Find Critical and Pseudo-Critical Edges in Minimum Spanning Tree
Problem
Given a weighted undirected connected graph with n vertices numbered from 0 to n - 1, and an array edges where edges[i] = [ai, bi, weighti] represents a bidirectional and weighted edge between nodes ai and bi. A minimum spanning tree (MST) is a subset of the graph's edges that connects all vertices without cycles and with the minimum possible total edge weight.
Find all the critical and pseudo-critical edges in the given graph's minimum spanning tree (MST). An MST edge whose deletion from the graph would cause the MST weight to increase is called a critical edge. On the other hand, a pseudo-critical edge is that which can appear in some MSTs but not all.
Note that you can return the indices of the edges in any order.
Examples
Example 1:
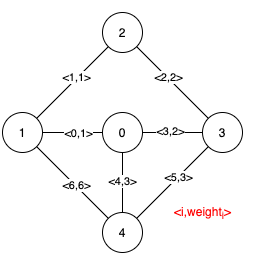
Input:
n = 5, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,2],[0,3,2],[0,4,3],[3,4,3],[1,4,6]]
Output:
[[0,1],[2,3,4,5]]
Explanation: The figure above describes the graph.
The following figure shows all the possible MSTs:
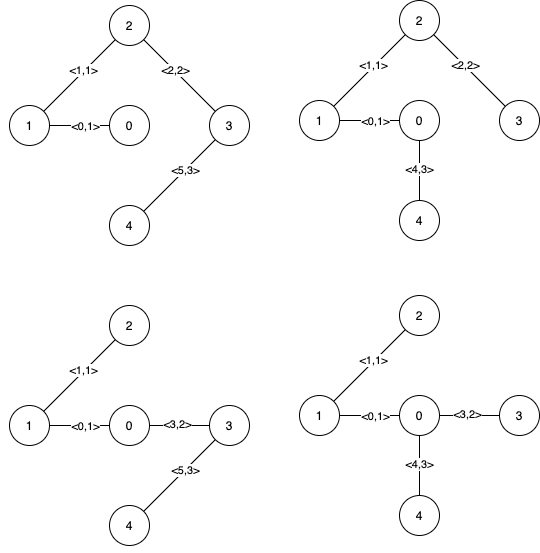 Notice that the two edges 0 and 1 appear in all MSTs, therefore they are critical edges, so we return them in the first list of the output.
The edges 2, 3, 4, and 5 are only part of some MSTs, therefore they are considered pseudo-critical edges. We add them to the second list of the output.
Notice that the two edges 0 and 1 appear in all MSTs, therefore they are critical edges, so we return them in the first list of the output.
The edges 2, 3, 4, and 5 are only part of some MSTs, therefore they are considered pseudo-critical edges. We add them to the second list of the output.
Example 2:
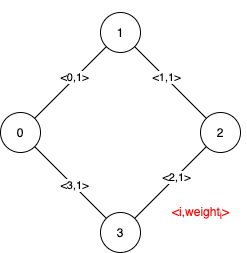
Input:
n = 4, edges = [[0,1,1],[1,2,1],[2,3,1],[0,3,1]]
Output:
[[],[0,1,2,3]]
Explanation: We can observe that since all 4 edges have equal weight, choosing any 3 edges from the given 4 will yield an MST. Therefore all 4 edges are pseudo-critical.
Solution
Method 1 - Union Find
Intuition
We use Kruskal's algorithm and Union Find to build the MST. For each edge, we check:
- If removing the edge increases the MST cost, it is critical.
- If forcing the edge into the MST does not increase the cost, it is pseudo-critical.
Approach
- Annotate each edge with its original index.
- Sort edges by weight.
- Compute the MST cost using all edges.
- For each edge:
- Exclude it and compute MST cost. If cost increases, it's critical.
- Force-include it and compute MST cost. If cost is unchanged, it's pseudo-critical.
