Count Pairs Of Nodes
Problem
You are given an undirected graph defined by an integer n, the number of nodes, and a 2D integer array edges, the edges in the graph, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an undirected edge between ui and
vi. You are also given an integer array queries.
Let incident(a, b) be defined as the number of edges that are connected to either node a or b.
The answer to the jth query is the number of pairs of nodes (a, b)
that satisfy both of the following conditions:
a < bincident(a, b) > queries[j]
Return an arrayanswers such thatanswers.length == queries.length
andanswers[j]is the answer of thejth query.
Note that there can be multiple edges between the same two nodes.
Examples
Example 1
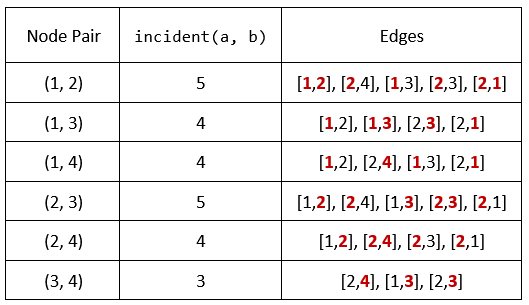
Input: n = 4, edges = [[1,2],[2,4],[1,3],[2,3],[2,1]], queries = [2,3]
Output: [6,5]
Explanation: The calculations for incident(a, b) are shown in the table above.
The answers for each of the queries are as follows:
- answers[0] = 6. All the pairs have an incident(a, b) value greater than 2.
- answers[1] = 5. All the pairs except (3, 4) have an incident(a, b) value greater than 3.
Example 2
Input: n = 5, edges = [[1,5],[1,5],[3,4],[2,5],[1,3],[5,1],[2,3],[2,5]], queries = [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: [10,10,9,8,6]
Constraints
2 <= n <= 2 * 10^41 <= edges.length <= 10^51 <= ui, vi <= nui != vi1 <= queries.length <= 200 <= queries[j] < edges.length
Solution
Method 1 – Degree Counting and Two Pointers
Intuition
The key is to count the number of pairs (a, b) such that the sum of their degrees (number of incident edges) minus the number of shared edges is greater than the query. We use sorting and two pointers to efficiently count such pairs for each query.
Approach
- Count the degree of each node (number of edges connected to it).
- For each edge, count the number of times each pair appears (to handle multiple edges between the same pair).
- Sort the degree array.
- For each query:
- Use two pointers to count pairs (a, b) with degree[a] + degree[b] > query.
- Subtract pairs where the sum is only greater due to shared edges.
- Return the answer for each query.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> countPairs(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& queries) {
vector<int> deg(n+1, 0);
map<pair<int,int>, int> cnt;
for (auto& e : edges) {
int u = min(e[0], e[1]), v = max(e[0], e[1]);
deg[u]++; deg[v]++;
cnt[{u,v}]++;
}
vector<int> sorted_deg = deg;
sort(sorted_deg.begin()+1, sorted_deg.end());
vector<int> ans;
for (int q : queries) {
int res = 0, l = 1, r = n;
while (l < r) {
if (sorted_deg[l] + sorted_deg[r] > q) {
res += r - l;
r--;
} else {
l++;
}
}
for (auto& [p, c] : cnt) {
int u = p.first, v = p.second;
if (deg[u] + deg[v] > q && deg[u] + deg[v] - c <= q) res--;
}
ans.push_back(res);
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func countPairs(n int, edges [][]int, queries []int) []int {
deg := make([]int, n+1)
cnt := map[[2]int]int{}
for _, e := range edges {
u, v := e[0], e[1]
if u > v { u, v = v, u }
deg[u]++; deg[v]++
cnt[[2]int{u, v}]++
}
sortedDeg := append([]int{}, deg[1:]...)
