Find All The Lonely Nodes
EasyUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
In a binary tree, a lonely node is a node that is the only child of its parent node. The root of the tree is not lonely because it does not have a parent node.
Given the root of a binary tree, return an array containing the values of all lonely nodes in the tree. Return the list in any order.
Examples
Example 1:
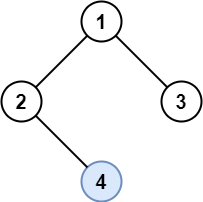
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4]
Output: [4]
Explanation: Light blue node is the only lonely node.
Node 1 is the root and is not lonely.
Nodes 2 and 3 have the same parent and are not lonely.
Example 2:
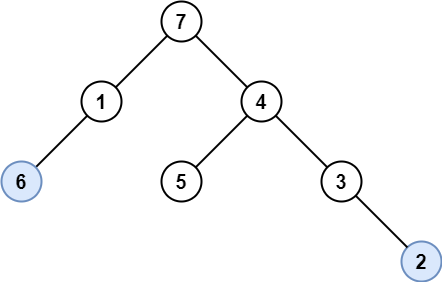
Input: root = [7,1,4,6,null,5,3,null,null,null,null,null,2]
Output: [6,2]
Explanation: Light blue nodes are lonely nodes.
Please remember that order doesn't matter, [2,6] is also an acceptable answer.
Example 3:
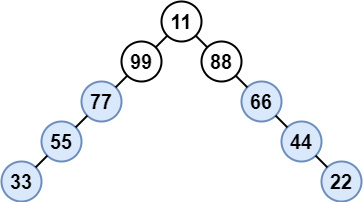
Input: root = [11,99,88,77,null,null,66,55,null,null,44,33,null,null,22]
Output: [77,55,33,66,44,22]
Explanation: Nodes 99 and 88 share the same parent. Node 11 is the root.
All other nodes are lonely.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the
treeis in the range[1, 1000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 10^6
Solution
Method 1 – DFS Traversal
Intuition
A node is lonely if it is the only child of its parent. We can traverse the tree using DFS, and for each node, check if it is the only child of its parent (i.e., its parent has only one child).
Approach
- Traverse the tree using DFS, passing the parent node.
- For each node, if its parent exists and the parent has only one child, add the node's value to the answer.
- Recurse on left and right children.
- Return the list of lonely node values.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> ans;
void dfs(TreeNode* node, TreeNode* parent) {
if (!node) return;
if (parent && (!parent->left || !parent->right)) ans.push_back(node->val);
dfs(node->left, node);
dfs(node->right, node);
}
vector<int> getLonelyNodes(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root, nullptr);
return ans;
}
};
Go
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left, Right *TreeNode
}
func getLonelyNodes(root *TreeNode) []int {
var ans []int
var dfs func(node, parent *TreeNode)
dfs = func(node, parent *TreeNode) {
if node == nil { return }
if parent != nil && (parent.Left == nil || parent.Right == nil) {
ans = append(ans, node.Val)
}
dfs(node.Left, node)
dfs(node.Right, node)
}
dfs(root, nil)
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
void dfs(TreeNode node, TreeNode parent) {
if (node == null) return;
if (parent != null && (parent.left == null || parent.right == null)) ans.add(node.val);
dfs(node.left, node);
dfs(node.right, node);
}
public List<Integer> getLonelyNodes(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, null);
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
val ans = mutableListOf<Int>()
fun getLonelyNodes(root: TreeNode?): List<Int> {
fun dfs(node: TreeNode?, parent: TreeNode?) {
if (node == null) return
if (parent != null && (parent.left == null || parent.right == null)) ans.add(node.`val`)
dfs(node.left, node)
dfs(node.right, node)
}
dfs(root, null)
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def getLonelyNodes(self, root: 'TreeNode') -> list[int]:
ans: list[int] = []
def dfs(node: 'TreeNode', parent: 'TreeNode') -> None:
if not node:
return
if parent and (not parent.left or not parent.right):
ans.append(node.val)
dfs(node.left, node)
dfs(node.right, node)
dfs(root, None)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn get_lonely_nodes(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<i32> {
fn dfs(node: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, parent: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, ans: &mut Vec<i32>) {
if let Some(n) = node {
if let Some(p) = &parent {
let p = p.borrow();
if p.left.is_none() || p.right.is_none() {
ans.push(n.borrow().val);
}
}
let left = n.borrow().left.clone();
let right = n.borrow().right.clone();
dfs(left, Some(n.clone()), ans);
dfs(right, Some(n.clone()), ans);
}
}
let mut ans = vec![];
dfs(root, None, &mut ans);
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
getLonelyNodes(root: TreeNode | null): number[] {
const ans: number[] = [];
function dfs(node: TreeNode | null, parent: TreeNode | null) {
if (!node) return;
if (parent && (!parent.left || !parent.right)) ans.push(node.val);
dfs(node.left, node);
dfs(node.right, node);
}
dfs(root, null);
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the tree. Each node is visited once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(h), where h is the height of the tree (recursion stack).