Design an Ordered Stream
EasyUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
There is a stream of n (idKey, value) pairs arriving in an arbitrary order, where idKey is an integer between 1 and n and value is a string. No two pairs have the same id.
Design a stream that returns the values in increasing order of their IDs by returning a chunk (list) of values after each insertion. The concatenation of all the chunks should result in a list of the sorted values.
Implement the OrderedStream class:
OrderedStream(int n)Constructs the stream to takenvalues.String[] insert(int idKey, String value)Inserts the pair(idKey, value)into the stream, then returns the largest possible chunk of currently inserted values that appear next in the order.
Examples
Example 1:
Input:
["OrderedStream", "insert", "insert", "insert", "insert", "insert"]
[[5], [3, "ccccc"], [1, "aaaaa"], [2, "bbbbb"], [5, "eeeee"], [4, "ddddd"]]
Output:
[null, [], ["aaaaa"], ["bbbbb", "ccccc"], [], ["ddddd", "eeeee"]]
Explanation
// Note that the values ordered by ID is ["aaaaa", "bbbbb", "ccccc", "ddddd", "eeeee"].
OrderedStream os = new OrderedStream(5);
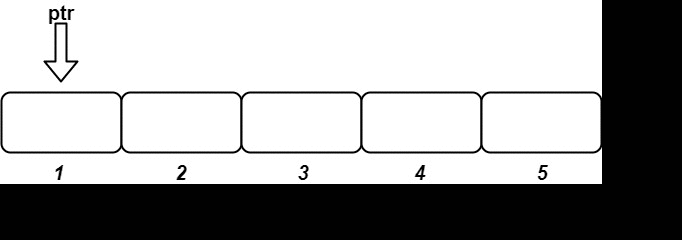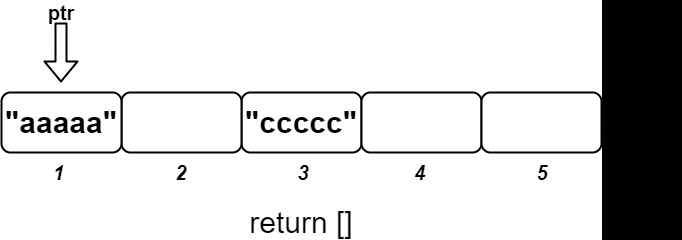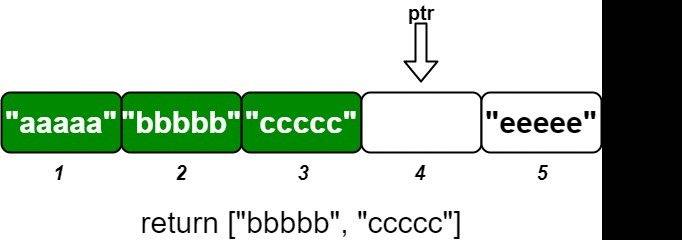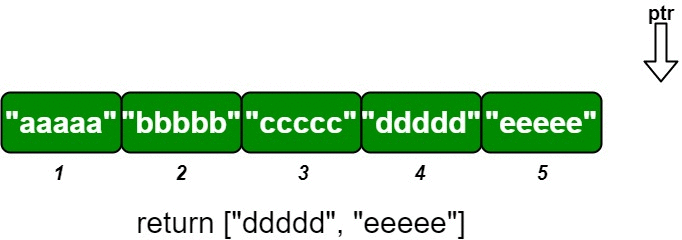
os.insert(3, "ccccc"); // Inserts (3, "ccccc"), returns [].
os.insert(1, "aaaaa"); // Inserts (1, "aaaaa"), returns ["aaaaa"].
os.insert(2, "bbbbb"); // Inserts (2, "bbbbb"), returns ["bbbbb", "ccccc"].
os.insert(5, "eeeee"); // Inserts (5, "eeeee"), returns [].
os.insert(4, "ddddd"); // Inserts (4, "ddddd"), returns ["ddddd", "eeeee"].
// Concatentating all the chunks returned:
// [] + ["aaaaa"] + ["bbbbb", "ccccc"] + [] + ["ddddd", "eeeee"] = ["aaaaa", "bbbbb", "ccccc", "ddddd", "eeeee"]
// The resulting order is the same as the order above.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 10001 <= id <= nvalue.length == 5valueconsists only of lowercase letters.- Each call to
insertwill have a uniqueid. - Exactly
ncalls will be made toinsert.
Solution
Method 1 - Using an array
The problem requires building a stream that can receive a series of (idKey, value) pairs and return the values in increasing order of their IDs. The goal is to manage the stream such that after each insertion, the largest possible chunk of values, starting from the smallest unprocessed ID, is returned.
Approach
- Initialization: Create an array to hold the values corresponding to each ID. Initialize a pointer to the smallest unprocessed ID (starting from 1).
- Insertion:
- Insert the value into the appropriate position in the array based on the given
idKey. - Start from the pointer and collect the largest chunk of consecutive values that have been inserted.
- Return the collected chunk and update the pointer to the next unprocessed ID.
- Insert the value into the appropriate position in the array based on the given
Code
Java
class OrderedStream {
private String[] stream;
private int ptr;
public OrderedStream(int n) {
stream = new String[n];
ptr = 0;
}
public String[] insert(int idKey, String value) {
stream[idKey - 1] = value;
List<String> chunk = new ArrayList<>();
while (ptr < stream.length && stream[ptr] != null) {
chunk.add(stream[ptr]);
ptr++;
}
return chunk.toArray(new String[0]);
}
}
Python
class OrderedStream:
def __init__(self, n: int):
self.stream: List[str] = [None] * n
self.ptr: int = 0
def insert(self, idKey: int, value: str) -> List[str]:
self.stream[idKey - 1] = value
ans: List[str] = []
while self.ptr < len(self.stream) and self.stream[self.ptr]:
ans.append(self.stream[self.ptr])
self.ptr += 1
return ans
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity: The time complexity for both the constructor and the
insertmethod isO(n)in the worst case, wherenis the number of elements in the stream. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)due to the storage required for the array of values.