Difference of Number of Distinct Values on Diagonals
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a 2D grid of size m x n, you should find the matrix answer of size
m x n.
The cell answer[r][c] is calculated by looking at the diagonal values of the cell grid[r][c]:
- Let
leftAbove[r][c]be the number of distinct values on the diagonal to the left and above the cellgrid[r][c]not including the cellgrid[r][c]itself. - Let
rightBelow[r][c]be the number of distinct values on the diagonal to the right and below the cellgrid[r][c], not including the cellgrid[r][c]itself. - Then
answer[r][c] = |leftAbove[r][c] - rightBelow[r][c]|.
A matrix diagonal is a diagonal line of cells starting from some cell in either the topmost row or leftmost column and going in the bottom-right direction until the end of the matrix is reached.
- For example, in the below diagram the diagonal is highlighted using the cell with indices
(2, 3)colored gray: - Red-colored cells are left and above the cell.
- Blue-colored cells are right and below the cell.
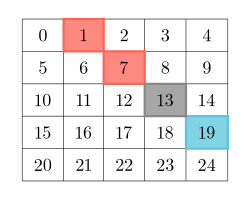
Return the matrix answer.
Examples
Example 1
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[3,1,5],[3,2,1]]
Output: Output: [[1,1,0],[1,0,1],[0,1,1]]
Explanation:
To calculate the `answer` cells:
answer | left-above elements | leftAbove | right-below elements | rightBelow | |leftAbove - rightBelow|
---|---|---|---|---|---
[0][0] | [] | 0 | [grid[1][1], grid[2][2]] | |{1, 1}| = 1 | 1
[0][1] | [] | 0 | [grid[1][2]] | |{5}| = 1 | 1
[0][2] | [] | 0 | [] | 0 | 0
[1][0] | [] | 0 | [grid[2][1]] | |{2}| = 1 | 1
[1][1] | [grid[0][0]] | |{1}| = 1 | [grid[2][2]] | |{1}| = 1 | 0
[1][2] | [grid[0][1]] | |{2}| = 1 | [] | 0 | 1
[2][0] | [] | 0 | [] | 0 | 0
[2][1] | [grid[1][0]] | |{3}| = 1 | [] | 0 | 1
[2][2] | [grid[0][0], grid[1][1]] | |{1, 1}| = 1 | [] | 0 | 1
Example 2
Input: grid = [[1]]
Output: Output: [[0]]
Constraints
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n, grid[i][j] <= 50
Solution
Method 1 – Diagonal Hash Sets
Intuition
For each cell, the diagonal to the left and above is all cells (r-1, c-1), (r-2, c-2), ... and the diagonal to the right and below is all cells (r+1, c+1), (r+2, c+2), ... We can precompute the distinct values for each diagonal in both directions using hash sets.
Approach
- For each diagonal (r-c is constant), traverse from top-left to bottom-right, collecting distinct values for left-above for each cell.
- For each diagonal, traverse from bottom-right to top-left, collecting distinct values for right-below for each cell.
- For each cell, answer[r][c] = |leftAbove[r][c] - rightBelow[r][c]|.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> differenceOfDistinctValues(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> left(m, vector<int>(n)), right(m, vector<int>(n));
// Left-above
for (int d = -(n-1); d <= m-1; ++d) {
unordered_set<int> s;
for (int i = max(0, d), j = i - d; i < m && j < n; ++i, ++j) {
left[i][j] = s.size();
s.insert(grid[i][j]);
}
}
// Right-below
for (int d = -(n-1); d <= m-1; ++d) {
unordered_set<int> s;
vector<pair<int,int>> cells;
for (int i = max(0, d), j = i - d; i < m && j < n; ++i, ++j)
cells.push_back({i, j});
for (int k = (int)cells.size()-1; k >= 0; --k) {
int i = cells[k].first, j = cells[k].second;
right[i][j] = s.size();
s.insert(grid[i][j]);
}
}
vector<vector<int>> ans(m, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
ans[i][j] = abs(left[i][j] - right[i][j]);
return ans;
}
};
Go
func differenceOfDistinctValues(grid [][]int) [][]int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
left := make([][]int, m)
right := make([][]int, m)
for i := range left {
left[i] = make([]int, n)
right[i] = make([]int, n)
}
for d := -(n-1); d <= m-1; d++ {
s := map[int]struct{}{}
for i, j := max(0, d), max(0, -d); i < m && j < n; i, j = i+1, j+1 {
left[i][j] = len(s)
s[grid[i][j]] = struct{}{}
}
}
for d := -(n-1); d <= m-1; d++ {
s := map[int]struct{}{}
cells := [][2]int{}
for i, j := max(0, d), max(0, -d); i < m && j < n; i, j = i+1, j+1 {
cells = append(cells, [2]int{i, j})
}
for k := len(cells)-1; k >= 0; k-- {
i, j := cells[k][0], cells[k][1]
right[i][j] = len(s)
s[grid[i][j]] = struct{}{}
}
}
ans := make([][]int, m)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = make([]int, n)
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
ans[i][j] = abs(left[i][j] - right[i][j])
}
}
return ans
}
func max(a, b int) int { if a > b { return a }; return b }
func abs(x int) int { if x < 0 { return -x }; return x }
Java
class Solution {
