Find the Last Marked Nodes in Tree
Problem
There exists an undirected tree with n nodes numbered 0 to n - 1.
You are given a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ui, vi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ui and vi in the tree.
Initially, all nodes are unmarked. After every second, you mark all unmarked nodes which have at least one marked node adjacent to them.
Return an array nodes where nodes[i] is the last node to get marked in the tree, if you mark node i at time t = 0. If nodes[i] has multiple answers for any node i, you can chooseany one answer.
Examples
Example 1:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2]]
Output: [2,2,1]
Explanation:
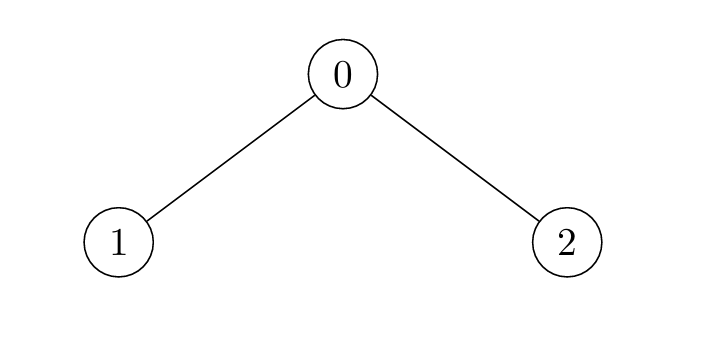
* For `i = 0`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[0] -> [0,1,2]`. Either 1 or 2 can be the answer.
* For `i = 1`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[1] -> [0,1] -> [0,1,2]`. Node 2 is marked last.
* For `i = 2`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[2] -> [0,2] -> [0,1,2]`. Node 1 is marked last.
Example 2:
Input: edges = [[0,1]]
Output: [1,0]
Explanation:
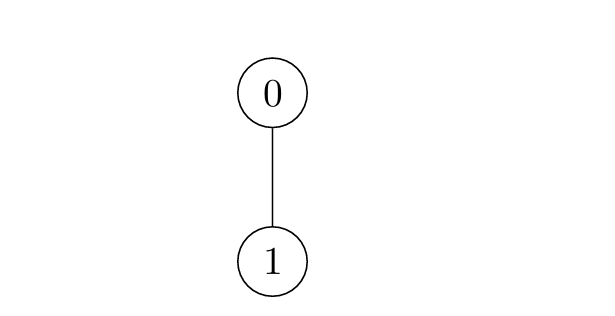
* For `i = 0`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[0] -> [0,1]`.
* For `i = 1`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[1] -> [0,1]`.
Example 3:
Input: edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[2,3],[2,4]]
Output: [3,3,1,1,1]
Explanation:
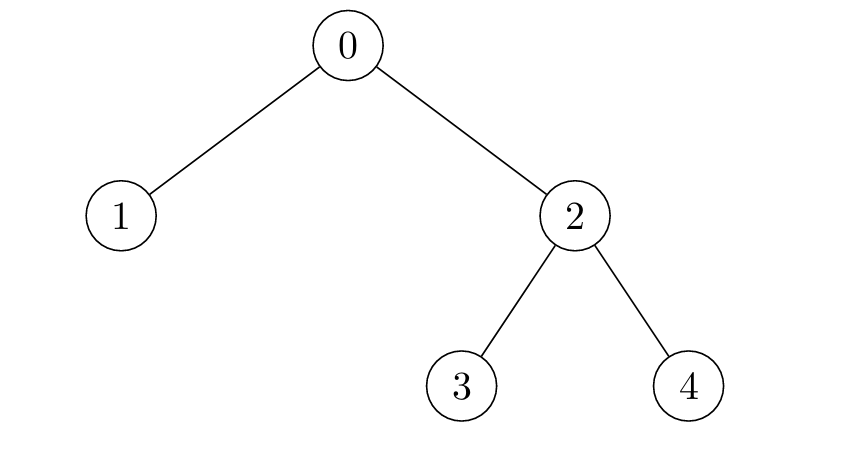
* For `i = 0`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[0] -> [0,1,2] -> [0,1,2,3,4]`.
* For `i = 1`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[1] -> [0,1] -> [0,1,2] -> [0,1,2,3,4]`.
* For `i = 2`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[2] -> [0,2,3,4] -> [0,1,2,3,4]`.
* For `i = 3`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[3] -> [2,3] -> [0,2,3,4] -> [0,1,2,3,4]`.
* For `i = 4`, the nodes are marked in the sequence: `[4] -> [2,4] -> [0,2,3,4] -> [0,1,2,3,4]`.
Constraints:
2 <= n <= 10^5edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= edges[i][0], edges[i][1] <= n - 1- The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
Solution
Method 1 – Farthest Node by BFS (Tree Diameter)
Intuition
When marking starts from a node, the last node to be marked is the farthest from the starting node. In a tree, this is always a leaf at the maximum distance. For each node, the answer is any node at the farthest distance from it.
Approach
- Build the adjacency list for the tree.
- For each node, run BFS to find the farthest node from it (the last to be marked).
- For efficiency, precompute the two endpoints of the tree's diameter (longest path in the tree).
- For each node, the farthest node is always one of the two diameter endpoints.
