Construct 2D Grid Matching Graph Layout
HardUpdated: Jul 7, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given a 2D integer array edges representing an undirected graph having n nodes, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] denotes an edge between nodes
ui and vi.
Construct a 2D grid that satisfies these conditions:
- The grid contains all nodes from
0ton - 1in its cells, with each node appearing exactly once. - Two nodes should be in adjacent grid cells (horizontally or vertically) if and only if there is an edge between them in
edges.
It is guaranteed that edges can form a 2D grid that satisfies the conditions.
Return a 2D integer array satisfying the conditions above. If there are multiple solutions, return any of them.
Examples
Example 1
Input: n = 4, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
Output: [[3,1],[2,0]]
Explanation:
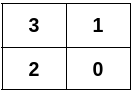
Example 2
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,1],[1,3],[2,3],[2,4]]
Output: [[4,2,3,1,0]]
Explanation:

Example 3
Input: n = 9, edges =
[[0,1],[0,4],[0,5],[1,7],[2,3],[2,4],[2,5],[3,6],[4,6],[4,7],[6,8],[7,8]]
Output: [[8,6,3],[7,4,2],[1,0,5]]
Explanation:
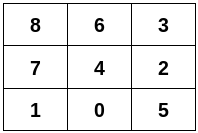
Constraints
2 <= n <= 5 * 10^41 <= edges.length <= 10^5edges[i] = [ui, vi]0 <= ui < vi < n- All the edges are distinct.
- The input is generated such that
edgescan form a 2D grid that satisfies the conditions.
Solution
Method 1 – BFS Grid Placement
Intuition
Since the graph can be embedded as a grid, we can use BFS to assign each node to a grid cell, starting from any node and placing its neighbors in adjacent cells. We keep track of used grid positions and node-to-position mappings, and reconstruct the grid at the end.
Approach
- Build the adjacency list from edges.
- Use BFS to assign each node to a unique grid cell, starting from node 0 at (0,0).
- For each node, try to place its neighbors in adjacent (up/down/left/right) cells that are not yet used.
- Track the min/max row and col to determine the grid bounds.
- After BFS, create a grid of the required size and fill in the node numbers at their positions.
- Return the grid.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> construct2DGrid(vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int n = 0;
for (auto& e : edges) n = max(n, max(e[0], e[1]));
n++;
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
map<pair<int,int>, int> pos2node;
map<int, pair<int,int>> node2pos;
queue<pair<int,int>> q;
set<pair<int,int>> used;
q.push({0,0});
node2pos[0] = {0,0};
pos2node[{0,0}] = 0;
used.insert({0,0});
vector<int> dr = {0,0,1,-1}, dc = {1,-1,0,0};
int idx = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
auto [r,c] = q.front(); q.pop();
int u = pos2node[{r,c}];
for (int v : g[u]) {
if (node2pos.count(v)) continue;
for (int d = 0; d < 4; ++d) {
int nr = r + dr[d], nc = c + dc[d];
if (!used.count({nr,nc})) {
node2pos[v] = {nr,nc};
pos2node[{nr,nc}] = v;
used.insert({nr,nc});
q.push({nr,nc});
break;
}
}
}
}
int minr=1e9,maxr=-1e9,minc=1e9,maxc=-1e9;
for (auto& [node, pos] : node2pos) {
minr = min(minr, pos.first);
maxr = max(maxr, pos.first);
minc = min(minc, pos.second);
maxc = max(maxc, pos.second);
}
int rows = maxr-minr+1, cols = maxc-minc+1;
vector<vector<int>> grid(rows, vector<int>(cols, -1));
for (auto& [node, pos] : node2pos) {
grid[pos.first-minr][pos.second-minc] = node;
}
return grid;
}
};
Go
func Construct2DGrid(edges [][]int) [][]int {
