Design In-Memory File System
Problem
Design a data structure that simulates an in-memory file system.
Implement the FileSystem class:
-
FileSystem()Initializes the object of the system. -
List<String> ls(String path)- If
pathis a file path, returns a list that only contains this file's name. - If
pathis a directory path, returns the list of file and directory names in this directory. The answer should in lexicographic order.
- If
-
void mkdir(String path)Makes a new directory according to the givenpath. The given directory path does not exist. If the middle directories in the path do not exist, you should create them as well. -
void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content)- If
filePathdoes not exist, creates that file containing givencontent. - If
filePathalready exists, appends the givencontentto original content.
- If
-
String readContentFromFile(String filePath)Returns the content in the file atfilePath.
Examples
Example 1:
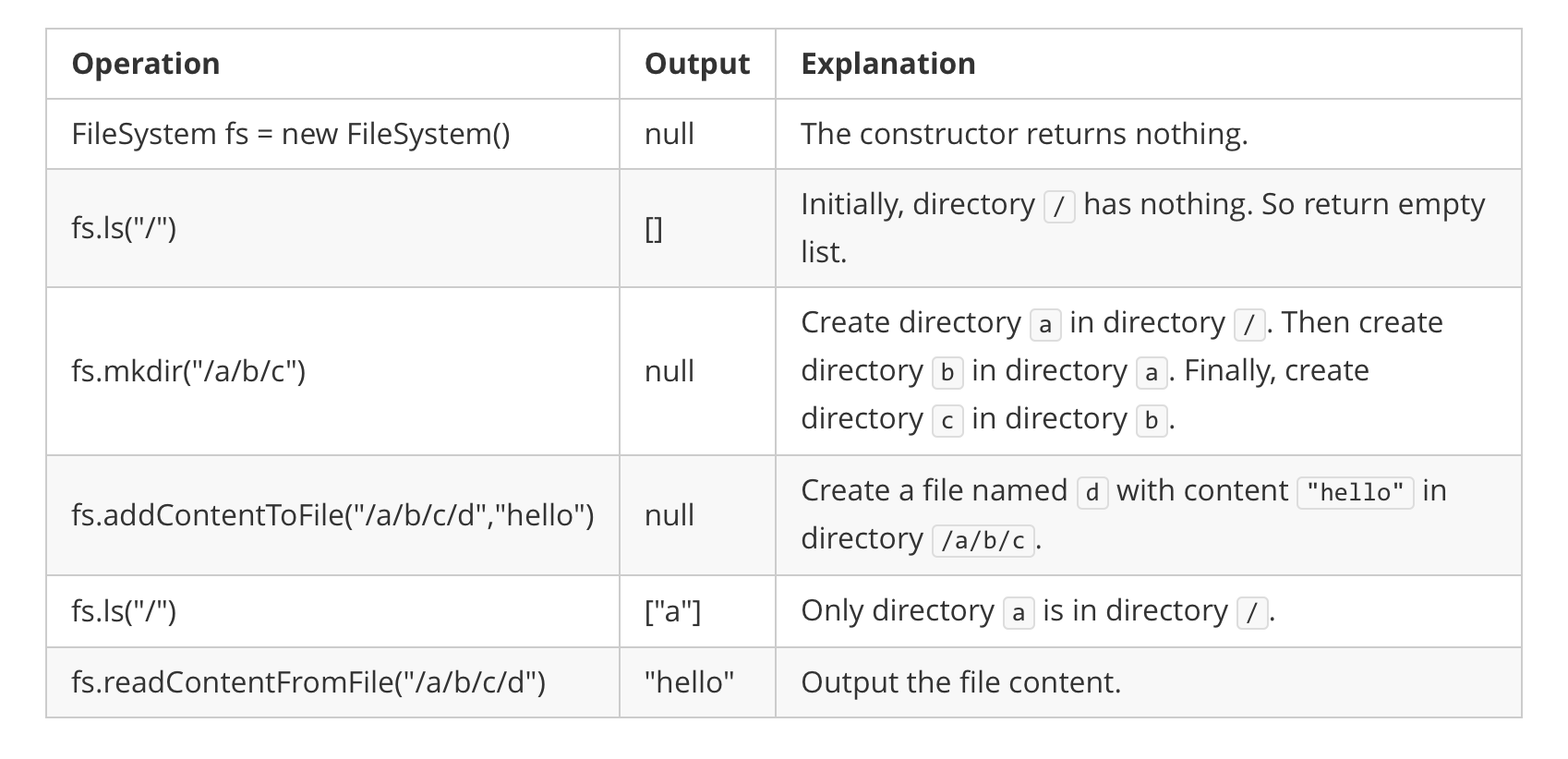
**Input**
["FileSystem", "ls", "mkdir", "addContentToFile", "ls", "readContentFromFile"]
[[], ["/"], ["/a/b/c"], ["/a/b/c/d", "hello"], ["/"], ["/a/b/c/d"]]
**Output**
[null, [], null, null, ["a"], "hello"]
**Explanation**
FileSystem fileSystem = new FileSystem();
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return []
fileSystem.mkdir("/a/b/c");
fileSystem.addContentToFile("/a/b/c/d", "hello");
fileSystem.ls("/"); // return ["a"]
fileSystem.readContentFromFile("/a/b/c/d"); // return "hello"
Constraints:
1 <= path.length, filePath.length <= 100pathandfilePathare absolute paths which begin with'/'and do not end with'/'except that the path is just"/".- You can assume that all directory names and file names only contain lowercase letters, and the same names will not exist in the same directory.
- You can assume that all operations will be passed valid parameters, and users will not attempt to retrieve file content or list a directory or file that does not exist.
- You can assume that the parent directory for the file in
addContentToFilewill exist. 1 <= content.length <= 50- At most
300calls will be made tols,mkdir,addContentToFile, andreadContentFromFile.
Solution
Method 1 – Trie (Prefix Tree) with Directory/File Nodes
Intuition
We can model the file system as a tree (trie), where each node is either a directory or a file. Directories map names to child nodes, and files store content. Traversing the path allows us to find or create directories/files as needed.
