Determine Color of a Chessboard Square
EasyUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given coordinates, a string that represents the coordinates of a square of the chessboard. Below is a chessboard for your reference.
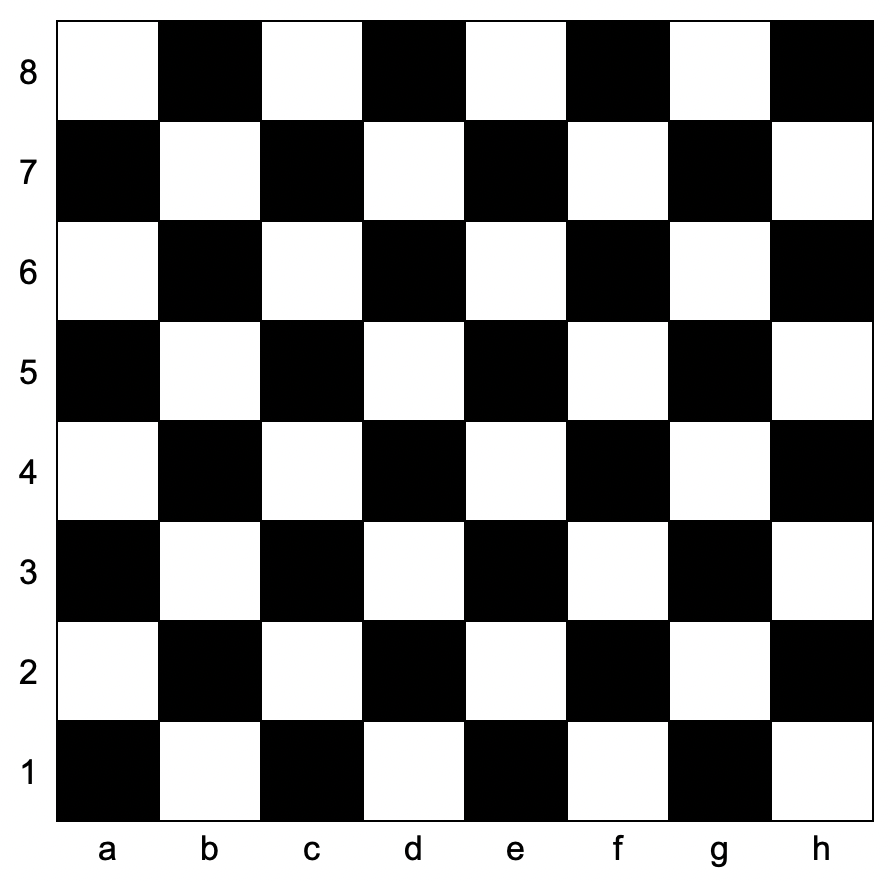
Return true if the square is white, andfalse if the square is black.
The coordinate will always represent a valid chessboard square. The coordinate will always have the letter first, and the number second.
Examples
Example 1
Input: coordinates = "a1"
Output: false
Explanation: From the chessboard above, the square with coordinates "a1" is black, so return false.
Example 2
Input: coordinates = "h3"
Output: true
Explanation: From the chessboard above, the square with coordinates "h3" is white, so return true.
Example 3
Input: coordinates = "c7"
Output: false
Constraints
coordinates.length == 2'a' <= coordinates[0] <= 'h''1' <= coordinates[1] <= '8'
Solution
Method 1 – Parity Check
Intuition
On a chessboard, the color of a square alternates every cell. The bottom-left square ('a1') is black. The color of a square is determined by the sum of its row and column indices: if the sum is even, it's black; if odd, it's white.
Approach
- Convert the column letter to a number (e.g., 'a' to 1, 'b' to 2, ..., 'h' to 8).
- Convert the row character to an integer.
- If the sum of the column and row is even, return false (black); if odd, return true (white).
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
bool squareIsWhite(string coordinates) {
int col = coordinates[0] - 'a' + 1;
int row = coordinates[1] - '0';
return (col + row) % 2 == 1;
}
};
Go
func squareIsWhite(coordinates string) bool {
col := int(coordinates[0]-'a') + 1
row := int(coordinates[1]-'0')
return (col+row)%2 == 1
}
Java
class Solution {
public boolean squareIsWhite(String coordinates) {
int col = coordinates.charAt(0) - 'a' + 1;
int row = coordinates.charAt(1) - '0';
return (col + row) % 2 == 1;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun squareIsWhite(coordinates: String): Boolean {
val col = coordinates[0] - 'a' + 1
val row = coordinates[1] - '0'
return (col + row) % 2 == 1
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def squareIsWhite(self, coordinates: str) -> bool:
col = ord(coordinates[0]) - ord('a') + 1
row = int(coordinates[1])
return (col + row) % 2 == 1
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn square_is_white(coordinates: String) -> bool {
let bytes = coordinates.as_bytes();
let col = (bytes[0] - b'a' + 1) as i32;
let row = (bytes[1] - b'0') as i32;
(col + row) % 2 == 1
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
squareIsWhite(coordinates: string): boolean {
const col = coordinates.charCodeAt(0) - 'a'.charCodeAt(0) + 1;
const row = Number(coordinates[1]);
return (col + row) % 2 === 1;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(1), as all operations are constant time. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1), as no extra space is used.