Code
C++
struct UnionFind {
vector<int> parent;
int count;
UnionFind(int n) : parent(n), count(n) {
iota(parent.begin(), parent.end(), 0);
}
int find(int x) {
if (parent[x] != x) parent[x] = find(parent[x]);
return parent[x];
}
bool unite(int x, int y) {
int rx = find(x), ry = find(y);
if (rx == ry) return false;
parent[rx] = ry; count--;
return true;
}
};
vector<vector<int>> findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
int m = edges.size();
vector<vector<int>> newEdges;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
auto e = edges[i];
newEdges.push_back({e[0], e[1], e[2], i});
}
sort(newEdges.begin(), newEdges.end(), [](auto& a, auto& b) { return a[2] < b[2]; });
auto buildMST = [&](int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges, int skip, int pick) {
UnionFind uf(n);
int cost = 0;
if (pick != -1) {
auto& e = edges[pick];
uf.unite(e[0], e[1]);
cost += e[2];
}
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); ++i) {
if (i == skip) continue;
auto& e = edges[i];
if (uf.unite(e[0], e[1])) cost += e[2];
}
return uf.count == 1 ? cost : INT_MAX;
};
int minCost = buildMST(n, newEdges, -1, -1);
vector<int> criticals, pseudos;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
int costWithout = buildMST(n, newEdges, i, -1);
if (costWithout > minCost) criticals.push_back(newEdges[i][3]);
else {
int costWith = buildMST(n, newEdges, -1, i);
if (costWith == minCost) pseudos.push_back(newEdges[i][3]);
}
}
return {criticals, pseudos};
}
Go
type UnionFind struct {
parent []int
count int
}
func NewUnionFind(n int) *UnionFind {
uf := &UnionFind{make([]int, n), n}
for i := range uf.parent {
uf.parent[i] = i
}
return uf
}
func (uf *UnionFind) Find(x int) int {
if uf.parent[x] != x {
uf.parent[x] = uf.Find(uf.parent[x])
}
return uf.parent[x]
}
func (uf *UnionFind) Union(x, y int) bool {
rx, ry := uf.Find(x), uf.Find(y)
if rx == ry {
return false
}
uf.parent[rx] = ry
uf.count--
return true
}
func findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(n int, edges [][]int) [][]int {
m := len(edges)
newEdges := make([][]int, m)
for i, e := range edges {
newEdges[i] = []int{e[0], e[1], e[2], i}
}
sort.Slice(newEdges, func(i, j int) bool { return newEdges[i][2] < newEdges[j][2] })
buildMST := func(skip, pick int) int {
uf := NewUnionFind(n)
cost := 0
if pick != -1 {
e := newEdges[pick]
uf.Union(e[0], e[1])
cost += e[2]
}
for i, e := range newEdges {
if i == skip {
continue
}
if uf.Union(e[0], e[1]) {
cost += e[2]
}
}
if uf.count == 1 {
return cost
}
return 1 << 30
}
minCost := buildMST(-1, -1)
criticals, pseudos := []int{}, []int{}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
if buildMST(i, -1) > minCost {
criticals = append(criticals, newEdges[i][3])
} else if buildMST(-1, i) == minCost {
pseudos = append(pseudos, newEdges[i][3])
}
}
return [][]int{criticals, pseudos}
}
Java
// ...existing code...
Kotlin
class UnionFind(n: Int) {
private val parent = IntArray(n) { it }
var count = n
fun find(x: Int): Int {
if (parent[x] != x) parent[x] = find(parent[x])
return parent[x]
}
fun union(x: Int, y: Int): Boolean {
val rx = find(x)
val ry = find(y)
if (rx == ry) return false
parent[rx] = ry
count--
return true
}
}
fun findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>): List<List<Int>> {
val m = edges.size
val newEdges = Array(m) { i -> intArrayOf(edges[i][0], edges[i][1], edges[i][2], i) }
newEdges.sortBy { it[2] }
fun buildMST(skip: Int, pick: Int): Int {
val uf = UnionFind(n)
var cost = 0
if (pick != -1) {
val e = newEdges[pick]
uf.union(e[0], e[1])
cost += e[2]
}
for (i in newEdges.indices) {
if (i == skip) continue
val e = newEdges[i]
if (uf.union(e[0], e[1])) cost += e[2]
}
return if (uf.count == 1) cost else Int.MAX_VALUE
}
val minCost = buildMST(-1, -1)
val criticals = mutableListOf<Int>()
val pseudos = mutableListOf<Int>()
for (i in 0 until m) {
if (buildMST(i, -1) > minCost) criticals.add(newEdges[i][3])
else if (buildMST(-1, i) == minCost) pseudos.add(newEdges[i][3])
}
return listOf(criticals, pseudos)
}
Python
class UnionFind:
def __init__(self, n):