- For each node, compare its distance to both endpoints and pick the farther one.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findLastMarkedNodes(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edges) {
vector<vector<int>> g(n);
for (auto& e : edges) {
g[e[0]].push_back(e[1]);
g[e[1]].push_back(e[0]);
}
auto bfs = [&](int start) {
vector<int> dist(n, -1);
queue<int> q;
dist[start] = 0;
q.push(start);
int far = start;
while (!q.empty()) {
int u = q.front(); q.pop();
far = u;
for (int v : g[u]) if (dist[v] == -1) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
return make_pair(far, dist);
};
int u = bfs(0).first;
auto [v, distU] = bfs(u);
auto [_, distV] = bfs(v);
vector<int> ans(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ans[i] = distU[i] >= distV[i] ? u : v;
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func findLastMarkedNodes(n int, edges [][]int) []int {
g := make([][]int, n)
for _, e := range edges {
g[e[0]] = append(g[e[0]], e[1])
g[e[1]] = append(g[e[1]], e[0])
}
bfs := func(start int) (int, []int) {
dist := make([]int, n)
for i := range dist { dist[i] = -1 }
q := []int{start}
dist[start] = 0
far := start
for len(q) > 0 {
u := q[0]; q = q[1:]
far = u
for _, v := range g[u] {
if dist[v] == -1 {
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1
q = append(q, v)
}
}
}
return far, dist
}
u, _ := bfs(0)
v, distU := bfs(u)
_, distV := bfs(v)
ans := make([]int, n)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if distU[i] >= distV[i] {
ans[i] = u
} else {
ans[i] = v
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int[] findLastMarkedNodes(int n, int[][] edges) {
List<Integer>[] g = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) g[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (var e : edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1]);
g[e[1]].add(e[0]);
}
int[] bfs(int start) {
int[] dist = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dist, -1);
Queue<Integer> q = new ArrayDeque<>();
dist[start] = 0;
q.add(start);
int far = start;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int u = q.poll();
far = u;
for (int v : g[u]) if (dist[v] == -1) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
q.add(v);
}
}
return new int[]{far, dist};
}
int u = bfs(0)[0];
int[] resU = bfs(u);
int v = resU[0];
int[] distU = (int[])resU[1];
int[] resV = bfs(v);
int[] distV = (int[])resV[1];
int[] ans = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ans[i] = distU[i] >= distV[i] ? u : v;
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun findLastMarkedNodes(n: Int, edges: Array<IntArray>): IntArray {
val g = Array(n) { mutableListOf<Int>() }
for (e in edges) {
g[e[0]].add(e[1])
g[e[1]].add(e[0])
}
fun bfs(start: Int): Pair<Int, IntArray> {
val dist = IntArray(n) { -1 }
val q = ArrayDeque<Int>()
dist[start] = 0
q.add(start)
var far = start
while (q.isNotEmpty()) {
val u = q.removeFirst()
far = u
for (v in g[u]) if (dist[v] == -1) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1
q.add(v)
}
}
return far to dist
}
val (u, _) = bfs(0)
val (v, distU) = bfs(u)
val (_, distV) = bfs(v)
return IntArray(n) { if (distU[it] >= distV[it]) u else v }
}
}
Python
def find_last_marked_nodes(n: int, edges: list[list[int]]) -> list[int]:
from collections import deque
g = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for u, v in edges:
g[u].append(v)
g[v].append(u)
def bfs(start: int) -> tuple[int, list[int]]:
dist = [-1] * n
q = deque([start])
dist[start] = 0
far = start
while q:
u = q.popleft()
far = u
for v in g[u]:
if dist[v] == -1:
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1
q.append(v)
return far, dist
u, _ = bfs(0)
v, distU = bfs(u)
_, distV = bfs(v)
ans = [u if distU[i] >= distV[i] else v for i in range(n)]
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn find_last_marked_nodes(n: i32, edges: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
use std::collections::VecDeque;
let n = n as usize;
let mut g = vec![vec![]; n];
for e in edges.iter() {
g[e[0] as usize].push(e[1] as usize);
g[e[1] as usize].push(e[0] as usize);
}
let bfs = |start: usize| -> (usize, Vec<i32>) {
let mut dist = vec![-1; n];
let mut q = VecDeque::new();
dist[start] = 0;
q.push_back(start);
let mut far = start;
while let Some(u) = q.pop_front() {
far = u;
for &v in &g[u] {
if dist[v] == -1 {
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
q.push_back(v);
}
}
}
(far, dist)
};
let (u, _) = bfs(0);
let (v, dist_u) = bfs(u);
let (_, dist_v) = bfs(v);
(0..n).map(|i| if dist_u[i] >= dist_v[i] { u as i32 } else { v as i32 }).collect()
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
findLastMarkedNodes(n: number, edges: number[][]): number[] {
const g: number[][] = Array.from({length: n}, () => []);
for (const [u, v] of edges) {
g[u].push(v);
g[v].push(u);
}
function bfs(start: number): [number, number[]] {
const dist = Array(n).fill(-1);
const q = [start];
dist[start] = 0;
let far = start;
while (q.length) {
const u = q.shift()!;
far = u;
for (const v of g[u]) {
if (dist[v] === -1) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return [far, dist];
}
const [u, _] = bfs(0);
const [v, distU] = bfs(u);
const [__, distV] = bfs(v);
return Array.from({length: n}, (_, i) => distU[i] >= distV[i] ? u : v);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), as each BFS traverses all nodes and we do three BFS. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for adjacency list and distance arrays.