Encode Number
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given a non-negative integer num, Return its encoding string.
The encoding is done by converting the integer to a string using a secret function that you should deduce from the following table:
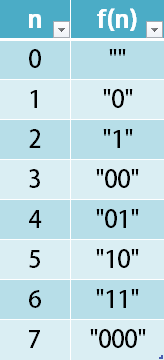
Examples
Example 1:
Input: num = 23
Output: "1000"
Example 2:
Input: num = 107
Output: "101100"
Constraints:
0 <= num <= 10^9
Solution
Method 1 – Binary Representation Minus One
Intuition
The encoding is the binary representation of num + 1, but with the leading '1' removed. This is because the encoding table matches the binary numbers from 1 upwards, skipping the leading bit.
Approach
- If
numis 0, return an empty string. - Convert
num + 1to its binary representation. - Remove the leading '1' from the binary string.
- Return the result.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
string encode(int num) {
if (num == 0) return "";
string ans;
num++;
while (num > 1) {
ans = char('0' + (num & 1)) + ans;
num >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func encode(num int) string {
if num == 0 {
return ""
}
num++
ans := ""
for num > 1 {
ans = string('0'+(num&1)) + ans
num >>= 1
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public String encode(int num) {
if (num == 0) return "";
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
num++;
while (num > 1) {
ans.insert(0, num & 1);
num >>= 1;
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun encode(num: Int): String {
if (num == 0) return ""
var n = num + 1
val ans = StringBuilder()
while (n > 1) {
ans.insert(0, n and 1)
n = n shr 1
}
return ans.toString()
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def encode(self, num: int) -> str:
if num == 0:
return ""
b = bin(num + 1)[3:]
return b
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn encode(num: i32) -> String {
if num == 0 {
return String::new();
}
let mut n = (num + 1) as u32;
let mut ans = String::new();
while n > 1 {
ans.insert(0, char::from(b'0' + (n & 1) as u8));
n >>= 1;
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
encode(num: number): string {
if (num === 0) return "";
let n = num + 1;
let ans = "";
while (n > 1) {
ans = (n & 1) + ans;
n >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(log n), since we process each bit of the number. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(log n), for the output string.