Extract Kth Character From The Rope Tree
Problem
You are given the root of a binary tree and an integer k. Besides the left and right children, every node of this tree has two other properties, a
string node.val containing only lowercase English letters (possibly empty) and a non-negative integer node.len. There are two types of nodes in this tree:
- Leaf : These nodes have no children,
node.len = 0, andnode.valis some non-empty string. - Internal : These nodes have at least one child (also at most two children),
node.len > 0, andnode.valis an empty string.
The tree described above is called a Rope binary tree. Now we define
S[node] recursively as follows:
- If
nodeis some leaf node,S[node] = node.val, - Otherwise if
nodeis some internal node,S[node] = concat(S[node.left], S[node.right])andS[node].length = node.len.
Return k-th character of the string S[root].
Note: If s and p are two strings, concat(s, p) is a string obtained by concatenating p to s. For example, concat("ab", "zz") = "abzz".
Examples
Example 1:
Input: root = [10,4,"abcpoe","g","rta"], k = 6
Output: "b"
Explanation: In the picture below, we put an integer on internal nodes that represents node.len, and a string on leaf nodes that represents node.val.
You can see that S[root] = concat(concat("g", "rta"), "abcpoe") = "grtaabcpoe". So S[root][5], which represents 6th character of it, is equal to "b".
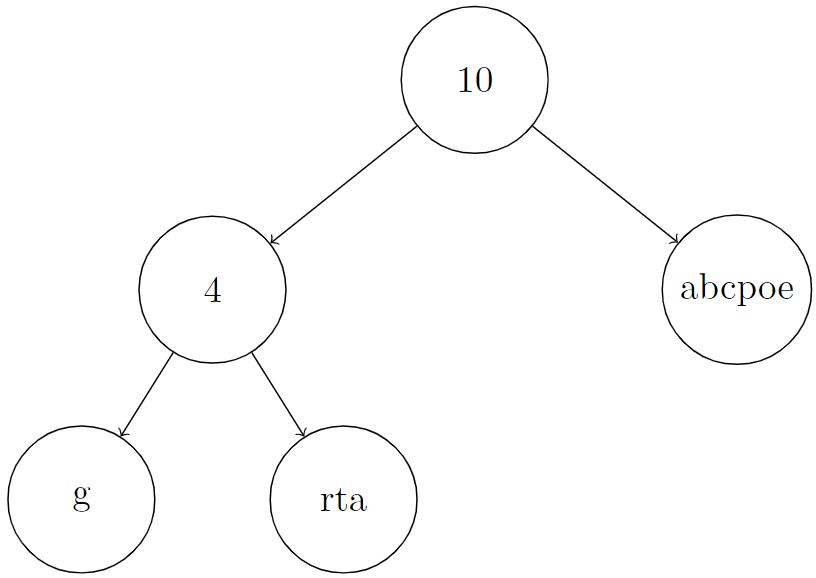
Example 2:
Input: root = [12,6,6,"abc","efg","hij","klm"], k = 3
Output: "c"
Explanation: In the picture below, we put an integer on internal nodes that represents node.len, and a string on leaf nodes that represents node.val.
You can see that S[root] = concat(concat("abc", "efg"), concat("hij", "klm")) = "abcefghijklm". So S[root][2], which represents the 3rd character of it, is equal to "c".
