Find Number of Coins to Place in Tree Nodes
Problem
You are given an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n -1, and rooted at node 0. You are given a 2D integer array edges of length
n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
You are also given a 0-indexed integer array cost of length n, where
cost[i] is the cost assigned to the ith node.
You need to place some coins on every node of the tree. The number of coins to be placed at node i can be calculated as:
- If size of the subtree of node
iis less than3, place1coin. - Otherwise, place an amount of coins equal to the maximum product of cost values assigned to
3distinct nodes in the subtree of nodei. If this product is negative , place0coins.
Return an arraycoin of sizen such thatcoin[i]is the number of coins placed at nodei .
Examples
Example 1
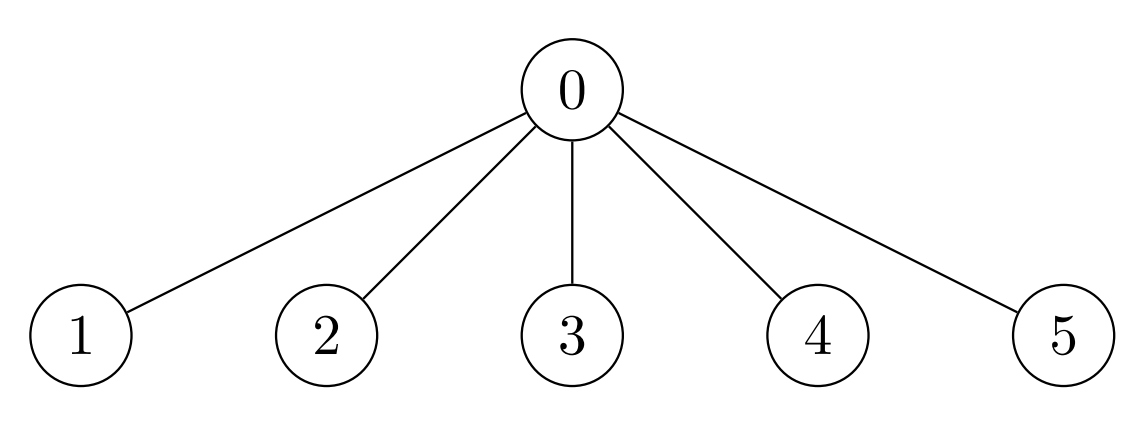
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5]], cost = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
Output: [120,1,1,1,1,1]
Explanation: For node 0 place 6 * 5 * 4 = 120 coins. All other nodes are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them.
Example 2
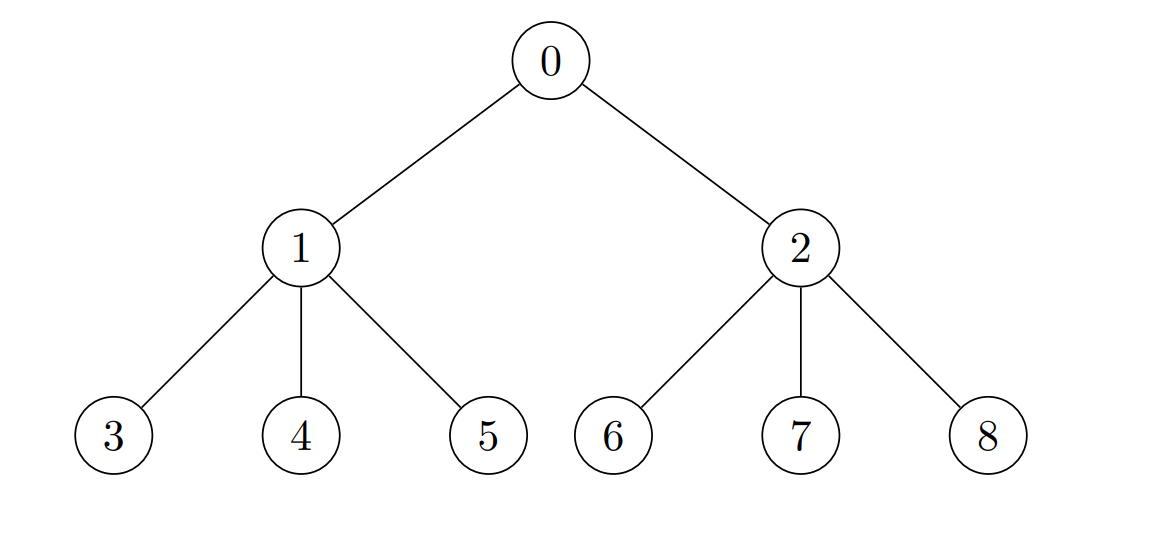
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[1,5],[2,6],[2,7],[2,8]], cost = [1,4,2,3,5,7,8,-4,2]
Output: [280,140,32,1,1,1,1,1,1]
Explanation: The coins placed on each node are:
- Place 8 * 7 * 5 = 280 coins on node 0.
