First Unique Character in a Stream of Characters
Find First Unique Character From a Stream of Characters
Problem
Given a string A denoting a stream of lowercase alphabets. You have to make new string B.
B is formed such that we have to find first non-repeating character each time a character is inserted to the stream and append it at the end to B. If no non-repeating character is found then append '#' at the end of B.
Examples
Example 1:
Input: A = "abadbc"
Output: "aabbdd"
Explanation:
"a" - first non repeating character 'a'
"ab" - first non repeating character is still 'a'
"aba" - first non repeating character 'b' (as 'a' repeats)
"abad" - first non repeating character 'b'
"abadb" - first non repeating character 'd'
"abadbc" - first non repeating character 'd'
Example 2:
Input: A = "aabcbc"
Output: "a -1 bbc -1"
You need to tell the first non-repeating character in O(1) time at any moment.
This problem is similar to [First Unique Character in a String](first-unique-character-in-a-string).
Solution
If we follow the second approach discussed here - [First Unique Character in a String](first-unique-character-in-a-string), i.e. using hashmap OR array as hashtable, then we need to store the stream so that we can traverse it one more time to find the first non-repeating character at any moment. So, we cannot properly use it.
We can also use Method 3, i.e. using LinkedHashMap and Set.
Method 4 will also not work, where are using CountIndex object. Because, we need to go through the count array every time first non-repeating element is queried. We can find the first non-repeating character from stream at any moment without traversing any array.
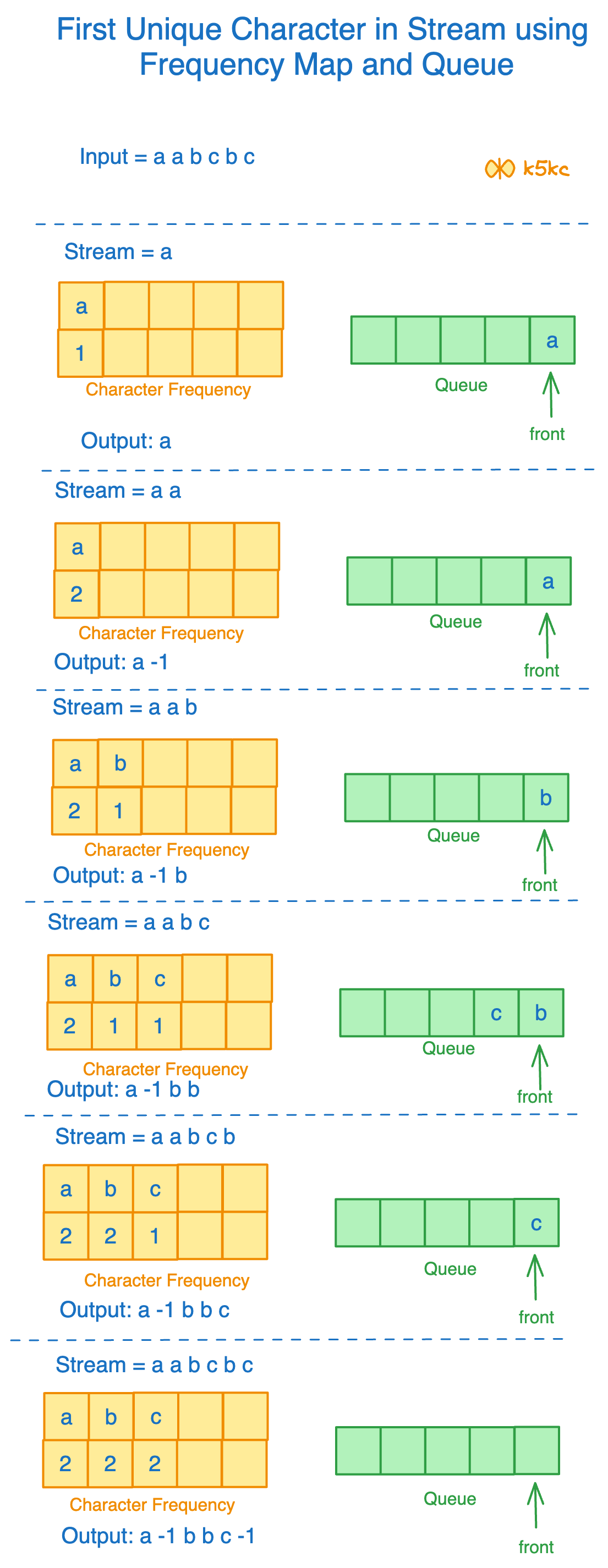
Method 1 - Using Queue and Hashmap
Algorithm
- Create a character array to store the frequency count of the characters.