n := 0
for _, e := range edges {
if e[0] > n { n = e[0] }
if e[1] > n { n = e[1] }
}
n++
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], e[1])
g[e[1]] = append(g[e[1]], e[0])
}
type pos struct{ r, c int }
pos2node := map[pos]int{}
node2pos := map[int]pos{}
used := map[pos]bool{}
q := []pos{{0, 0}}
node2pos[0] = pos{0, 0}
pos2node[pos{0, 0}] = 0
used[pos{0, 0}] = true
dr := []int{0, 0, 1, -1}
dc := []int{1, -1, 0, 0}
for len(q) > 0 {
p := q[0]; q = q[1:]
u := pos2node[p]
for _, v := range g[u] {
if _, ok := node2pos[v]; ok { continue }
for d := 0; d < 4; d++ {
nr, nc := p.r+dr[d], p.c+dc[d]
np := pos{nr, nc}
if !used[np] {
node2pos[v] = np
pos2node[np] = v
used[np] = true
q = append(q, np)
break
}
}
}
}
minr, maxr, minc, maxc := 1<<30, -1<<30, 1<<30, -1<<30
for _, p := range node2pos {
if p.r < minr { minr = p.r }
if p.r > maxr { maxr = p.r }
if p.c < minc { minc = p.c }
if p.c > maxc { maxc = p.c }
}
rows, cols := maxr-minr+1, maxc-minc+1
grid := make([][]int, rows)
for i := range grid { grid[i] = make([]int, cols) }
for node, p := range node2pos {
grid[p.r-minr][p.c-minc] = node
}
return grid
}
Java
class Solution {
public int[][] construct2DGrid(int[][] edges) {
int n = 0;
for (int[] e : edges) n = Math.max(n, Math.max(e[0], e[1]));
n++;
List<List<Integer>> g = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) g.add(new ArrayList<>());
for (int[] e : edges) {
g.get(e[0]).add(e[1]);
g.get(e[1]).add(e[0]);
}
Map<String, Integer> pos2node = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, int[]> node2pos = new HashMap<>();
Queue<int[]> q = new LinkedList<>();
Set<String> used = new HashSet<>();
q.offer(new int[]{0,0});
node2pos.put(0, new int[]{0,0});
pos2node.put("0,0", 0);
used.add("0,0");
int[] dr = {0,0,1,-1}, dc = {1,-1,0,0};
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int[] p = q.poll();
int u = pos2node.get(p[0]+","+p[1]);
for (int v : g.get(u)) {
if (node2pos.containsKey(v)) continue;
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
int nr = p[0]+dr[d], nc = p[1]+dc[d];
String key = nr+","+nc;
if (!used.contains(key)) {
node2pos.put(v, new int[]{nr,nc});
pos2node.put(key, v);
used.add(key);
q.offer(new int[]{nr,nc});
break;
}
}
}
}
int minr=Integer.MAX_VALUE,maxr=Integer.MIN_VALUE,minc=Integer.MAX_VALUE,maxc=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int[] pos : node2pos.values()) {
minr = Math.min(minr, pos[0]);
maxr = Math.max(maxr, pos[0]);
minc = Math.min(minc, pos[1]);
maxc = Math.max(maxc, pos[1]);
}
int rows = maxr-minr+1, cols = maxc-minc+1;
int[][] grid = new int[rows][cols];
for (Map.Entry<Integer, int[]> entry : node2pos.entrySet()) {
int[] pos = entry.getValue();
grid[pos[0]-minr][pos[1]-minc] = entry.getKey();
}
return grid;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun construct2DGrid(edges: Array<IntArray>): Array<IntArray> {
var n = 0
for (e in edges) n = maxOf(n, maxOf(e[0], e[1]))
n++
val g = Array(n) { mutableListOf<Int>() }
for (e in edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1])
g[e[1]].add(e[0])
}
val pos2node = mutableMapOf<Pair<Int,Int>, Int>()
val node2pos = mutableMapOf<Int, Pair<Int,Int>>()
val used = mutableSetOf<Pair<Int,Int>>()
val q = ArrayDeque<Pair<Int,Int>>()
q.add(0 to 0)
node2pos[0] = 0 to 0
pos2node[0 to 0] = 0
used.add(0 to 0)
val dr = listOf(0,0,1,-1)
val dc = listOf(1,-1,0,0)
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val (r,c) = q.removeFirst()
val u = pos2node[r to c]!!