Approach
- Define a node class with a map for children and a string for file content (empty for directories).
- For
ls(path), traverse to the node. If it's a file, return its name; if a directory, return sorted list of children. - For
mkdir(path), traverse and create directories as needed. - For
addContentToFile(filePath, content), traverse to the file node, creating directories/files as needed, and append content. - For
readContentFromFile(filePath), traverse to the file node and return its content.
Code
C++
class FileSystem {
struct Node {
map<string, Node*> ch;
string content;
Node() : content("") {}
} *root;
vector<string> split(const string& path) {
vector<string> res;
stringstream ss(path);
string s;
while (getline(ss, s, '/')) if (!s.empty()) res.push_back(s);
return res;
}
Node* traverse(const string& path) {
auto v = root;
for (auto& p : split(path)) v = v->ch[p];
return v;
}
public:
FileSystem() { root = new Node(); }
vector<string> ls(string path) {
auto v = root;
auto parts = split(path);
for (auto& p : parts) v = v->ch[p];
if (!v->content.empty()) return {parts.back()};
vector<string> ans;
for (auto& [k, _] : v->ch) ans.push_back(k);
return ans;
}
void mkdir(string path) {
auto v = root;
for (auto& p : split(path)) if (!v->ch.count(p)) v->ch[p] = new Node(), v = v->ch[p]; else v = v->ch[p];
}
void addContentToFile(string filePath, string content) {
auto v = root;
auto parts = split(filePath);
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < parts.size(); ++i) {
if (!v->ch.count(parts[i])) v->ch[parts[i]] = new Node();
v = v->ch[parts[i]];
}
if (!v->ch.count(parts.back())) v->ch[parts.back()] = new Node();
v = v->ch[parts.back()];
v->content += content;
}
string readContentFromFile(string filePath) {
return traverse(filePath)->content;
}
};
Go
type Node struct {
ch map[string]*Node
content string
}
type FileSystem struct {
root *Node
}
func Constructor() FileSystem {
return FileSystem{&Node{ch: map[string]*Node{}}}
}
func split(path string) []string {
var res []string
for _, s := range strings.Split(path, "/") {
if s != "" {
res = append(res, s)
}
}
return res
}
func (fs *FileSystem) traverse(path string) *Node {
v := fs.root
for _, p := range split(path) {
v = v.ch[p]
}
return v
}
func (fs *FileSystem) Ls(path string) []string {
v := fs.root
parts := split(path)
for _, p := range parts {
v = v.ch[p]
}
if v.content != "" {
