Correct a Binary Tree
Problem
You have a binary tree with a small defect. There is exactly one invalid node where its right child incorrectly points to another node at the same depth but to the invalid node 's right.
Given the root of the binary tree with this defect, root, return the root of the binary tree afterremoving this invalid node and every node underneath it (minus the node it incorrectly points to).
Custom testing:
The test input is read as 3 lines:
TreeNode rootint fromNode(not available tocorrectBinaryTree)int toNode(not available tocorrectBinaryTree)
After the binary tree rooted at root is parsed, the TreeNode with value of fromNode will have its right child pointer pointing to the TreeNode with a value of toNode. Then, root is passed to correctBinaryTree.
Examples
Example 1:
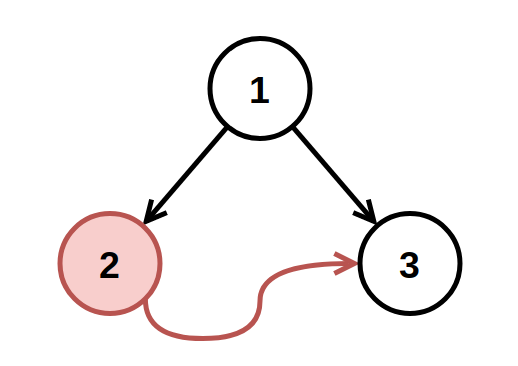
Input: root = [1,2,3], fromNode = 2, toNode = 3
Output: [1,null,3]
Explanation: The node with value 2 is invalid, so remove it.
Example 2:
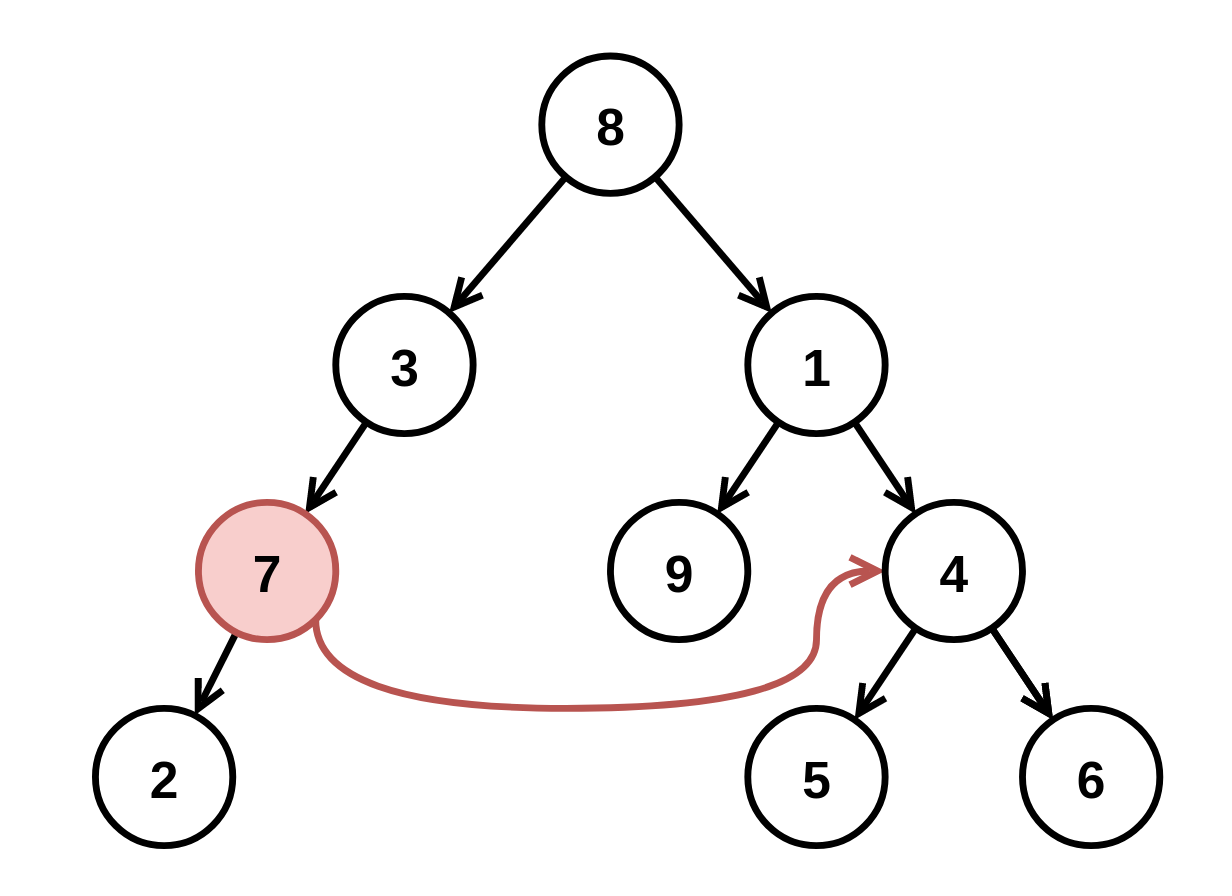
Input: root = [8,3,1,7,null,9,4,2,null,null,null,5,6], fromNode = 7, toNode = 4
Output: [8,3,1,null,null,9,4,null,null,5,6]
Explanation: The node with value 7 is invalid, so remove it and the node underneath it, node 2.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[3, 10^4]. -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9- All
Node.valare unique. fromNode != toNodefromNodeandtoNodewill exist in the tree and will be on the same depth.toNodeis to the right offromNode.fromNode.rightisnullin the initial tree from the test data.
