Flip Binary Tree To Match Preorder Traversal
Problem
You are given the root of a binary tree with n nodes, where each node is uniquely assigned a value from 1 to n. You are also given a sequence of
n values voyage, which is the desired pre-order traversal of the binary tree.
Any node in the binary tree can be flipped by swapping its left and right subtrees. For example, flipping node 1 will have the following effect:
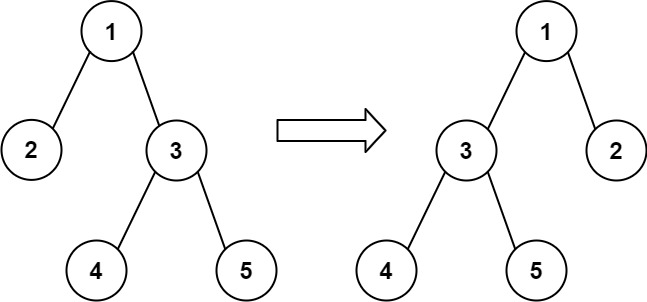
Flip the smallest number of nodes so that the pre-order traversal of the tree matches voyage.
Return _a list of the values of allflipped nodes. You may return the answer in any order. If it is impossible to flip the nodes in the tree to make the pre-order traversal match _voyage , return the list[-1].
Examples
Example 1

Input: root = [1,2], voyage = [2,1]
Output: [-1]
Explanation: It is impossible to flip the nodes such that the pre-order traversal matches voyage.
Example 2

Input: root = [1,2,3], voyage = [1,3,2]
Output: [1]
Explanation: Flipping node 1 swaps nodes 2 and 3, so the pre-order traversal matches voyage.
Example 3

Input: root = [1,2,3], voyage = [1,2,3]
Output: []
Explanation: The tree's pre-order traversal already matches voyage, so no nodes need to be flipped.
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is
n. n == voyage.length1 <= n <= 1001 <= Node.val, voyage[i] <= n- All the values in the tree are unique.
- All the values in
voyageare unique.
Solution
Method 1 – Greedy Preorder Traversal with Flips
Intuition
The key idea is to simulate a preorder traversal and compare each visited node with the expected value in voyage. If the left child does not match the next expected value, we flip the current node (swap left and right) and continue. If at any point the node value does not match the expected value in voyage, it is impossible to match.
Approach
- Use a pointer (index) to track the current position in
voyage. - Traverse the tree in preorder:
- If the current node's value does not match
voyage[index], return failure. - If the left child exists and does not match the next expected value, flip the node (swap left and right) and record the node's value.
- Recursively process left and right children.
- If the current node's value does not match
- If traversal completes successfully, return the list of flipped nodes; otherwise, return
[-1].
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> flipMatchVoyage(TreeNode* root, vector<int>& voyage) {
vector<int> ans;
int idx = 0;
if (dfs(root, voyage, idx, ans)) return ans;
return vector<int>{-1};
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* node, vector<int>& v, int& i, vector<int>& ans) {
if (!node) return true;
if (node->val != v[i++]) return false;
if (node->left && node->left->val != v[i]) {
ans.push_back(node->val);
return dfs(node->right, v, i, ans) && dfs(node->left, v, i, ans);
}
return dfs(node->left, v, i, ans) && dfs(node->right, v, i, ans);
}
};
Go
type TreeNode struct {
Val int
Left *TreeNode
Right *TreeNode
}
func flipMatchVoyage(root *TreeNode, voyage []int) []int {
var ans []int
idx := 0
var dfs func(*TreeNode) bool
dfs = func(node *TreeNode) bool {
if node == nil { return true }
if node.Val != voyage[idx] { return false }
idx++
if node.Left != nil && node.Left.Val != voyage[idx] {
ans = append(ans, node.Val)
return dfs(node.Right) && dfs(node.Left)
}
return dfs(node.Left) && dfs(node.Right)
}
if !dfs(root) { return []int{-1} }
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
private int idx = 0;
private List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
public List<Integer> flipMatchVoyage(TreeNode root, int[] voyage) {
if (dfs(root, voyage)) return ans;
return Arrays.asList(-1);
}
private boolean dfs(TreeNode node, int[] v) {
if (node == null) return true;
if (node.val != v[idx++]) return false;
if (node.left != null && node.left.val != v[idx]) {
ans.add(node.val);
return dfs(node.right, v) && dfs(node.left, v);
}
return dfs(node.left, v) && dfs(node.right, v);
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
private var idx = 0
private val ans = mutableListOf<Int>()
fun flipMatchVoyage(root: TreeNode?, voyage: IntArray): List<Int> {
return if (dfs(root, voyage)) ans else listOf(-1)
}
private fun dfs(node: TreeNode?, v: IntArray): Boolean {
if (node == null) return true
if (node.`val` != v[idx++]) return false
if (node.left != null && node.left.`val` != v[idx]) {
ans.add(node.`val`)
return dfs(node.right, v) && dfs(node.left, v)
}
return dfs(node.left, v) && dfs(node.right, v)
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def flipMatchVoyage(self, root: 'TreeNode', voyage: list[int]) -> list[int]:
ans: list[int] = []
idx = 0
def dfs(node: 'TreeNode') -> bool:
nonlocal idx
if not node:
return True
if node.val != voyage[idx]:
return False
idx += 1
if node.left and node.left.val != voyage[idx] if idx < len(voyage) else False:
ans.append(node.val)
return dfs(node.right) and dfs(node.left)
return dfs(node.left) and dfs(node.right)
return ans if dfs(root) else [-1]
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn flip_match_voyage(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, voyage: Vec<i32>) -> Vec<i32> {
fn dfs(node: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, v: &Vec<i32>, idx: &mut usize, ans: &mut Vec<i32>) -> bool {
if let Some(n) = node {
let n = n.borrow();
if n.val != v[*idx] { return false; }
*idx += 1;
if n.left.is_some() && n.left.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().val != v.get(*idx).copied().unwrap_or(-1) {
ans.push(n.val);
return dfs(n.right.clone(), v, idx, ans) && dfs(n.left.clone(), v, idx, ans);
}
return dfs(n.left.clone(), v, idx, ans) && dfs(n.right.clone(), v, idx, ans);
}
true
}
let mut ans = vec![];
let mut idx = 0;
if dfs(root, &voyage, &mut idx, &mut ans) { ans } else { vec![-1] }
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
flipMatchVoyage(root: TreeNode | null, voyage: number[]): number[] {
let ans: number[] = [];
let idx = 0;
function dfs(node: TreeNode | null): boolean {
if (!node) return true;
if (node.val !== voyage[idx++]) return false;
if (node.left && node.left.val !== voyage[idx]) {
ans.push(node.val);
return dfs(node.right) && dfs(node.left);
}
return dfs(node.left) && dfs(node.right);
}
return dfs(root) ? ans : [-1];
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n)wherenis the number of nodes, since each node is visited once in preorder. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(h)wherehis the height of the tree, due to recursion stack.