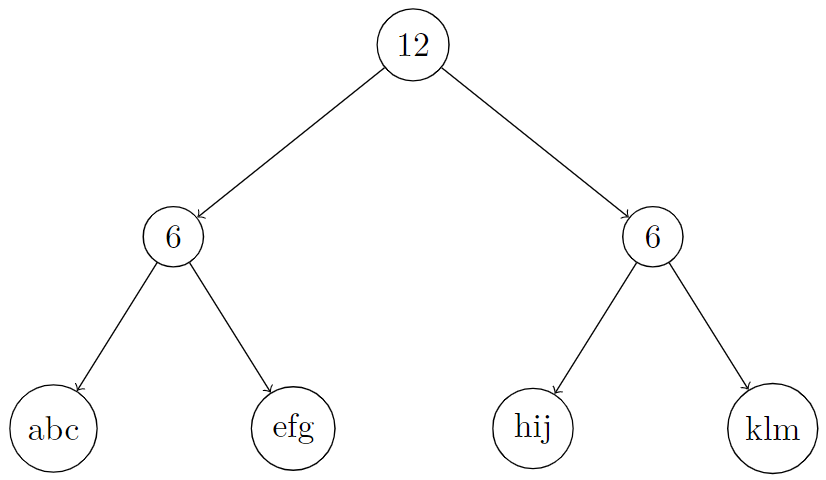
Example 3:
Input: root = ["ropetree"], k = 8
Output: "e"
Explanation: In the picture below, we put an integer on internal nodes that represents node.len, and a string on leaf nodes that represents node.val.
You can see that S[root] = "ropetree". So S[root][7], which represents 8th character of it, is equal to "e".
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 103] node.valcontains only lowercase English letters0 <= node.val.length <= 500 <= node.len <= 10^4- for leaf nodes,
node.len = 0andnode.valis non-empty - for internal nodes,
node.len > 0andnode.valis empty 1 <= k <= S[root].length
Solution
Method 1 – Recursive Traversal Using Lengths
Intuition
The rope tree is designed so that each internal node's length is the sum of its children's strings. To find the k-th character, we can recursively decide whether to go left or right based on the lengths, without building the whole string.
Approach
- At each node:
- If it's a leaf, return the k-th character from its value.
- Otherwise, check the length of the left subtree.
- If k is less than or equal to the left subtree's length, recurse left.
- Otherwise, subtract the left length and recurse right.
- Continue until a leaf is reached.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
char getKthCharacter(TreeNode* root, int k) {
if (!root->left && !root->right) return root->val[k-1];
int leftLen = root->left ? root->left->len : 0;
if (k <= leftLen) return getKthCharacter(root->left, k);
return getKthCharacter(root->right, k - leftLen);
}
};
Go
func getKthCharacter(root *TreeNode, k int) byte {
if root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil {
return root.Val[k-1]
}
leftLen := 0
if root.Left != nil {
leftLen = root.Left.Len
}
if k <= leftLen {
return getKthCharacter(root.Left, k)
}
return getKthCharacter(root.Right, k-leftLen)
}
Java
class Solution {
public char getKthCharacter(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return root.val.charAt(k-1);
int leftLen = root.left != null ? root.left.len : 0;
if (k <= leftLen)
return getKthCharacter(root.left, k);
return getKthCharacter(root.right, k - leftLen);
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun getKthCharacter(root: TreeNode, k: Int): Char {
if (root.left == null && root.right == null)
return root.`val`[k-1]
val leftLen = root.left?.len ?: 0
return if (k <= leftLen)
getKthCharacter(root.left!!, k)
else
getKthCharacter(root.right!!, k - leftLen)
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def getKthCharacter(self, root: 'TreeNode', k: int) -> str:
if not root.left and not root.right:
return root.val[k-1]
left_len = root.left.len if root.left else 0
if k <= left_len:
return self.getKthCharacter(root.left, k)
return self.getKthCharacter(root.right, k - left_len)
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn get_kth_character(root: &TreeNode, k: usize) -> char {
if root.left.is_none() && root.right.is_none() {
return root.val.chars().nth(k-1).unwrap();
}
let left_len = root.left.as_ref().map_or(0, |l| l.len);
if k <= left_len {
return Solution::get_kth_character(root.left.as_ref().unwrap(), k);
}
Solution::get_kth_character(root.right.as_ref().unwrap(), k - left_len)
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
getKthCharacter(root: TreeNode, k: number): string {
if (!root.left && !root.right) return root.val[k-1];
const leftLen = root.left ? root.left.len : 0;
if (k <= leftLen) return this.getKthCharacter(root.left, k);
return this.getKthCharacter(root.right, k - leftLen);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(h), where h is the height of the tree, since we only traverse one path from root to leaf. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(h), due to the recursion stack.