Solution
Method 1 – BFS with HashSet 1
Intuition
The invalid node's right child points to another node at the same depth but to its right. If we traverse the tree level by level (BFS) from right to left, we can use a set to track all nodes seen so far at the current level. When we find a node whose right child is already in the set, that node is the invalid one and should be removed.
Approach
- Use BFS to traverse the tree level by level, but process nodes from right to left at each level.
- For each node, if its right child is in the set of seen nodes, mark this node as the invalid node to remove.
- Remove the invalid node by setting its parent's left or right pointer to null.
- Return the root after removal.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* correctBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
unordered_set<TreeNode*> seen;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
vector<TreeNode*> level;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) level.push_back(q.front()), q.pop();
for (int i = sz-1; i >= 0; --i) {
TreeNode* node = level[i];
if (node->right && seen.count(node->right)) {
node = nullptr;
return root;
}
seen.insert(node);
if (node->right) q.push(node->right);
if (node->left) q.push(node->left);
}
}
return root;
}
};
Go
func correctBinaryTree(root *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
type pair struct{node, parent *TreeNode; isLeft bool}
q := []pair{{root, nil, false}}
for len(q) > 0 {
next := []pair{}
seen := map[*TreeNode]bool{}
for i := len(q)-1; i >= 0; i-- {
p := q[i]
node := p.node
if node.Right != nil && seen[node.Right] {
if p.parent != nil {
if p.isLeft { p.parent.Left = nil } else { p.parent.Right = nil }
} else {
return nil
}
return root
}
seen[node] = true
if node.Left != nil { next = append(next, pair{node.Left, node, true}) }
if node.Right != nil { next = append(next, pair{node.Right, node, false}) }
}
q = next
}
return root
}
Java
class Solution {
public TreeNode correctBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
Set<TreeNode> seen = new HashSet<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int sz = q.size();
List<TreeNode> level = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) level.add(q.poll());
for (int i = sz-1; i >= 0; --i) {
TreeNode node = level.get(i);
if (node.right != null && seen.contains(node.right)) {
node = null;
return root;
}
seen.add(node);
if (node.right != null) q.offer(node.right);
if (node.left != null) q.offer(node.left);
}
}
return root;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun correctBinaryTree(root: TreeNode?): TreeNode? {
val q = ArrayDeque<TreeNode?>()
val seen = mutableSetOf<TreeNode?>()
q.add(root)
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val level = mutableListOf<TreeNode?>()
repeat(q.size) { level.add(q.removeFirst()) }
for (i in level.size-1 downTo 0) {
val node = level[i]
if (node?.right != null && node.right in seen) {
// Remove node
return root
}
seen.add(node)
node?.right?.let { q.add(it) }
node?.left?.let { q.add(it) }
}
}
return root
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def correctBinaryTree(self, root: 'Optional[TreeNode]') -> 'Optional[TreeNode]':
from collections import deque
q = deque([(root, None, False)]) # node, parent, is_left
while q:
next_level = []
seen = set()
for node, parent, is_left in reversed(q):
if node.right and node.right in seen:
if parent:
if is_left:
parent.left = None
else:
parent.right = None
return root
else:
return None
seen.add(node)
if node.left:
next_level.append((node.left, node, True))
if node.right:
next_level.append((node.right, node, False))
q = next_level
return root
Rust
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::collections::{HashSet, VecDeque};
impl Solution {
pub fn correct_binary_tree(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
if root.is_none() {
return root;
}
let mut queue = VecDeque::new();
queue.push_back((root.clone(), None, false)); // (node, parent, is_left_child)
while !queue.is_empty() {
let mut next_level = VecDeque::new();
let mut seen = HashSet::new();
// Process current level from right to left
while let Some((node_opt, parent_opt, is_left)) = queue.pop_back() {
if let Some(node) = node_opt {
let node_borrow = node.borrow();
// Check if right child is already seen (invalid node)
if let Some(ref right_child) = node_borrow.right {
if seen.contains(&(right_child.as_ptr() as *const _)) {
// Found invalid node, remove it
drop(node_borrow); // Release borrow before mutation
if let Some(parent) = parent_opt {
let mut parent_borrow = parent.borrow_mut();
if is_left {
parent_borrow.left = None;
} else {
parent_borrow.right = None;
}
} else {
// Invalid node is root (shouldn't happen in this problem)
return None;
}
return root;
}
}
// Mark current node as seen
seen.insert(node.as_ptr() as *const _);
// Add children to next level
if let Some(ref left_child) = node_borrow.left {
next_level.push_back((Some(left_child.clone()), Some(node.clone()), true));
}
if let Some(ref right_child) = node_borrow.right {
next_level.push_back((Some(right_child.clone()), Some(node.clone()), false));
}
}
}
queue = next_level;
}
root
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
correctBinaryTree(root: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null {
let q: [TreeNode, TreeNode | null, boolean][] = [[root!, null, false]];
while (q.length) {
let next: [TreeNode, TreeNode | null, boolean][] = [];
let seen = new Set<TreeNode>();
for (let i = q.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
let [node, parent, isLeft] = q[i];
if (node.right && seen.has(node.right)) {
if (parent) {
if (isLeft) parent.left = null;
else parent.right = null;
return root;
} else {
return null;
}
}
seen.add(node);
if (node.left) next.push([node.left, node, true]);
if (node.right) next.push([node.right, node, false]);
}
q = next;
}
return root;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the tree, as each node is visited once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the queue and set used in BFS.