- Create a queue to store the characters.
- Traverse the string.
- And the character and increment the frequency count.
- If the queue contains repeating characters, remove the character from the queue.
- If the queue contains repeating non-repeating characters, display the front element of the queue and break the while loop.
- If the queue is empty, i.e., no more non-repeating characters are present, -1 is printed.
Dry Run
Code
Java
public String firstNonRepeatingCharacter(String str) {
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
int[] freq = new int[26];
// queue to store the characters
Queue<Character> queue = new LinkedList<Character> ();
// traverse whole stream of characters
for (int i = 0; i<str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
// push the character into the queue
queue.add(ch);
// increment the frequency count
freq[ch - 'a']++;
// check for the non repeating character
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
// when the character is repeated
if (freq[queue.peek() - 'a'] > 1) {
queue.remove();
}
// when the character is not repeating
else {
ans.append(queue.peek() + " ");
break;
}
}
// if there is no non-repeating character
if (queue.isEmpty()) {
ans.append("-1 ");
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
Complexity
- Time Complexity: O(n) as the string is traversed once.
- Space Complexity: O(n) as extra space is required to store the characters in the queue.
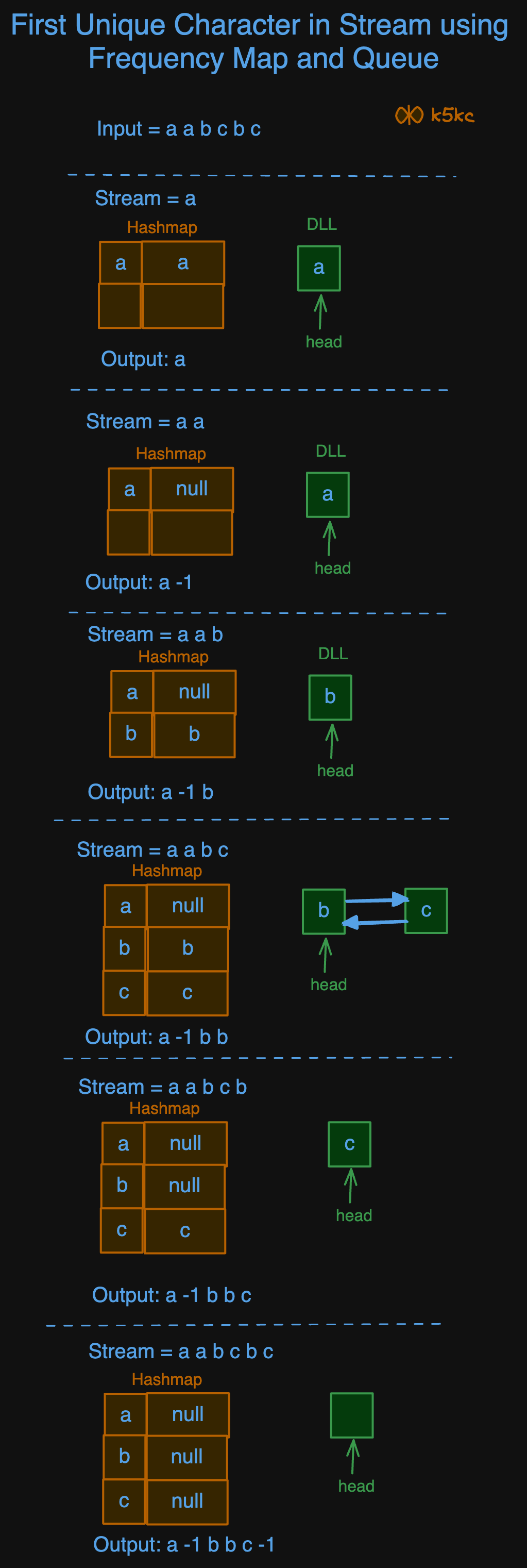
Method 2 - Using DLL (Doubly Linked List) and Hashmap
The Doubly Linked List stores the characters, and the hashmap stores the character as the key and the node( storing the character) as the value. If the hashmap does not contain the character, the character is stored in the hashmap and doubly linked list. Else, the value of the character is set to null in the hashmap.
