Object-Oriented Design for a Parking Lot
Problem
Design an object-oriented multi-floor parking lot system that supports multiple entry/exit points, ticket issuance and payment, spot types (compact, large, handicapped, motorbike, electric), capacity tracking, per-hour pricing, and charging stations for electric vehicles. The system should allow admins and attendants to manage floors and spots; customers should be able to obtain tickets and pay via panels or attendants.
All existing diagrams and example code have been preserved and reorganized to the canonical OOD template.
Solution
1. Requirements Analysis
Functional Requirements:
- Support multiple floors with multiple entry/exit panels.
- Issue parking tickets at entrance panels and close them at exits.
- Accept payments via exit panels, info portals, or attendants (cash/card).
- Track different spot types (Handicapped, Compact, Large, Motorbike, Electric).
- Support vehicle types and map vehicles to compatible spot types.
- Display available spots per type on floor display boards.
- Enforce capacity limits and refuse entry when full.
- Support per-hour rate models and compute fees.
Non-Functional Requirements:
- Reliability: ticketing and payment must be durable and consistent.
- Scalability: handle many concurrent entries/exits and updates across floors.
- Usability: clear displays for drivers and simple attendant portals.
Constraints & Assumptions:
- Each physical copy (parking spot) is uniquely identifiable per floor.
- Electric spots include charging/payment panels.
2. Use Case Diagram
Actors: Admin, Customer, ParkingAttendant, System
Use Cases: Add/Modify Floors & Spots, Issue Ticket, Scan/Pay Ticket, Update Rates, Show Availability
graph TD subgraph ParkingLot UC1(Add/Remove/Edit Floor) UC2(Add/Remove/Edit Spot) UC3(Take Ticket) UC4(Scan/Pay Ticket) UC5(Update Rates) UC6(Show Availability) end Admin --> UC1 Admin --> UC2 Customer --> UC3 Customer --> UC4 Attendant --> UC4 System --> UC6

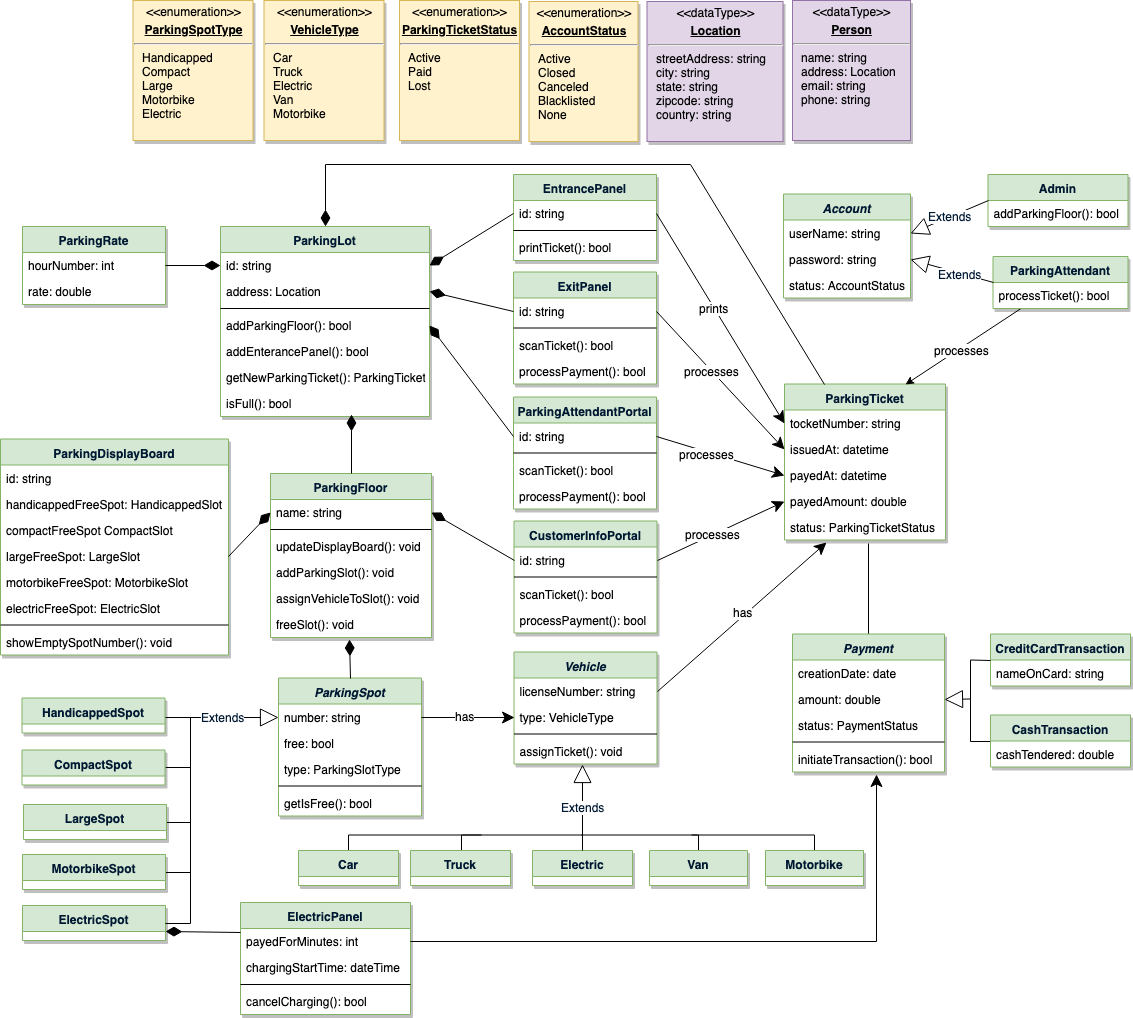
3. Class Diagram
Core classes and responsibilities:
- ParkingLot: singleton orchestrator for floors, panels, and active tickets.
