Find Servers That Handled Most Number of Requests
Problem
You have k servers numbered from 0 to k-1 that are being used to handle multiple requests simultaneously. Each server has infinite computational capacity but cannot handle more than one request at a time. The requests are assigned to servers according to a specific algorithm:
- The
ith(0-indexed) request arrives. - If all servers are busy, the request is dropped (not handled at all).
- If the
(i % k)thserver is available, assign the request to that server. - Otherwise, assign the request to the next available server (wrapping around the list of servers and starting from 0 if necessary). For example, if the
ithserver is busy, try to assign the request to the(i+1)thserver, then the(i+2)thserver, and so on.
You are given a strictly increasing array arrival of positive integers, where arrival[i] represents the arrival time of the ith request, and another array load, where load[i] represents the load of the ith request (the time it takes to complete). Your goal is to find the busiest server(s). A server is considered busiest if it handled the most number of requests successfully among all the servers.
Return a list containing the IDs (0-indexed) of thebusiest server(s). You may return the IDs in any order.
Examples
Example 1
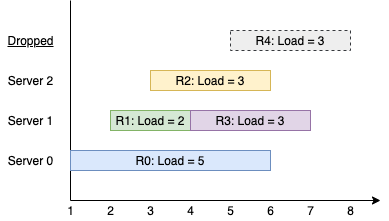
Input: k = 3, arrival = [1,2,3,4,5], load = [5,2,3,3,3]
Output: [1]
Explanation:
All of the servers start out available.
The first 3 requests are handled by the first 3 servers in order.
Request 3 comes in. Server 0 is busy, so it's assigned to the next available server, which is 1.
Request 4 comes in. It cannot be handled since all servers are busy, so it is dropped.
Servers 0 and 2 handled one request each, while server 1 handled two requests. Hence server 1 is the busiest server.
Example 2
Input: k = 3, arrival = [1,2,3,4], load = [1,2,1,2]
Output: [0]
Explanation:
The first 3 requests are handled by first 3 servers.
Request 3 comes in. It is handled by server 0 since the server is available.
Server 0 handled two requests, while servers 1 and 2 handled one request each. Hence server 0 is the busiest server.
Example 3
Input: k = 3, arrival = [1,2,3], load = [10,12,11]
Output: [0,1,2]
Explanation: Each server handles a single request, so they are all considered the busiest.
Constraints
1 <= k <= 10^51 <= arrival.length, load.length <= 10^5arrival.length == load.length1 <= arrival[i], load[i] <= 10^9arrivalis strictly increasing.
Solution
Method 1 – Priority Queue and Ordered Set
Intuition
We need to efficiently assign requests to available servers, always picking the next available server in a circular manner. We use a min-heap to track when each server becomes free and an ordered set (or balanced BST) to track available servers. For each request, we free up servers whose jobs are done, then assign the request to the correct server if possible.
Approach
- Use a min-heap to store busy servers as
(end_time, server_id). - Use an ordered set (e.g., TreeSet in Java, SortedSet in Python, or std::set in C++) to store available server ids.
- For each request:
- Free up servers whose end_time <= arrival[i] and add them back to the available set.
- Find the smallest server id >= (i % k) in the available set; if not found, wrap around to the smallest id.
- If a server is available, assign the request, update its count, and push it to the heap with its new end_time.
- If no server is available, drop the request.
- After all requests, find the server(s) with the maximum count.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> busiestServers(int k, vector<int>& arrival, vector<int>& load) {
set<int> avail;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) avail.insert(i);
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<>> busy;
vector<int> cnt(k);
for (int i = 0; i < arrival.size(); ++i) {
while (!busy.empty() && busy.top().first <= arrival[i]) {
avail.insert(busy.top().second);
busy.pop();
}
if (avail.empty()) continue;
auto it = avail.lower_bound(i % k);
if (it == avail.end()) it = avail.begin();
int sid = *it;
avail.erase(it);
cnt[sid]++;
busy.emplace(arrival[i] + load[i], sid);
}
int mx = *max_element(cnt.begin(), cnt.end());
vector<int> ans;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) if (cnt[i] == mx) ans.push_back(i);
return ans;
}
};
Go
func busiestServers(k int, arrival []int, load []int) []int {
avail := make([]int, k)
for i := 0; i < k; i++ { avail[i] = i }
cnt := make([]int, k)
busy := &BusyHeap{}
heap.Init(busy)
for i := 0; i < len(arrival); i++ {
for busy.Len() > 0 && (*busy)[0][0] <= arrival[i] {
avail = append(avail, (*busy)[0][1])
heap.Pop(busy)
}
if len(avail) == 0 { continue }
idx := sort.SearchInts(avail, i%k)
if idx == len(avail) { idx = 0 }
sid := avail[idx]
avail = append(avail[:idx], avail[idx+1:]...)