Algorithm
- Create a hashmap to store the character and node.
- Create a doubly linked list to store the characters.
- Traverse the string.
- If the hashmap does not contain the character:
- Add character to the doubly linked list.
- Add the node containing character to the hashmap with character as the key.
- Add the character stored in the head of the doubly linked list to the resultant string.
- If the hashmap contains the character:
- If the character is repeating and the node is not null, delete the node and store the value as null in the hashmap.
- If the head is null, add -1 to the resultant string. Else add the character value of the head node.
Dry Run
Code:
// function that returns the string of first non repeating characters
public static String firstNonRepeatingCharacter(String str) {
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
// hashmap to store the character and node
HashMap<Character, Node> map = new HashMap<Character, Node> ();
// doubly linked list
DLLList dll = new DLLList();
for (int i = 0; i<str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
// if the hashmap does not contain the character
if (!map.containsKey(ch)) {
// add the node to the doubly linked list
dll.addNode(ch);
// add the character to hashmap
map.put(ch, dll.tail);
// add the character to the resultant string
ans.append(dll.head.ch + " ");
} else {
// if the character is encountered for the second time
if (hashmap.get(ch) != null) {
dll.deleteNode(hashmap.get(ch));
// replace the node of the respective character with null
hashmap.replace(ch, null);
}
if (dll.head == null) {
ans.append("-1 ");
} else {
ans.append(dll.head.ch + " ");
}
}
}
return ans.toString();
}
DLLNode:
class DLLNode {
char ch;
DLLNode previous;
DLLNode next;
Node(char ch) {
this.ch = ch;
}
}
DLLList Class:
public class DLLList {
// head and tail of the doubly linked list
Node head = null, tail = null;
// add node at the end of the doubly linked list
public void addNode(char ch) {
DLLNode newNode = new Node(ch);
// if doubly linked list is empty
if (head == null) {
head = tail = newNode;
return;
}
// if doubly linked list is not empty
tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = tail;
tail = newNode;
}
// delete the node of the doubly linked list
void deleteNode(DLLNode del) {
// if doubly linked list is empty or the node to be deleted is empty
if (head == null || del == null) {
return;
}
// delete head node
if (head == del) {
head = del.next;
}
// delete tail node
if (tail == del)
tail = tail.prev;
// change next pointer only if node to be deleted is not the tail node
if (del.next != null) {
del.next.prev = del.prev;
}
// change previous pointer only if node to be deleted is not the first node
if (del.prev != null) {
del.prev.next = del.next;
}
return;
}
}
Complexity
- Time Complexity: O(n) as the string is traversed once.
- Space Complexity: O(n) as extra space is required to store the doubly linked list and the hashmap.
Method 3 - Using LinkedHashSet for DLL and HashSet for Boolean Array
The contains method can be improved by LinkedHashSet. Below is an implementation of finding first unique using LinkedHashset. Note that we also need a hashset to track which element repeated. This is O(n) time and O(n) space solution. Here is the code:
public String firstNonRepeatingCharacter(String str) {
StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder();
Set<Character> seen = new HashSet<>();
Set<Character> uniq = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// traverse whole stream of characters
for (int i = 0; i<str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (!seen.contains(ch)) {
seen.add(ch);
uniq.add(ch);
} else {
uniq.remove(ch);
}
ans.append(uniq.size() == 0 ? "-1" : uniq.iterator().next();
}
return ans.toString();
}
Complexity
- Time complexity - O(n) for addition of n characters and O(1) for getting first 1 non repeating character. So,
O(n). - Space complexity - O(n)