Depth of BST Given Insertion Order
Problem
You are given a 0-indexed integer array order of length n, a
permutation of integers from 1 to n representing the order of insertion into a binary search tree.
A binary search tree is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
The binary search tree is constructed as follows:
order[0]will be the root of the binary search tree.- All subsequent elements are inserted as the child of any existing node such that the binary search tree properties hold.
Return thedepth of the binary search tree.
A binary tree's depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
Examples
Example 1:
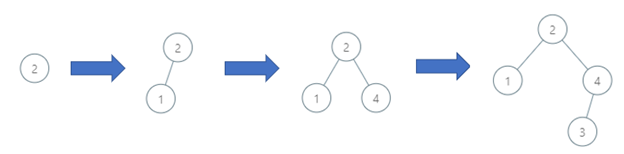
Input: order = [2,1,4,3]
Output: 3
Explanation: The binary search tree has a depth of 3 with path 2->3->4.
Example 2:
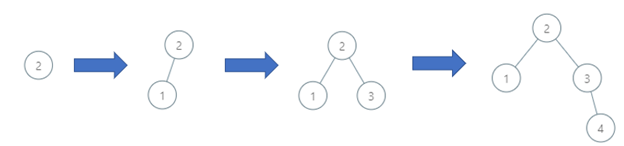
Input: order = [2,1,3,4]
Output: 3
Explanation: The binary search tree has a depth of 3 with path 2->3->4.
Example 3:
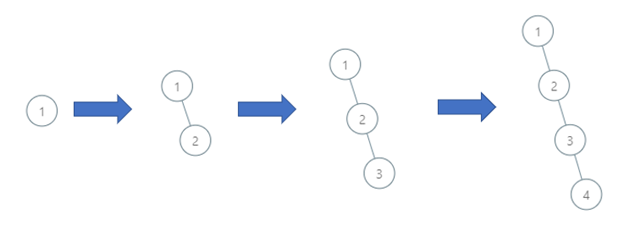
Input: order = [1,2,3,4]
Output: 4
Explanation: The binary search tree has a depth of 4 with path 1->2->3->4.
Constraints:
n == order.length1 <= n <= 10^5orderis a permutation of integers between1andn.
Solution
Method 1 – Ordered Set / Map for Predecessor and Successor Depths
Intuition
To efficiently compute the depth of the BST as we insert each value, we can use an ordered set or map to keep track of inserted values and their depths. For each new value, its depth is one more than the maximum depth of its predecessor or successor (if they exist). The answer is the maximum depth after all insertions.
Approach
- Use an ordered map (e.g., TreeMap in Java, std::map in C++, or SortedDict in Python) to store inserted values and their depths.
- For each value in the insertion order:
- Find the predecessor (largest value less than current) and successor (smallest value greater than current) in the map.
- The depth of the current value is
max(depth of predecessor, depth of successor) + 1. - Insert the value and its depth into the map.
- The answer is the maximum depth in the map.
Code
C++
#include <map>
class Solution {
public:
int bstDepth(vector<int>& order) {
map<int, int> mp;
int ans = 0;
for (int x : order) {
auto it = mp.lower_bound(x);
int d = 1;
if (it != mp.end()) d = max(d, it->second + 1);
if (it != mp.begin()) {
--it;
d = max(d, it->second + 1);
}
mp[x] = d;
ans = max(ans, d);
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
import "sort"
func bstDepth(order []int) int {
type pair struct{v, d int}
arr := []pair{}
ans := 0
for _, x := range order {
i := sort.Search(len(arr), func(i int) bool { return arr[i].v >= x })
d := 1
if i < len(arr) && arr[i].v > x {
d = max(d, arr[i].d+1)
}
if i > 0 {
d = max(d, arr[i-1].d+1)
}
arr = append(arr, pair{x, d})
sort.Slice(arr, func(i, j int) bool { return arr[i].v < arr[j].v })
if d > ans {
ans = d
}
}
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a } else { return b } }
Java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int bstDepth(int[] order) {
TreeMap<Integer, Integer> mp = new TreeMap<>();
int ans = 0;
for (int x : order) {
Integer pred = mp.lowerKey(x);
Integer succ = mp.higherKey(x);
int d = 1;
if (succ != null) d = Math.max(d, mp.get(succ) + 1);
if (pred != null) d = Math.max(d, mp.get(pred) + 1);
mp.put(x, d);
ans = Math.max(ans, d);
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
import java.util.TreeMap
class Solution {
fun bstDepth(order: IntArray): Int {
val mp = TreeMap<Int, Int>()
var ans = 0
for (x in order) {
val pred = mp.lowerKey(x)
val succ = mp.higherKey(x)
var d = 1
if (succ != null) d = maxOf(d, mp[succ]!! + 1)
if (pred != null) d = maxOf(d, mp[pred]!! + 1)
mp[x] = d
ans = maxOf(ans, d)
}
return ans
}
}
Python
from sortedcontainers import SortedDict
class Solution:
def bstDepth(self, order: list[int]) -> int:
mp = SortedDict()
ans = 0
for x in order:
idx = mp.bisect_left(x)
d = 1
if idx < len(mp):
d = max(d, mp.values()[idx] + 1)
if idx > 0:
d = max(d, mp.values()[idx-1] + 1)
mp[x] = d
ans = max(ans, d)
return ans
Rust
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
impl Solution {
pub fn bst_depth(order: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let mut mp = BTreeMap::new();
let mut ans = 0;
for &x in &order {
let mut d = 1;
if let Some((&succ, &ds)) = mp.range(x+1..).next() {
d = d.max(ds + 1);
}
if let Some((&pred, &dp)) = mp.range(..x).next_back() {
d = d.max(dp + 1);
}
mp.insert(x, d);
ans = ans.max(d);
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
bstDepth(order: number[]): number {
const arr: [number, number][] = [];
let ans = 0;
for (const x of order) {
let i = 0;
while (i < arr.length && arr[i][0] < x) i++;
let d = 1;
if (i < arr.length) d = Math.max(d, arr[i][1] + 1);
if (i > 0) d = Math.max(d, arr[i-1][1] + 1);
arr.push([x, d]);
arr.sort((a, b) => a[0] - b[0]);
ans = Math.max(ans, d);
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n log n), wherenis the length of the order array, due to ordered map/set operations. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the map/set storing inserted values and their depths.