for (v in g[u]) {
if (node2pos.containsKey(v)) continue
for (d in 0..3) {
val nr = r + dr[d]; val nc = c + dc[d]
if ((nr to nc) !in used) {
node2pos[v] = nr to nc
pos2node[nr to nc] = v
used.add(nr to nc)
q.add(nr to nc)
break
}
}
}
}
var minr=Int.MAX_VALUE; var maxr=Int.MIN_VALUE; var minc=Int.MAX_VALUE; var maxc=Int.MIN_VALUE
for ((_, pos) in node2pos) {
minr = minOf(minr, pos.first)
maxr = maxOf(maxr, pos.first)
minc = minOf(minc, pos.second)
maxc = maxOf(maxc, pos.second)
}
val rows = maxr-minr+1; val cols = maxc-minc+1
val grid = Array(rows) { IntArray(cols) }
for ((node, pos) in node2pos) {
grid[pos.first-minr][pos.second-minc] = node
}
return grid
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def construct2DGrid(self, edges: list[list[int]]) -> list[list[int]]:
from collections import deque, defaultdict
n = 0
for u, v in edges:
n = max(n, u, v)
n += 1
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v in edges:
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
pos2node = {}
node2pos = {}
used = set()
q = deque([(0, 0)])
node2pos[0] = (0, 0)
pos2node[(0, 0)] = 0
used.add((0, 0))
dr = [0, 0, 1, -1]
dc = [1, -1, 0, 0]
while q:
r, c = q.popleft()
u = pos2node[(r, c)]
for v in g[u]:
if v in node2pos:
continue
for d in range(4):
nr, nc = r + dr[d], c + dc[d]
if (nr, nc) not in used:
node2pos[v] = (nr, nc)
pos2node[(nr, nc)] = v
used.add((nr, nc))
q.append((nr, nc))
break
minr = min(pos[0] for pos in node2pos.values())
maxr = max(pos[0] for pos in node2pos.values())
minc = min(pos[1] for pos in node2pos.values())
maxc = max(pos[1] for pos in node2pos.values())
rows, cols = maxr - minr + 1, maxc - minc + 1
grid = [[-1] * cols for _ in range(rows)]
for node, (r, c) in node2pos.items():
grid[r - minr][c - minc] = node
return grid
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn construct_2d_grid(edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
use std::collections::{VecDeque, HashMap, HashSet};
let mut n = 0;
for e in &edges {
n = n.max(e[0]).max(e[1]);
}
n += 1;
let mut g = vec![vec![]; n as usize];
for e in &edges {
g[e[0] as usize].push(e[1] as usize);
g[e[1] as usize].push(e[0] as usize);
}
let mut pos2node = HashMap::new();
let mut node2pos = HashMap::new();
let mut used = HashSet::new();
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
q.push_back((0, 0));
node2pos.insert(0, (0, 0));
pos2node.insert((0, 0), 0);
used.insert((0, 0));
let dr = [0, 0, 1, -1];
let dc = [1, -1, 0, 0];
while let Some((r, c)) = q.pop_front() {
let u = *pos2node.get(&(r, c)).unwrap();
for &v in &g[u] {
if node2pos.contains_key(&v) { continue; }
for d in 0..4 {
let nr = r + dr[d];
let nc = c + dc[d];
if !used.contains(&(nr, nc)) {
node2pos.insert(v, (nr, nc));
pos2node.insert((nr, nc), v);
used.insert((nr, nc));
q.push_back((nr, nc));
break;
}
}
}
}
let minr = node2pos.values().map(|x| x.0).min().unwrap();
let maxr = node2pos.values().map(|x| x.0).max().unwrap();
let minc = node2pos.values().map(|x| x.1).min().unwrap();
let maxc = node2pos.values().map(|x| x.1).max().unwrap();
let rows = (maxr - minr + 1) as usize;
let cols = (maxc - minc + 1) as usize;
let mut grid = vec![vec![-1; cols]; rows];
for (&node, &(r, c)) in &node2pos {
grid[(r - minr) as usize][(c - minc) as usize] = node as i32;
}
grid
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
construct2DGrid(edges: number[][]): number[][] {
let n = 0;
for (const [u, v] of edges) n = Math.max(n, u, v);
n++;
const g: number[][] = Array.from({length: n}, () => []);
for (const [u, v] of edges) {
g[u].push(v);
g[v].push(u);
}
const pos2node = new Map<string, number>();
const node2pos = new Map<number, [number, number]>();
const used = new Set<string>();
const q: [number, number][] = [[0, 0]];
node2pos.set(0, [0, 0]);
pos2node.set('0,0', 0);
used.add('0,0');
const dr = [0, 0, 1, -1], dc = [1, -1, 0, 0];
while (q.length) {
const [r, c] = q.shift()!;
const u = pos2node.get(`${r},${c}`)!;
for (const v of g[u]) {
if (node2pos.has(v)) continue;
for (let d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
const nr = r + dr[d], nc = c + dc[d];
const key = `${nr},${nc}`;
if (!used.has(key)) {
node2pos.set(v, [nr, nc]);
pos2node.set(key, v);
used.add(key);
q.push([nr, nc]);
break;
}
}
}
}
let minr = Infinity, maxr = -Infinity, minc = Infinity, maxc = -Infinity;
for (const [_, [r, c]] of node2pos) {
minr = Math.min(minr, r);
maxr = Math.max(maxr, r);
minc = Math.min(minc, c);
maxc = Math.max(maxc, c);
}
const rows = maxr - minr + 1, cols = maxc - minc + 1;
const grid: number[][] = Array.from({length: rows}, () => Array(cols).fill(-1));
for (const [node, [r, c]] of node2pos) {
grid[r - minr][c - minc] = node;
}
return grid;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is the number of nodes. Each node and edge is processed once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the grid and mappings.