return []string{parts[len(parts)-1]}
}
ans := make([]string, 0, len(v.ch))
for k := range v.ch {
ans = append(ans, k)
}
sort.Strings(ans)
return ans
}
func (fs *FileSystem) Mkdir(path string) {
v := fs.root
for _, p := range split(path) {
if _, ok := v.ch[p]; !ok {
v.ch[p] = &Node{ch: map[string]*Node{}}
}
v = v.ch[p]
}
}
func (fs *FileSystem) AddContentToFile(filePath, content string) {
v := fs.root
parts := split(filePath)
for i := 0; i+1 < len(parts); i++ {
if _, ok := v.ch[parts[i]]; !ok {
v.ch[parts[i]] = &Node{ch: map[string]*Node{}}
}
v = v.ch[parts[i]]
}
if _, ok := v.ch[parts[len(parts)-1]]; !ok {
v.ch[parts[len(parts)-1]] = &Node{ch: map[string]*Node{}}
}
v = v.ch[parts[len(parts)-1]]
v.content += content
}
func (fs *FileSystem) ReadContentFromFile(filePath string) string {
return fs.traverse(filePath).content
}
Java
public class FileSystem {
static class Node {
Map<String, Node> ch = new HashMap<>();
String content = "";
}
Node root;
public FileSystem() { root = new Node(); }
private String[] split(String path) {
return Arrays.stream(path.split("/")).filter(s -> !s.isEmpty()).toArray(String[]::new);
}
private Node traverse(String path) {
Node v = root;
for (String p : split(path)) v = v.ch.get(p);
return v;
}
public List<String> ls(String path) {
Node v = root;
String[] parts = split(path);
for (String p : parts) v = v.ch.get(p);
if (!v.content.isEmpty()) return List.of(parts[parts.length-1]);
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>(v.ch.keySet());
Collections.sort(ans);
return ans;
}
public void mkdir(String path) {
Node v = root;
for (String p : split(path)) v = v.ch.computeIfAbsent(p, k -> new Node());
}
public void addContentToFile(String filePath, String content) {
Node v = root;
String[] parts = split(filePath);
for (int i = 0; i + 1 < parts.length; i++) v = v.ch.computeIfAbsent(parts[i], k -> new Node());
v = v.ch.computeIfAbsent(parts[parts.length-1], k -> new Node());
v.content += content;
}
public String readContentFromFile(String filePath) {
return traverse(filePath).content;
}
}
Kotlin
class FileSystem {
class Node {
val ch = mutableMapOf<String, Node>()
var content = ""
}
private val root = Node()
private fun split(path: String) = path.split("/").filter { it.isNotEmpty() }
private fun traverse(path: String): Node {
var v = root
for (p in split(path)) v = v.ch[p]!!
return v
}
fun ls(path: String): List<String> {
var v = root
val parts = split(path)
for (p in parts) v = v.ch[p]!!
