Find Nearest Right Node in Binary Tree
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given the root of a binary tree and a node u in the tree, return thenearest node on the same level that is to the right of u , or return null ifu is the rightmost node in its level.
Examples
Example 1:
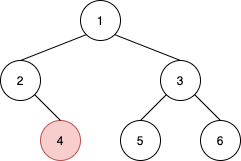
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,4,5,6], u = 4
Output: 5
Explanation: The nearest node on the same level to the right of node 4 is node 5.
Example 2:
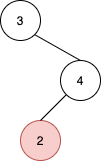
Input: root = [3,null,4,2], u = 2
Output: null
Explanation: There are no nodes to the right of 2.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 1 <= Node.val <= 10^5- All values in the tree are distinct.
uis a node in the binary tree rooted atroot.
Solution
Method 1 – Level Order Traversal (BFS)
Intuition
To find the nearest right node of u on the same level, we can perform a level order traversal (BFS) and, for each level, look for u. If we find u, the next node in the queue (if any) is the answer.
Approach
- Use a queue to perform BFS, storing nodes level by level.
- For each level, iterate through all nodes:
- If the current node is
u, return the next node in the queue (if any) for this level. - Otherwise, enqueue its children.
- If the current node is
- If
uis the rightmost node at its level, return null.
Code
C++
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* findNearestRightNode(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* u) {
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while (!q.empty()) {
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) {
TreeNode* node = q.front(); q.pop();
if (node == u) return i == sz-1 ? nullptr : q.front();
if (node->left) q.push(node->left);
if (node->right) q.push(node->right);
}
}
return nullptr;
}
};
Go
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func findNearestRightNode(root, u *TreeNode) *TreeNode {
q := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
sz := len(q)
for i := 0; i < sz; i++ {
node := q[0]
q = q[1:]
if node == u {
if i == sz-1 { return nil }
return q[0]
}
if node.Left != nil { q = append(q, node.Left) }
if node.Right != nil { q = append(q, node.Right) }
}
}
return nil
}
Java
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left, right;
}
class Solution {
public TreeNode findNearestRightNode(TreeNode root, TreeNode u) {
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int sz = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if (node == u) return i == sz-1 ? null : q.peek();
if (node.left != null) q.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) q.offer(node.right);
}
}
return null;
}
}
Kotlin
data class TreeNode(var `val`: Int, var left: TreeNode? = null, var right: TreeNode? = null)
class Solution {
fun findNearestRightNode(root: TreeNode?, u: TreeNode?): TreeNode? {
val q = ArrayDeque<TreeNode?>()
q.add(root)
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val sz = q.size
for (i in 0 until sz) {
val node = q.removeFirst()
if (node == u) return if (i == sz-1) null else q.first()
node?.left?.let { q.add(it) }
node?.right?.let { q.add(it) }
}
}
return null
}
}
Python
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
class Solution:
def findNearestRightNode(self, root: TreeNode, u: TreeNode) -> TreeNode | None:
from collections import deque
q = deque([root])
while q:
sz = len(q)
for i in range(sz):
node = q.popleft()
if node == u:
return None if i == sz-1 else q[0]
if node.left:
q.append(node.left)
if node.right:
q.append(node.right)
return None
Rust
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
impl Solution {
pub fn find_nearest_right_node(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, u: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>> {
use std::collections::VecDeque;
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
if let Some(r) = root.clone() { q.push_back(r); }
while !q.is_empty() {
let sz = q.len();
for i in 0..sz {
let node = q.pop_front().unwrap();
if Some(node.clone()) == u {
return if i == sz-1 { None } else { Some(q.front().unwrap().clone()) };
}
let n = node.borrow();
if let Some(left) = n.left.clone() { q.push_back(left); }
if let Some(right) = n.right.clone() { q.push_back(right); }
}
}
None
}
}
TypeScript
class TreeNode {
val: number;
left: TreeNode | null;
right: TreeNode | null;
constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {
this.val = val ?? 0;
this.left = left ?? null;
this.right = right ?? null;
}
}
class Solution {
findNearestRightNode(root: TreeNode | null, u: TreeNode | null): TreeNode | null {
if (!root || !u) return null;
const q: (TreeNode | null)[] = [root];
while (q.length) {
const sz = q.length;
for (let i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
const node = q.shift()!;
if (node === u) return i === sz-1 ? null : q[0];
if (node.left) q.push(node.left);
if (node.right) q.push(node.right);
}
}
return null;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the tree. Each node is visited once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(w), where w is the maximum width of the tree (queue size at the largest level).