public int[][] differenceOfDistinctValues(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
int[][] left = new int[m][n], right = new int[m][n];
for (int d = -(n-1); d <= m-1; ++d) {
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = Math.max(0, d), j = i - d; i < m && j < n; ++i, ++j) {
left[i][j] = s.size();
s.add(grid[i][j]);
}
}
for (int d = -(n-1); d <= m-1; ++d) {
Set<Integer> s = new HashSet<>();
List<int[]> cells = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = Math.max(0, d), j = i - d; i < m && j < n; ++i, ++j)
cells.add(new int[]{i, j});
for (int k = cells.size()-1; k >= 0; --k) {
int i = cells.get(k)[0], j = cells.get(k)[1];
right[i][j] = s.size();
s.add(grid[i][j]);
}
}
int[][] ans = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
ans[i][j] = Math.abs(left[i][j] - right[i][j]);
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun differenceOfDistinctValues(grid: Array<IntArray>): Array<IntArray> {
val m = grid.size
val n = grid[0].size
val left = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
val right = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
for (d in -(n-1)..(m-1)) {
val s = mutableSetOf<Int>()
var i = maxOf(0, d)
var j = i - d
while (i < m && j < n) {
left[i][j] = s.size
s.add(grid[i][j])
i++
j++
}
}
for (d in -(n-1)..(m-1)) {
val s = mutableSetOf<Int>()
val cells = mutableListOf<Pair<Int, Int>>()
var i = maxOf(0, d)
var j = i - d
while (i < m && j < n) {
cells.add(i to j)
i++
j++
}
for (k in cells.size-1 downTo 0) {
val (ii, jj) = cells[k]
right[ii][jj] = s.size
s.add(grid[ii][jj])
}
}
val ans = Array(m) { IntArray(n) }
for (i in 0 until m)
for (j in 0 until n)
ans[i][j] = kotlin.math.abs(left[i][j] - right[i][j])
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def differenceOfDistinctValues(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> list[list[int]]:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
left = [[0]*n for _ in range(m)]
right = [[0]*n for _ in range(m)]
for d in range(-(n-1), m):
s = set()
i, j = max(0, d), max(0, -d)
while i < m and j < n:
left[i][j] = len(s)
s.add(grid[i][j])
i += 1
j += 1
for d in range(-(n-1), m):
s = set()
cells = []
i, j = max(0, d), max(0, -d)
while i < m and j < n:
cells.append((i, j))
i += 1
j += 1
for i, j in reversed(cells):
right[i][j] = len(s)
s.add(grid[i][j])
ans = [[abs(left[i][j] - right[i][j]) for j in range(n)] for i in range(m)]
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn difference_of_distinct_values(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut left = vec![vec![0; n]; m];
let mut right = vec![vec![0; n]; m];
for d in -(n as isize - 1)..=(m as isize - 1) {
let mut s = std::collections::HashSet::new();
let mut i = std::cmp::max(0, d) as usize;
let mut j = (i as isize - d) as usize;
while i < m && j < n {
left[i][j] = s.len() as i32;
s.insert(grid[i][j]);
i += 1;
j += 1;
}
}
for d in -(n as isize - 1)..=(m as isize - 1) {
let mut s = std::collections::HashSet::new();
let mut cells = vec![];
let mut i = std::cmp::max(0, d) as usize;
let mut j = (i as isize - d) as usize;
while i < m && j < n {
cells.push((i, j));
i += 1;
j += 1;
}
for &(i, j) in cells.iter().rev() {
right[i][j] = s.len() as i32;
s.insert(grid[i][j]);
}
}
let mut ans = vec![vec![0; n]; m];
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
ans[i][j] = (left[i][j] - right[i][j]).abs();
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
differenceOfDistinctValues(grid: number[][]): number[][] {
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
const left = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(0));
const right = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(0));
for (let d = -(n-1); d <= m-1; ++d) {
const s = new Set<number>();
for (let i = Math.max(0, d), j = i - d; i < m && j < n; ++i, ++j) {
left[i][j] = s.size;
s.add(grid[i][j]);
}
}
for (let d = -(n-1); d <= m-1; ++d) {
const s = new Set<number>();
const cells: [number, number][] = [];
for (let i = Math.max(0, d), j = i - d; i < m && j < n; ++i, ++j)
cells.push([i, j]);
for (let k = cells.length-1; k >= 0; --k) {
const [i, j] = cells[k];
right[i][j] = s.size;
s.add(grid[i][j]);
}
}
const ans = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array(n).fill(0));
for (let i = 0; i < m; ++i)
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j)
ans[i][j] = Math.abs(left[i][j] - right[i][j]);
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n), as each cell is visited a constant number of times. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * n), for the auxiliary matrices.