Diagonal Traverse 2
MediumUpdated: Sep 1, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a 2D integer array nums, return all elements of nums in diagonal order as shown in the below images.
Examples
Example 1:
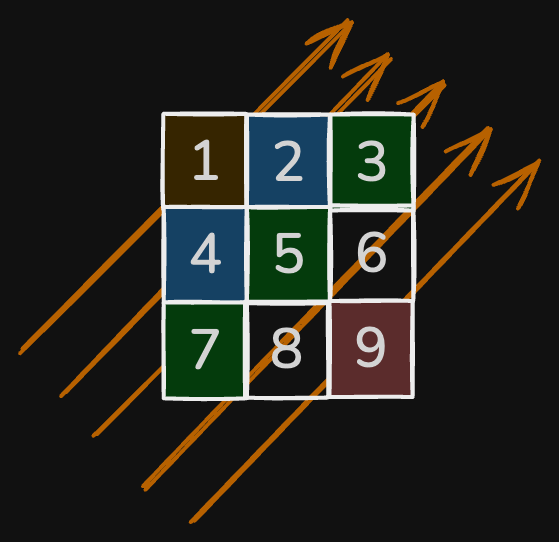
Input: nums = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [1,4,2,7,5,3,8,6,9]
Example 2:
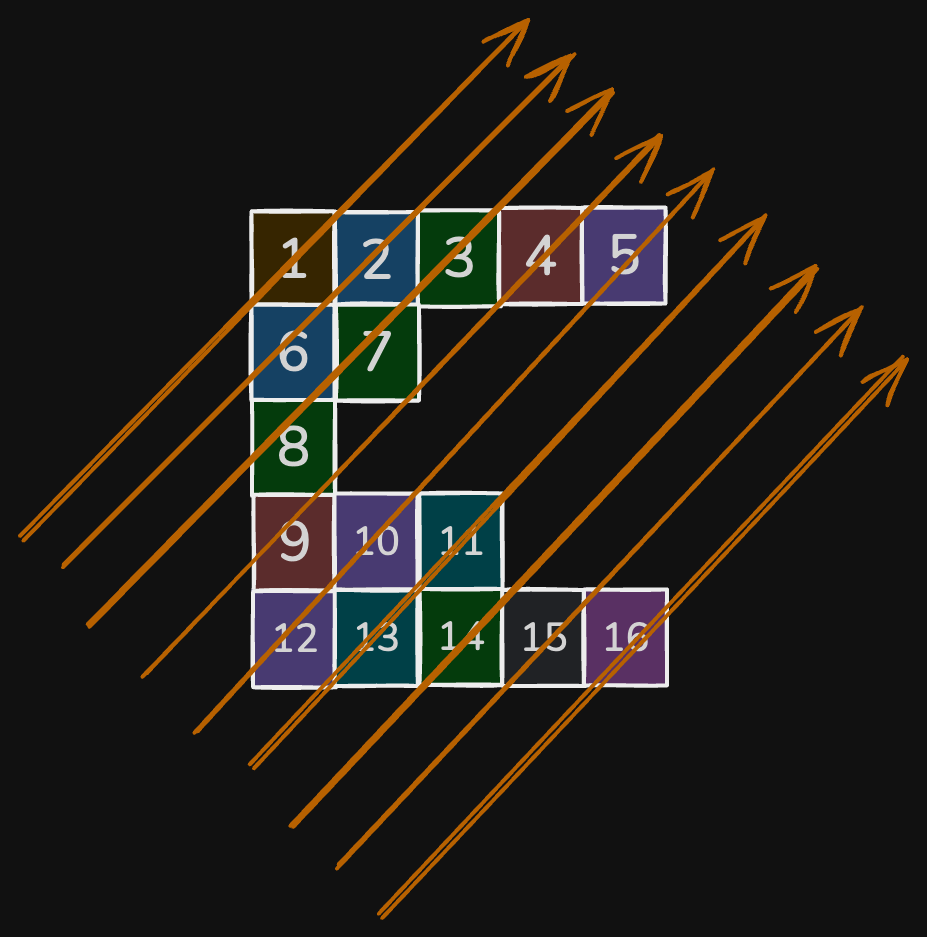
Input: nums = [[1,2,3,4,5],[6,7],[8],[9,10,11],[12,13,14,15,16]]
Output: [1,6,2,8,7,3,9,4,12,10,5,13,11,14,15,16]
Solution
Method 1 - Using hashmap
Here is the approach:
- Using a HashMap to Group Elements by Diagonals:
- Traverse the matrix and use a hashmap to collect elements that belong to the same diagonal.
- The key for each diagonal in the hashmap is the sum of the row and column indices.
- Extract Elements from the HashMap:
- Read the diagonals from the hashmap in increasing order of their keys and collect elements.
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public int[] findDiagonalOrder(List<List<Integer>> nums) {
Map<Integer, List<Integer>> diagonals = new HashMap<>();
int maxKey = 0;
int size = 0;
// Traverse the matrix and populate the diagonals hashmap
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums.get(i).size(); j++) {
diagonals.putIfAbsent(i + j, new ArrayList<>());
diagonals.get(i + j).add(nums.get(i).get(j));
maxKey = Math.max(maxKey, i + j);
size++;
}
}
// Read the diagonals from the hashmap in increasing order of their keys
int[] result = new int[size];
int index = 0;
for (int key = 0; key <= maxKey; key++) {
if (diagonals.containsKey(key)) {
for (int value : diagonals.get(key)) {
result[index++] = value;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def findDiagonalOrder(self, nums: List[List[int]]) -> List[int]:
diagonals: Dict[int, List[int]] = defaultdict(list)
max_key = 0
total_elements = 0
# Traverse the matrix and populate the diagonals defaultdict
for i in range(len(nums)):
for j in range(len(nums[i])):
diagonals[i + j].append(nums[i][j])
max_key = max(max_key, i + j)
total_elements += 1
# Read the diagonals from the defaultdict in increasing order of their keys
result = []
for key in range(max_key + 1):
if key in diagonals:
result.extend(diagonals[key])
return result
Complexity
- Time:
O(m * n), wheremis the number of rows andnis the number of columns. This is because we visit each element exactly once. - Space:
O(m * n), for storing the elements in the hashmap and the result list.