if (v.content.isNotEmpty()) return listOf(parts.last())
return v.ch.keys.sorted()
}
fun mkdir(path: String) {
var v = root
for (p in split(path)) v = v.ch.getOrPut(p) { Node() }
}
fun addContentToFile(filePath: String, content: String) {
var v = root
val parts = split(filePath)
for (i in 0 until parts.size - 1) v = v.ch.getOrPut(parts[i]) { Node() }
v = v.ch.getOrPut(parts.last()) { Node() }
v.content += content
}
fun readContentFromFile(filePath: String): String {
return traverse(filePath).content
}
}
Python
class FileSystem:
class Node:
def __init__(self):
self.ch = {}
self.content = ''
def __init__(self):
self.root = self.Node()
def _split(self, path: str) -> list[str]:
return [p for p in path.split('/') if p]
def _traverse(self, path: str) -> 'FileSystem.Node':
v = self.root
for p in self._split(path):
v = v.ch[p]
return v
def ls(self, path: str) -> list[str]:
v = self.root
parts = self._split(path)
for p in parts:
v = v.ch[p]
if v.content:
return [parts[-1]]
return sorted(v.ch.keys())
def mkdir(self, path: str) -> None:
v = self.root
for p in self._split(path):
if p not in v.ch:
v.ch[p] = self.Node()
v = v.ch[p]
def addContentToFile(self, filePath: str, content: str) -> None:
v = self.root
parts = self._split(filePath)
for i in range(len(parts)-1):
if parts[i] not in v.ch:
v.ch[parts[i]] = self.Node()
v = v.ch[parts[i]]
if parts[-1] not in v.ch:
v.ch[parts[-1]] = self.Node()
v = v.ch[parts[-1]]
v.content += content
def readContentFromFile(self, filePath: str) -> str:
return self._traverse(filePath).content
Rust
use std::collections::BTreeMap;
struct Node {
ch: BTreeMap<String, Node>,
content: String,
}
struct FileSystem {
root: Node,
}
impl FileSystem {
fn new() -> Self {
FileSystem { root: Node { ch: BTreeMap::new(), content: String::new() } }
}
fn split(path: &str) -> Vec<&str> {
path.split('/').filter(|s| !s.is_empty()).collect()
}
fn traverse<'a>(mut v: &'a mut Node, path: &str) -> &'a mut Node {
for p in Self::split(path) {
v = v.ch.get_mut(p).unwrap();
}
v
}
fn ls(&self, path: &str) -> Vec<String> {
let mut v = &self.root;
let parts = Self::split(path);
for p in &parts {
v = v.ch.get(*p).unwrap();
}
if !v.content.is_empty() {
return vec![parts.last().unwrap().to_string()];
}
v.ch.keys().cloned().collect()
}
fn mkdir(&mut self, path: &str) {
let mut v = &mut self.root;
for p in Self::split(path) {
v = v.ch.entry(p.to_string()).or_insert(Node { ch: BTreeMap::new(), content: String::new() });
}
}
fn add_content_to_file(&mut self, file_path: &str, content: &str) {
let mut v = &mut self.root;
let parts = Self::split(file_path);
for i in 0..parts.len()-1 {
v = v.ch.entry(parts[i].to_string()).or_insert(Node { ch: BTreeMap::new(), content: String::new() });
}
v = v.ch.entry(parts.last().unwrap().to_string()).or_insert(Node { ch: BTreeMap::new(), content: String::new() });
v.content += content;
}
fn read_content_from_file(&self, file_path: &str) -> String {
let mut v = &self.root;
for p in Self::split(file_path) {
v = v.ch.get(p).unwrap();
}
v.content.clone()
}
}
TypeScript
class Node {
ch: Map<string, Node> = new Map();
content = '';
}
class FileSystem {
private root = new Node();
private split(path: string): string[] {
return path.split('/').filter(Boolean);
}
private traverse(path: string): Node {
let v = this.root;
for (const p of this.split(path)) v = v.ch.get(p)!;
return v;
}
ls(path: string): string[] {
let v = this.root;
const parts = this.split(path);
for (const p of parts) v = v.ch.get(p)!;
if (v.content) return [parts[parts.length-1]];
return Array.from(v.ch.keys()).sort();
}
mkdir(path: string): void {
let v = this.root;
for (const p of this.split(path)) {
if (!v.ch.has(p)) v.ch.set(p, new Node());
v = v.ch.get(p)!;
}
}
addContentToFile(filePath: string, content: string): void {
let v = this.root;
const parts = this.split(filePath);
for (let i = 0; i < parts.length - 1; i++) {
if (!v.ch.has(parts[i])) v.ch.set(parts[i], new Node());
v = v.ch.get(parts[i])!;
}
if (!v.ch.has(parts[parts.length-1])) v.ch.set(parts[parts.length-1], new Node());
v = v.ch.get(parts[parts.length-1])!;
v.content += content;
}
readContentFromFile(filePath: string): string {
return this.traverse(filePath).content;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(L + k log k)forls(whereLis path length,kis number of children),O(L)for other operations. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(N), whereNis the total number of nodes (directories/files) and file content stored.