Convert BST to Greater Sum Tree
Problem
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree (BST), convert it to a Greater Tree such that every key of the original BST is changed to the original key plus the sum of all keys greater than the original key in BST.
Examples
Example 1:
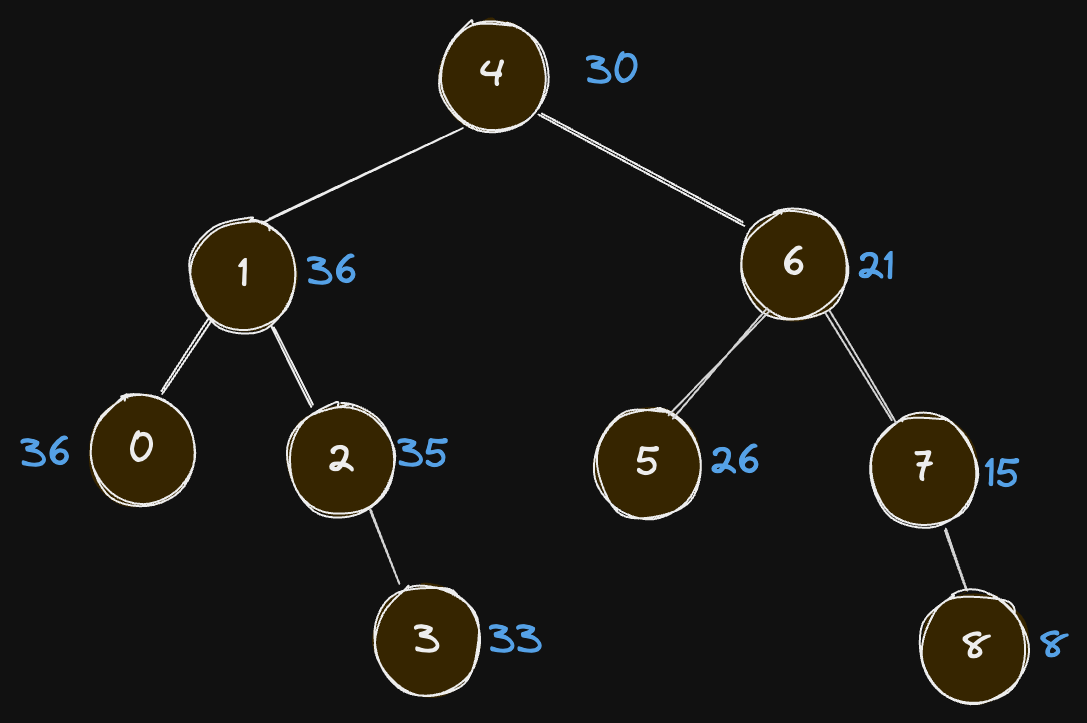
Input:
root = [4,1,6,0,2,5,7,null,null,null,3,null,null,null,8]
Output:
[30,36,21,36,35,26,15,null,null,null,33,null,null,null,8]
Example 2:
Input:
root = [0,null,1]
Output:
[1,null,1]
Solution
Method 1 - Brute Force
Naive approach will be for every node, traverse the tree and find out all the nodes which are greater and update the node. But the time complexity of this approach will be O(n^2).
Method 2 - Recursive Reverse Inorder Traversal
Since this is a BST, the right most node in the BST is the biggest node among all the nodes. So, we can start from right, i.e. we do a reverse inorder traversal to traverse the nodes of the tree in descending order. Since we are visiting the nodes in the decreasing order, all we care about is maintaining the running sum of the nodes visited thus far.
In the process, we keep track of the running sum of all nodes which we have traversed thus far.
Video Explanation
Here is the video explanation: <div class="youtube-embed"><iframe src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/b37dAlprb6k" frameborder="0" allowfullscreen></iframe></div>
Code
Java
Using global variables
public class Solution {
private int sum = 0;
public TreeNode bstToGst(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
bstToGst(root.right); //visit the right node first
sum += root.val; //update the sum for the next node
root.val = sum;
bstToGst(root.left);
return root;
}
}
Without using global variables with object
class Solution {
public TreeNode bstToGst(TreeNode root) {
reverseInorder(root, new TreeNode(0));
return root;
}
private void reverseInorder(TreeNode root, TreeNode sum) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
int right = reverseInorder(root.right, sum);
sum.val += root.val;
root.val = sum.val;
return reverseInorder(root.left, sum);
}
}
Without using global variables with primitive
We can also just passed the primitive sum, but return int in reverseInorder() method.
class Solution {
public TreeNode bstToGst(TreeNode root) {
reverseInorder(root, 0);
return root;
}
private int reverseInorder(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root == null) {
return sum;
}
int right = reverseInorder(root.right, sum); // pass in provided sum for accumulation
root.val = root.val + right;
return reverseInorder(root.left, root.val); // pass in updated sum
}
}
Python
Using Global variables
# Using global variable
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.sum = 0
def bstToGst(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None:
return None
self.bstToGst(root.right)
self.sum += root.val
root.val = self.sum
self.bstToGst(root.left)
return root
Without using global variables with object
# Without global variable, using object
class Solution:
def bstToGst(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
class Sum:
def __init__(self):
self.val = 0
def reverseInorder(node: Optional[TreeNode], sum_obj: Sum) -> None:
if node is None:
return
reverseInorder(node.right, sum_obj)
sum_obj.val += node.val
node.val = sum_obj.val
reverseInorder(node.left, sum_obj)
reverseInorder(root, Sum())
return root
Without global variable, using primitive
class SolutionPrimitive:
def bstToGst(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
def reverseInorder(node: Optional[TreeNode], acc: int) -> int:
if node is None:
return acc
right_sum = reverseInorder(node.right, acc)
node.val += right_sum
return reverseInorder(node.left, node.val)
reverseInorder(root, 0)
return root
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is number of nodes in tree. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)for using recursive stack
Method 3 - Iterative Reverse Inorder Traversal
Initially, use curr to point to the root,
- push into Stack the right-most path of current subtree;
- pop out a node, update sum and the node value;
- point
currto the node's left child, if any; Repeat the above till the stack is empty andcurrhas no left child.
Code
Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode bstToGst(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> stk = new ArrayDeque<>();
TreeNode curr = root;
int sum = 0;
while (curr != null || !stk.isEmpty()) {
while (curr != null) { // save right-most path of the current subtree
stk.push(curr);
curr = curr.right;
}
curr = stk.pop(); // pop out by reversed in-order.
sum += curr.val; // update sum.
curr.val = sum; // update node value.
curr = curr.left; // move to left branch.
}
return root;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def bstToGst(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
stack: list[TreeNode] = []
curr = root
total = 0
while curr is not None or stack:
while curr is not None:
stack.append(curr)
curr = curr.right
curr = stack.pop()
total += curr.val
curr.val = total
curr = curr.left
return root
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is number of nodes in tree. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)for using stack