Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Postorder Traversal
Problem
Given two integer arrays inorder and postorder where inorder is the inorder traversal of a binary tree and postorder is the postorder traversal of the same tree, construct and return the binary tree.
Examples
Example 1:
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
Input: inorder = [9,3,15,20,7], postorder = [9,15,7,20,3]
Output: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Solution
Method 1 - Recursion
We can solve the problem similar to [Construct Binary Tree from Inorder and Preorder Traversal](construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-preorder-traversal).
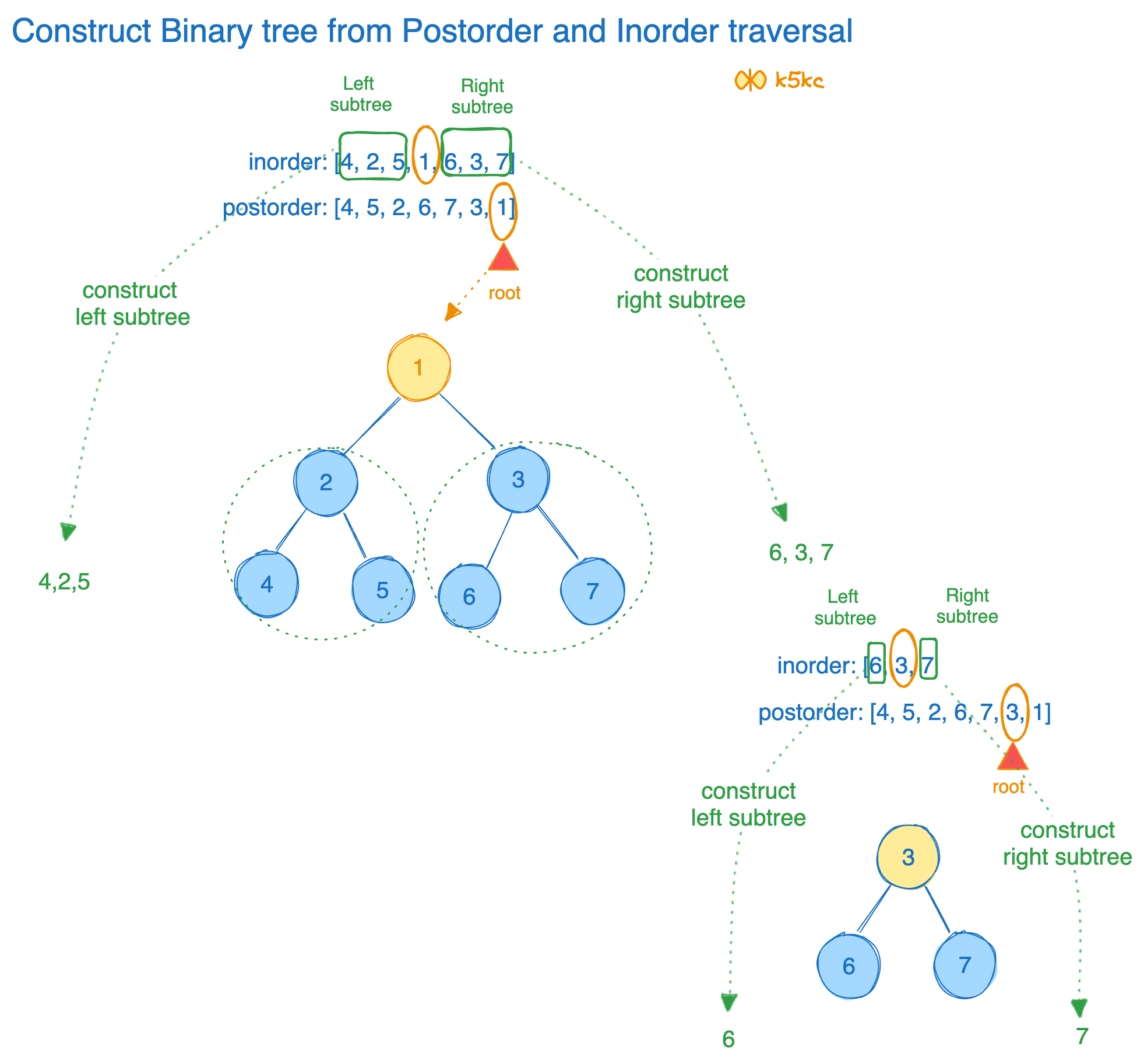
Lets look at the binary tree:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
The inorder and postorder traversal are:
inorder = [4, 2, 5, 1, 6, 3, 7]
postorder = [4, 5, 2, 6, 7, 3, 1]
How does postorder[] array helps?
The last element in postorder[] acts as the root of the tree (in this case, 1).
How does inorder[] array helps?
inorder[] helps determine the left and right subtrees of the root. Elements appearing before the root in inorder[] belong to the left subtree, while elements appearing after belong to the right subtree. In our case, it is [4, 2, 5] on left and [6, 3, 7] on right. (See picture below).
Code
Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
// Call the recursive function with full arrays and return the result
return buildTree(inorder, 0, inorder.length - 1, postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
private TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int inStart, int inEnd, int[] postorder, int postStart, int postEnd) {
// Base case
if (inStart > inEnd || postStart > postEnd) {
return null;
}
// Find the root node from the last element of postorder traversal
int rootVal = postorder[postEnd];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);
// Find the index of the root node in inorder traversal
int rootIndex = 0;
for (int i = inStart; i <= inEnd; i++) {
if (inorder[i] == rootVal) {
rootIndex = i;
break;
}
}
// Recursively build the left and right subtrees
int leftSize = rootIndex - inStart;
int rightSize = inEnd - rootIndex;
root.left = buildTree(inorder, inStart, rootIndex - 1, postorder, postStart, postStart + leftSize - 1);
root.right = buildTree(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inEnd, postorder, postEnd - rightSize, postEnd - 1);
return root;
}
}