- Place 7 * 5 * 4 = 140 coins on node 1.
- Place 8 * 2 * 2 = 32 coins on node 2.
- All other nodes are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them.
Example 3
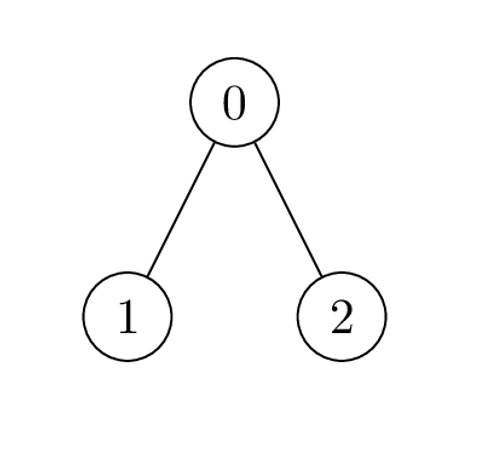
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]], cost = [1,2,-2]
Output: [0,1,1]
Explanation: Node 1 and 2 are leaves with subtree of size 1, place 1 coin on each of them. For node 0 the only possible product of cost is 2 * 1 * -2 = -4. Hence place 0 coins on node 0.
Constraints
2 <= n <= 2 * 10^4edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < ncost.length == n1 <= |cost[i]| <= 10^4- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
Method 1 – DFS with Heap for Top 3 Products
Intuition
For each node, we need to find the maximum product of any 3 costs in its subtree. We can use DFS to collect the top 3 largest and bottom 2 smallest costs in the subtree (to handle negative products). For each node, if the subtree size is less than 3, place 1 coin. Otherwise, compute the maximum product of any 3 costs (either the product of the top 3 largest or the product of the 2 smallest and the largest, to handle negatives). If the product is negative, place 0 coins.
Approach
- Build the tree as an adjacency list.
- Use DFS to traverse the tree and for each node:
- Collect all costs in the subtree.
- If the subtree size < 3, place 1 coin.
- Otherwise, find the top 3 largest and bottom 2 smallest costs.
- Compute the maximum product of any 3 costs.
- If the product is negative, place 0 coins; else, place product coins.
- Return the coins for all nodes.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> placedCoins(vector<vector<int>>& edges, vector<int>& cost) {
int n = cost.size();
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
vector<int> ans(n);
function<vector<int>(int,int)> dfs = [&](int u, int p) -> vector<int> {
vector<int> vals = {cost[u]};
for (int v : g[u]) if (v != p) {
auto sub = dfs(v, u);
vals.insert(vals.end(), sub.begin(), sub.end());
}
if (vals.size() < 3) ans[u] = 1;
else {
sort(vals.begin(), vals.end());
int n = vals.size();
long long prod1 = 1LL * vals[n-1] * vals[n-2] * vals[n-3];
long long prod2 = 1LL * vals[0] * vals[1] * vals[n-1];
long long prod = max(prod1, prod2);
ans[u] = prod < 0 ? 0 : prod;
}
return vals;
};
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
};
Go
func placedCoins(edges [][]int, cost []int) []int {
n := len(cost)
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], e[1])
g[e[1]] = append(g[e[1]], e[0])
}
ans := make([]int, n)
var dfs func(u, p int) []int
dfs = func(u, p int) []int {
vals := []int{cost[u]}
for _, v := range g[u] {
if v != p {
vals = append(vals, dfs(v, u)...)