cnt[sid]++
heap.Push(busy, [2]int{arrival[i] + load[i], sid})
}
mx := 0
for _, v := range cnt { if v > mx { mx = v } }
ans := []int{}
for i, v := range cnt { if v == mx { ans = append(ans, i) } }
return ans
}
// BusyHeap implements heap.Interface for [2]int{end_time, server_id}
type BusyHeap [][2]int
func (h BusyHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h BusyHeap) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i][0] < h[j][0] }
func (h BusyHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *BusyHeap) Push(x any) { *h = append(*h, x.([2]int)) }
func (h *BusyHeap) Pop() any { old := *h; x := old[len(old)-1]; *h = old[:len(old)-1]; return x }
Java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> busiestServers(int k, int[] arrival, int[] load) {
TreeSet<Integer> avail = new TreeSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) avail.add(i);
PriorityQueue<int[]> busy = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(a -> a[0]));
int[] cnt = new int[k];
for (int i = 0; i < arrival.length; i++) {
while (!busy.isEmpty() && busy.peek()[0] <= arrival[i]) {
avail.add(busy.poll()[1]);
}
if (avail.isEmpty()) continue;
Integer sid = avail.ceiling(i % k);
if (sid == null) sid = avail.first();
avail.remove(sid);
cnt[sid]++;
busy.offer(new int[]{arrival[i] + load[i], sid});
}
int mx = Arrays.stream(cnt).max().getAsInt();
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) if (cnt[i] == mx) ans.add(i);
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun busiestServers(k: Int, arrival: IntArray, load: IntArray): List<Int> {
val avail = java.util.TreeSet<Int>()
for (i in 0 until k) avail.add(i)
val busy = java.util.PriorityQueue(compareBy<Pair<Int,Int>> { it.first })
val cnt = IntArray(k)
for (i in arrival.indices) {
while (busy.isNotEmpty() && busy.peek().first <= arrival[i]) {
avail.add(busy.poll().second)
}
val sid = avail.ceiling(i % k) ?: avail.firstOrNull() ?: continue
avail.remove(sid)
cnt[sid]++
busy.add(Pair(arrival[i] + load[i], sid))
}
val mx = cnt.maxOrNull() ?: 0
return cnt.withIndex().filter { it.value == mx }.map { it.index }
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def busiestServers(self, k: int, arrival: list[int], load: list[int]) -> list[int]:
import heapq, bisect
avail = list(range(k))
busy = [] # (end_time, server_id)
cnt = [0] * k
for i, t in enumerate(arrival):
while busy and busy[0][0] <= t:
_, sid = heapq.heappop(busy)
bisect.insort(avail, sid)
if not avail:
continue
idx = bisect.bisect_left(avail, i % k)
if idx == len(avail):
idx = 0
sid = avail.pop(idx)
cnt[sid] += 1
heapq.heappush(busy, (t + load[i], sid))
mx = max(cnt)
return [i for i, v in enumerate(cnt) if v == mx]
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn busiest_servers(k: i32, arrival: Vec<i32>, load: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
use std::collections::{BTreeSet, BinaryHeap};
let k = k as usize;
let mut avail: BTreeSet<usize> = (0..k).collect();
let mut busy = std::collections::BinaryHeap::new(); // min-heap by Reverse
let mut cnt = vec![0; k];
for (i, &t) in arrival.iter().enumerate() {
while let Some(std::cmp::Reverse((end, sid))) = busy.peek() {
if *end > t { break; }
let std::cmp::Reverse((end, sid)) = busy.pop().unwrap();
avail.insert(sid);
}
if avail.is_empty() { continue; }
let mut sid = *avail.range(i%k..).next().unwrap_or_else(|| avail.iter().next().unwrap());
avail.remove(&sid);
cnt[sid] += 1;
busy.push(std::cmp::Reverse((t + load[i], sid)));
}
let mx = *cnt.iter().max().unwrap();
(0..k).filter(|&i| cnt[i] == mx).map(|i| i as i32).collect()
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
busiestServers(k: number, arrival: number[], load: number[]): number[] {
const avail: number[] = Array.from({length: k}, (_, i) => i);
const busy: [number, number][] = [];
const cnt = Array(k).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < arrival.length; i++) {
while (busy.length && busy[0][0] <= arrival[i]) {
const [, sid] = busy.shift()!;
const idx = avail.findIndex(x => x > sid);
avail.splice(idx < 0 ? avail.length : idx, 0, sid);
}
if (!avail.length) continue;
let idx = avail.findIndex(x => x >= i % k);
if (idx === -1) idx = 0;
const sid = avail.splice(idx, 1)[0];
cnt[sid]++;
let j = 0;
while (j < busy.length && busy[j][0] <= arrival[i] + load[i]) j++;
busy.splice(j, 0, [arrival[i] + load[i], sid]);
}
const mx = Math.max(...cnt);
return cnt.map((v, i) => v === mx ? i : -1).filter(x => x !== -1);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n log k), wherenis the number of requests andkis the number of servers, due to heap and set operations. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(k), for the available set, heap, and count array.