sort.Ints(sortedDeg)
ans := make([]int, len(queries))
for i, q := range queries {
res := 0
l, r := 0, n-1
for l < r {
if sortedDeg[l]+sortedDeg[r] > q {
res += r - l
r--
} else {
l++
}
}
for p, c := range cnt {
u, v := p[0], p[1]
if deg[u]+deg[v] > q && deg[u]+deg[v]-c <= q {
res--
}
}
ans[i] = res
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int[] countPairs(int n, int[][] edges, int[] queries) {
int[] deg = new int[n+1];
Map<Long, Integer> cnt = new HashMap<>();
for (int[] e : edges) {
int u = Math.min(e[0], e[1]), v = Math.max(e[0], e[1]);
deg[u]++; deg[v]++;
long key = ((long)u << 32) | v;
cnt.put(key, cnt.getOrDefault(key, 0) + 1);
}
int[] sortedDeg = Arrays.copyOfRange(deg, 1, n+1);
Arrays.sort(sortedDeg);
int[] ans = new int[queries.length];
for (int k = 0; k < queries.length; k++) {
int q = queries[k], res = 0, l = 0, r = n-1;
while (l < r) {
if (sortedDeg[l] + sortedDeg[r] > q) {
res += r - l;
r--;
} else {
l++;
}
}
for (Map.Entry<Long, Integer> entry : cnt.entrySet()) {
int u = (int)(entry.getKey() >> 32), v = (int)(entry.getKey() & 0xFFFFFFFFL);
if (deg[u] + deg[v] > q && deg[u] + deg[v] - entry.getValue() <= q) res--;
}
ans[k] = res;
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun countPairs(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>, queries: IntArray): IntArray {
val deg = IntArray(n+1)
val cnt = mutableMapOf<Pair<Int,Int>, Int>()
for (e in edges) {
val u = minOf(e[0], e[1])
val v = maxOf(e[0], e[1])
deg[u]++; deg[v]++
cnt[u to v] = cnt.getOrDefault(u to v, 0) + 1
}
val sortedDeg = deg.slice(1..n).sorted()
val ans = IntArray(queries.size)
for ((k, q) in queries.withIndex()) {
var res = 0
var l = 0; var r = n-1
while (l < r) {
if (sortedDeg[l] + sortedDeg[r] > q) {
res += r - l
r--
} else {
l++
}
}
for ((p, c) in cnt) {
val (u, v) = p
if (deg[u] + deg[v] > q && deg[u] + deg[v] - c <= q) res--
}
ans[k] = res
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def countPairs(self, n: int, edges: list[list[int]], queries: list[int]) -> list[int]:
deg = [0] * (n+1)
cnt = {}
for u, v in edges:
if u > v:
u, v = v, u
deg[u] += 1
deg[v] += 1
cnt[(u, v)] = cnt.get((u, v), 0) + 1
sorted_deg = sorted(deg[1:])
ans = []
for q in queries:
res = 0
l, r = 0, n-1
while l < r:
if sorted_deg[l] + sorted_deg[r] > q:
res += r - l
r -= 1
else:
l += 1
for (u, v), c in cnt.items():
if deg[u] + deg[v] > q and deg[u] + deg[v] - c <= q:
res -= 1
ans.append(res)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn count_pairs(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, queries: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
use std::collections::HashMap;
let n = n as usize;
let mut deg = vec![0; n+1];
let mut cnt = HashMap::new();
for e in &edges {
let (mut u, mut v) = (e[0] as usize, e[1] as usize);
if u > v { std::mem::swap(&mut u, &mut v); }
deg[u] += 1;
deg[v] += 1;
*cnt.entry((u, v)).or_insert(0) += 1;
}
let mut sorted_deg = deg[1..].to_vec();
sorted_deg.sort();
let mut ans = vec![];
for &q in &queries {
let mut res = 0;
let (mut l, mut r) = (0, n-1);
while l < r {
if sorted_deg[l] + sorted_deg[r] > q {
res += (r - l) as i32;
r -= 1;
} else {
l += 1;
}
}
for (&(u, v), &c) in &cnt {
if deg[u] + deg[v] > q && deg[u] + deg[v] - c <= q {
res -= 1;
}
}
ans.push(res);
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
countPairs(n: number, edges: number[][], queries: number[]): number[] {
const deg = Array(n+1).fill(0);
const cnt: Record<string, number> = {};
for (const [u0, v0] of edges) {
let u = u0, v = v0;
if (u > v) [u, v] = [v, u];
deg[u]++;
deg[v]++;
const key = `${u},${v}`;
cnt[key] = (cnt[key] || 0) + 1;
}
const sortedDeg = deg.slice(1).sort((a, b) => a - b);
const ans: number[] = [];
for (const q of queries) {
let res = 0, l = 0, r = n-1;
while (l < r) {
if (sortedDeg[l] + sortedDeg[r] > q) {
res += r - l;
r--;
} else {
l++;
}
}
for (const key in cnt) {
const [u, v] = key.split(',').map(Number);
if (deg[u] + deg[v] > q && deg[u] + deg[v] - cnt[key] <= q) res--;
}
ans.push(res);
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n log n + m + qn)where n is the number of nodes, m is the number of edges, and q is the number of queries. Sorting and two pointers dominate. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n + m)for degree and edge count storage.