}
}
if len(vals) < 3 {
ans[u] = 1
} else {
sort.Ints(vals)
n := len(vals)
prod1 := vals[n-1] * vals[n-2] * vals[n-3]
prod2 := vals[0] * vals[1] * vals[n-1]
prod := prod1
if prod2 > prod1 { prod = prod2 }
if prod < 0 { ans[u] = 0 } else { ans[u] = prod }
}
return vals
}
dfs(0, -1)
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int[] placedCoins(int[][] edges, int[] cost) {
int n = cost.length;
List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) g[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int[] e : edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1]);
g[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
int[] ans = new int[n];
dfs(0, -1, g, cost, ans);
return ans;
}
private List<Integer> dfs(int u, int p, List<Integer>[] g, int[] cost, int[] ans) {
List<Integer> vals = new ArrayList<>();
vals.add(cost[u]);
for (int v : g[u]) if (v != p) vals.addAll(dfs(v, u, g, cost, ans));
if (vals.size() < 3) ans[u] = 1;
else {
Collections.sort(vals);
int n = vals.size();
long prod1 = 1L * vals.get(n-1) * vals.get(n-2) * vals.get(n-3);
long prod2 = 1L * vals.get(0) * vals.get(1) * vals.get(n-1);
long prod = Math.max(prod1, prod2);
ans[u] = prod < 0 ? 0 : (int)prod;
}
return vals;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun placedCoins(edges: Array<IntArray>, cost: IntArray): IntArray {
val n = cost.size
val g = Array(n) { mutableListOf<Int>() }
for (e in edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1])
g[e[1]].add(e[0])
}
val ans = IntArray(n)
fun dfs(u: Int, p: Int): List<Int> {
val vals = mutableListOf(cost[u])
for (v in g[u]) if (v != p) vals.addAll(dfs(v, u))
if (vals.size < 3) ans[u] = 1
else {
vals.sort()
val n = vals.size
val prod1 = vals[n-1].toLong() * vals[n-2] * vals[n-3]
val prod2 = vals[0].toLong() * vals[1] * vals[n-1]
val prod = maxOf(prod1, prod2)
ans[u] = if (prod < 0) 0 else prod.toInt()
}
return vals
}
dfs(0, -1)
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def placedCoins(self, edges: list[list[int]], cost: list[int]) -> list[int]:
from collections import defaultdict
n = len(cost)
g = defaultdict(list)
for a, b in edges:
g[a].append(b)
g[b].append(a)
ans = [0] * n
def dfs(u, p):
vals = [cost[u]]
for v in g[u]:
if v != p:
vals += dfs(v, u)
if len(vals) < 3:
ans[u] = 1
else:
vals.sort()
prod1 = vals[-1] * vals[-2] * vals[-3]
prod2 = vals[0] * vals[1] * vals[-1]
prod = max(prod1, prod2)
ans[u] = 0 if prod < 0 else prod
return vals
dfs(0, -1)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn placed_coins(edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>, cost: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
use std::collections::HashMap;
let n = cost.len();
let mut g = vec![vec![]; n];
for e in &edges {
g[e[0] as usize].push(e[1] as usize);
g[e[1] as usize].push(e[0] as usize);
}
let mut ans = vec![0; n];
fn dfs(u: usize, p: i32, g: &Vec<Vec<usize>>, cost: &Vec<i32>, ans: &mut Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut vals = vec![cost[u]];
for &v in &g[u] {
if v as i32 != p {
vals.extend(dfs(v, u as i32, g, cost, ans));
}
}
if vals.len() < 3 {
ans[u] = 1;
} else {
vals.sort();
let n = vals.len();
let prod1 = vals[n-1] as i64 * vals[n-2] as i64 * vals[n-3] as i64;
let prod2 = vals[0] as i64 * vals[1] as i64 * vals[n-1] as i64;
let prod = prod1.max(prod2);
ans[u] = if prod < 0 { 0 } else { prod as i32 };
}
vals
}
dfs(0, -1, &g, &cost, &mut ans);
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
placedCoins(edges: number[][], cost: number[]): number[] {
const n = cost.length;
const g: number[][] = Array.from({length: n}, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
g[a].push(b);
g[b].push(a);
}
const ans: number[] = Array(n).fill(0);
function dfs(u: number, p: number): number[] {
const vals = [cost[u]];
for (const v of g[u]) if (v !== p) vals.push(...dfs(v, u));
if (vals.length < 3) ans[u] = 1;
else {
vals.sort((a, b) => a - b);
const n = vals.length;
const prod1 = vals[n-1] * vals[n-2] * vals[n-3];
const prod2 = vals[0] * vals[1] * vals[n-1];
const prod = Math.max(prod1, prod2);
ans[u] = prod < 0 ? 0 : prod;
}
return vals;
}
dfs(0, -1);
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n^2), where n is the number of nodes. Each node may aggregate all costs in its subtree. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n^2), for storing all subtree costs at each node.