self.parent = list(range(n))
self.count = n
def find(self, x):
if self.parent[x] != x:
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x])
return self.parent[x]
def union(self, x, y):
rx, ry = self.find(x), self.find(y)
if rx == ry:
return False
self.parent[rx] = ry
self.count -= 1
return True
def findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(n, edges):
m = len(edges)
newEdges = [e + [i] for i, e in enumerate(edges)]
newEdges.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
def buildMST(skip, pick):
uf = UnionFind(n)
cost = 0
if pick != -1:
e = newEdges[pick]
uf.union(e[0], e[1])
cost += e[2]
for i, e in enumerate(newEdges):
if i == skip:
continue
if uf.union(e[0], e[1]):
cost += e[2]
return cost if uf.count == 1 else float('inf')
minCost = buildMST(-1, -1)
criticals, pseudos = [], []
for i in range(m):
if buildMST(i, -1) > minCost:
criticals.append(newEdges[i][3])
elif buildMST(-1, i) == minCost:
pseudos.append(newEdges[i][3])
return [criticals, pseudos]
Rust
struct UnionFind {
parent: Vec<usize>,
count: usize,
}
impl UnionFind {
fn new(n: usize) -> Self {
UnionFind { parent: (0..n).collect(), count: n }
}
fn find(&mut self, x: usize) -> usize {
if self.parent[x] != x {
self.parent[x] = self.find(self.parent[x]);
}
self.parent[x]
}
fn union(&mut self, x: usize, y: usize) -> bool {
let rx = self.find(x);
let ry = self.find(y);
if rx == ry { return false; }
self.parent[rx] = ry;
self.count -= 1;
true
}
}
fn find_critical_and_pseudo_critical_edges(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let m = edges.len();
let mut new_edges: Vec<Vec<i32>> = edges.iter().enumerate().map(|(i, e)| vec![e[0], e[1], e[2], i as i32]).collect();
new_edges.sort_by_key(|e| e[2]);
let build_mst = |skip: Option<usize>, pick: Option<usize>| -> i32 {
let mut uf = UnionFind::new(n as usize);
let mut cost = 0;
if let Some(pick_idx) = pick {
let e = &new_edges[pick_idx];
uf.union(e[0] as usize, e[1] as usize);
cost += e[2];
}
for (i, e) in new_edges.iter().enumerate() {
if Some(i) == skip { continue; }
if uf.union(e[0] as usize, e[1] as usize) {
cost += e[2];
}
}
if uf.count == 1 { cost } else { i32::MAX }
};
let min_cost = build_mst(None, None);
let mut criticals = vec![];
let mut pseudos = vec![];
for i in 0..m {
if build_mst(Some(i), None) > min_cost {
criticals.push(new_edges[i][3]);
} else if build_mst(None, Some(i)) == min_cost {
pseudos.push(new_edges[i][3]);
}
}
vec![criticals, pseudos]
}
TypeScript
class UnionFind {
parent: number[];
count: number;
constructor(n: number) {
this.parent = Array.from({ length: n }, (_, i) => i);
this.count = n;
}
find(x: number): number {
if (this.parent[x] !== x) this.parent[x] = this.find(this.parent[x]);
return this.parent[x];
}
union(x: number, y: number): boolean {
const rx = this.find(x), ry = this.find(y);
if (rx === ry) return false;
this.parent[rx] = ry;
this.count--;
return true;
}
}
function findCriticalAndPseudoCriticalEdges(n: number, edges: number[][]): number[][] {
const m = edges.length;
const newEdges = edges.map((e, i) => [...e, i]);
newEdges.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]);
function buildMST(skip: number, pick: number): number {
const uf = new UnionFind(n);
let cost = 0;
if (pick !== -1) {
const e = newEdges[pick];
uf.union(e[0], e[1]);
cost += e[2];
}
for (let i = 0; i < newEdges.length; i++) {
if (i === skip) continue;
const e = newEdges[i];
if (uf.union(e[0], e[1])) cost += e[2];
}
return uf.count === 1 ? cost : Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER;
}
const minCost = buildMST(-1, -1);
const criticals: number[] = [], pseudos: number[] = [];
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
if (buildMST(i, -1) > minCost) criticals.push(newEdges[i][3]);
else if (buildMST(-1, i) === minCost) pseudos.push(newEdges[i][3]);
}
return [criticals, pseudos];
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(E^2 * α(N)), whereEis the number of edges andNis the number of nodes (α is the inverse Ackermann function for Union Find). - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(E + N).