- ParkingFloor: contains spots, display board, and info portals.
- ParkingSpot & subclasses: model spot types and occupancy.
- ParkingTicket: issued at entry, closed at exit with payment details.
- Account / Admin / ParkingAttendant: user roles and actions they may perform.
- ParkingRate: defines per-hour pricing rules.
- ParkingDisplayBoard: shows free spot numbers per type.
- ElectricPanel: handles EV charging and payment.
classDiagram class ParkingLot { +String name +Address address } class ParkingFloor { +String name +List<ParkingSpot> spots } class ParkingSpot { +int number +ParkingSpotType type +is_free() } class ParkingTicket { +String ticketNumber +DateTime issuedAt +DateTime closedAt } class ParkingDisplayBoard { +show_empty_spot_number() } class ParkingRate { +get_rate_for_hours() } class Account { +String user_name +AccountStatus status } ParkingLot "1" -- "1..*" ParkingFloor : has ParkingFloor "1" -- "1..*" ParkingSpot : contains ParkingFloor "1" -- "1" ParkingDisplayBoard : shows
4. Activity Diagram
Activity: Customer paying for a parking ticket
graph TD A[Customer arrives, takes ticket] --> B[Park vehicle] B --> C[On exit, scan ticket at exit panel] C --> D[Calculate fee based on ParkingRate] D --> E{Payment via card or cash?} E -- Card --> F[Process payment via Payment gateway] E -- Cash --> G[Attendant collects cash] F --> H[Mark ticket PAID and release exit] G --> H
5. High-Level Code Implementation
The original, detailed Python skeletons have been preserved (shortened only where appropriate to follow the skeleton guideline). Key enums, classes, and methods are below for quick reference.
from enum import Enum
class VehicleType(Enum):
CAR = 1
TRUCK = 2
ELECTRIC = 3
VAN = 4
MOTORBIKE = 5
class ParkingSpotType(Enum):
HANDICAPPED = 1
COMPACT = 2
LARGE = 3
MOTORBIKE = 4
ELECTRIC = 5
class AccountStatus(Enum):
ACTIVE = 1
BLOCKED = 2
BANNED = 3
class ParkingTicketStatus(Enum):
ACTIVE = 1
PAID = 2
LOST = 3
class Address:
def __init__(self, street, city, state, zip_code, country):
self.__street_address = street
self.__city = city
self.__state = state
self.__zip_code = zip_code
self.__country = country
class Person():
def __init__(self, name, address, email, phone):
self.__name = name
self.__address = address
self.__email = email
self.__phone = phone
class Account:
def __init__(self, user_name, password, person, status=AccountStatus.ACTIVE):
self.__user_name = user_name
self.__password = password
self.__person = person
self.__status = status
def reset_password(self):
pass
class ParkingSpot:
def __init__(self, number, parking_spot_type):
self.__number = number
self.__free = True
self.__vehicle = None
self.__parking_spot_type = parking_spot_type
def is_free(self):
return self.__free
def assign_vehicle(self, vehicle):
self.__vehicle = vehicle
self.__free = False
def remove_vehicle(self):
self.__vehicle = None
self.__free = True
class ParkingFloor:
def __init__(self, name):
self.__name = name
self.__handicapped_spots = {}
self.__compact_spots = {}
self.__large_spots = {}
self.__motorbike_spots = {}
self.__electric_spots = {}
self.__info_portals = {}
self.__display_board = ParkingDisplayBoard()
def add_parking_spot(self, spot):
# simplified: add spot to correct mapping
pass
class ParkingDisplayBoard:
def __init__(self, id=None):
self.__id = id
self.__handicapped_free_spot = None
self.__compact_free_spot = None
self.__large_free_spot = None
self.__motorbike_free_spot = None
self.__electric_free_spot = None
def show_empty_spot_number(self):
message = ""
if self.__handicapped_free_spot and self.__handicapped_free_spot.is_free():
message += "Free Handicapped: " + str(self.__handicapped_free_spot.get_number())
else:
message += "Handicapped is full"
# ... other spot types
print(message)
class ParkingLot:
# singleton ParkingLot to ensure only one object in the system
instance = None
class __OnlyOne:
def __init__(self, name, address):
self.__name = name
self.__address = address
self.__parking_rate = None
self.__entrance_panels = {}
self.__exit_panels = {}
self.__parking_floors = {}
self.__active_tickets = {}
def __init__(self, name, address):
if not ParkingLot.instance:
ParkingLot.instance = ParkingLot.__OnlyOne(name, address)
else:
ParkingLot.instance.__name = name
ParkingLot.instance.__address = address
def get_new_parking_ticket(self, vehicle):
# synchronized access to issue a ticket
ticket = ParkingTicket()
# persist and update counts
return ticket
class Transaction:
def process_payment(self, amount: float, method: str) -> bool:
return True
