Find And Replace in String
Problem
You are given a 0-indexed string s that you must perform k replacement operations on. The replacement operations are given as three 0-indexed parallel arrays, indices, sources, and targets, all of length k.
To complete the ith replacement operation:
- Check if the substring
sources[i]occurs at indexindices[i]in the original strings. - If it does not occur, do nothing.
- Otherwise if it does occur, replace that substring with
targets[i].
For example, if s = "_ab_ cd", indices[i] = 0, sources[i] = "ab", and
targets[i] = "eee", then the result of this replacement will be "_eee_ cd".
All replacement operations must occur simultaneously , meaning the replacement operations should not affect the indexing of each other. The testcases will be generated such that the replacements will not overlap.
- For example, a testcase with
s = "abc",indices = [0, 1], andsources = ["ab","bc"]will not be generated because the"ab"and"bc"replacements overlap.
Return _theresulting string after performing all replacement operations on _s.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters in a string.
Examples
Example 1

Input: s = "abcd", indices = [0, 2], sources = ["a", "cd"], targets = ["eee", "ffff"]
Output: "eeebffff"
Explanation:
"a" occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with "eee".
"cd" occurs at index 2 in s, so we replace it with "ffff".
Example 2
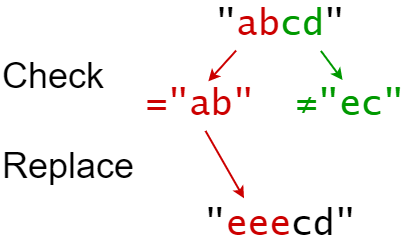
Input: s = "abcd", indices = [0, 2], sources = ["ab","ec"], targets = ["eee","ffff"]
Output: "eeecd"
Explanation:
"ab" occurs at index 0 in s, so we replace it with "eee".
"ec" does not occur at index 2 in s, so we do nothing.
Constraints
1 <= s.length <= 1000k == indices.length == sources.length == targets.length1 <= k <= 1000 <= indexes[i] < s.length1 <= sources[i].length, targets[i].length <= 50sconsists of only lowercase English letters.sources[i]andtargets[i]consist of only lowercase English letters.
Solution
Method 1 – Sort and Greedy Replace
Intuition
We want to perform multiple replacements in a string, but replacements can overlap or affect each other. To avoid issues, we process the replacements in order of increasing index, and build the result string by checking at each index if a replacement should occur.
Approach
- Pair up each replacement as (index, source, target) and sort by index.
- Iterate through the string
swith a pointeri. - For each replacement, if the current index matches and the source matches the substring, append the target to the result and skip the length of the source.
- Otherwise, append the current character and move to the next index.
- Continue until the end of the string.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
string findReplaceString(string s, vector<int>& indices, vector<string>& sources, vector<string>& targets) {
vector<tuple<int, string, string>> ops;
for (int i = 0; i < indices.size(); ++i)
ops.emplace_back(indices[i], sources[i], targets[i]);
sort(ops.begin(), ops.end());
string ans;
int i = 0, k = 0, n = s.size();
while (i < n) {
if (k < ops.size() && i == get<0>(ops[k]) && s.substr(i, get<1>(ops[k]).size()) == get<1>(ops[k])) {
ans += get<2>(ops[k]);
i += get<1>(ops[k]).size();
++k;
} else {
ans += s[i++];
if (k < ops.size() && i > get<0>(ops[k])) ++k;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
import "sort"
func findReplaceString(s string, indices []int, sources, targets []string) string {
type op struct{idx int; src, tgt string}
ops := make([]op, len(indices))
for i := range indices {
ops[i] = op{indices[i], sources[i], targets[i]}
}
sort.Slice(ops, func(i, j int) bool { return ops[i].idx < ops[j].idx })
ans := ""
i, k, n := 0, 0, len(s)
for i < n {
if k < len(ops) && i == ops[k].idx && i+len(ops[k].src) <= n && s[i:i+len(ops[k].src)] == ops[k].src {
ans += ops[k].tgt
i += len(ops[k].src)
k++
} else {
ans += string(s[i])
i++
if k < len(ops) && i > ops[k].idx { k++ }
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public String findReplaceString(String s, int[] indices, String[] sources, String[] targets) {
int n = s.length(), k = indices.length;
int[] match = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(match, -1);
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
if (s.startsWith(sources[i], indices[i])) match[indices[i]] = i;
}
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ) {
if (match[i] >= 0) {
ans.append(targets[match[i]]);
i += sources[match[i]].length();
} else {
ans.append(s.charAt(i++));
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun findReplaceString(s: String, indices: IntArray, sources: Array<String>, targets: Array<String>): String {
val n = s.length
val match = IntArray(n) { -1 }
for (i in indices.indices) {
if (s.startsWith(sources[i], indices[i])) match[indices[i]] = i
}
val ans = StringBuilder()
var i = 0
while (i < n) {
if (match[i] >= 0) {
ans.append(targets[match[i]])
i += sources[match[i]].length
} else {
ans.append(s[i])
i++
}
}
return ans.toString()
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def findReplaceString(self, s: str, indices: list[int], sources: list[str], targets: list[str]) -> str:
n = len(s)
match = [-1] * n
for i, idx in enumerate(indices):
if s.startswith(sources[i], idx):
match[idx] = i
ans = []
i = 0
while i < n:
if match[i] >= 0:
ans.append(targets[match[i]])
i += len(sources[match[i]])
else:
ans.append(s[i])
i += 1
return ''.join(ans)
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn find_replace_string(s: String, indices: Vec<i32>, sources: Vec<String>, targets: Vec<String>) -> String {
let n = s.len();
let mut match_idx = vec![-1; n];
let s_bytes = s.as_bytes();
for (i, &idx) in indices.iter().enumerate() {
let idx = idx as usize;
let src = sources[i].as_bytes();
if idx + src.len() <= n && &s_bytes[idx..idx+src.len()] == src {
match_idx[idx] = i as i32;
}
}
let mut ans = String::new();
let mut i = 0;
while i < n {
if match_idx[i] >= 0 {
let k = match_idx[i] as usize;
ans.push_str(&targets[k]);
i += sources[k].len();
} else {
ans.push(s_bytes[i] as char);
i += 1;
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
findReplaceString(s: string, indices: number[], sources: string[], targets: string[]): string {
const n = s.length;
const match = Array(n).fill(-1);
for (let i = 0; i < indices.length; i++) {
if (s.startsWith(sources[i], indices[i])) match[indices[i]] = i;
}
let ans = '';
let i = 0;
while (i < n) {
if (match[i] >= 0) {
ans += targets[match[i]];
i += sources[match[i]].length;
} else {
ans += s[i];
i++;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n + k * m), where n is the length of s, k is the number of replacements, and m is the average length of sources. Each replacement is checked and applied in linear time. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n + k), for the match array and result string.