
impl CBTInserter {
pub fn new(root: TreeNode) -> Self {
let mut t = VecDeque::new();
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
let r = Box::new(root);
t.push_back(r.clone());
while let Some(n) = t.pop_front() {
if n.left.is_none() || n.right.is_none() {
q.push_back(n.clone());
}
if let Some(ref l) = n.left { t.push_back(l.clone()); }
if let Some(ref r) = n.right { t.push_back(r.clone()); }
}
CBTInserter { r, q }
}
pub fn insert(&mut self, v: i32) -> i32 {
let n = self.q.front().unwrap().clone();
let node = Box::new(TreeNode::new(v));
if n.left.is_none() {
n.left = Some(node);
} else {
n.right = Some(node);
self.q.pop_front();
}
self.q.push_back(node);
n.val
}
pub fn get_root(&self) -> Box<TreeNode> {
self.r.clone()
}
}
TypeScript
class CBTInserter {
private r: TreeNode;
private q: TreeNode[] = [];
constructor(root: TreeNode) {
this.r = root;
const t: TreeNode[] = [root];
while (t.length) {
const n = t.shift()!;
if (!n.left || !n.right) this.q.push(n);
if (n.left) t.push(n.left);
if (n.right) t.push(n.right);
}
}
insert(v: number): number {
const n = this.q[0];
const node = new TreeNode(v);
if (!n.left) n.left = node;
else { n.right = node; this.q.shift(); }
this.q.push(node);
return n.val;
}
get_root(): TreeNode {
return this.r;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(1)per insert - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)