Get Biggest Three Rhombus Sums in a Grid
Problem
You are given an m x n integer matrix grid.
A rhombus sum is the sum of the elements that form the border of a regular rhombus shape in grid. The rhombus must have the shape of a square rotated 45 degrees with each of the corners centered in a grid cell.
Below is an image of four valid rhombus shapes with the corresponding colored cells that should be included in each rhombus sum :
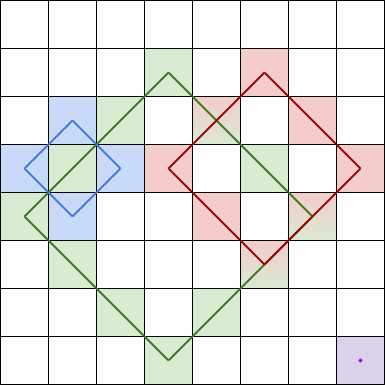
Note that the rhombus can have an area of 0, which is depicted by the purple rhombus in the bottom right corner.
Return _the biggest threedistinct rhombus sums in the _grid
indescending order . If there are less than three distinct values, return all of them.
Examples
Example 1
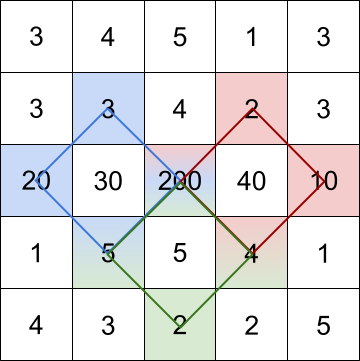
Input: grid = [[3,4,5,1,3],[3,3,4,2,3],[20,30,200,40,10],[1,5,5,4,1],[4,3,2,2,5]]
Output: [228,216,211]
Explanation: The rhombus shapes for the three biggest distinct rhombus sums are depicted above.
- Blue: 20 + 3 + 200 + 5 = 228
- Red: 200 + 2 + 10 + 4 = 216
- Green: 5 + 200 + 4 + 2 = 211
Example 2
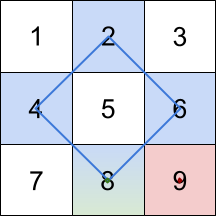
Input: grid = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
Output: [20,9,8]
Explanation: The rhombus shapes for the three biggest distinct rhombus sums are depicted above.
- Blue: 4 + 2 + 6 + 8 = 20
- Red: 9 (area 0 rhombus in the bottom right corner)
- Green: 8 (area 0 rhombus in the bottom middle)
Example 3
Input: grid = [[7,7,7]]
Output: [7]
Explanation: All three possible rhombus sums are the same, so return [7].
Constraints
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 501 <= grid[i][j] <= 10^5
Solution
Method 1 – Prefix Sums and Set for Unique Rhombus Sums
Intuition
To efficiently compute the sum of rhombus borders for all possible centers and sizes, we can use prefix sums along diagonals. For each cell, try all possible rhombus sizes, sum the border, and collect unique sums. Finally, return the top three largest unique sums.
Approach
- Precompute prefix sums for both diagonals (\ and /) for fast border sum calculation.
- For each cell in the grid, try all possible rhombus sizes (from 0 up to the largest that fits).
- For each rhombus, calculate the sum of its border using the prefix sums.
- Store all unique sums in a set.
- Return the three largest unique sums in descending order.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getBiggestThree(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
set<int> s;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
s.insert(grid[i][j]);
for (int k = 1; i - k >= 0 && i + k < m && j - k >= 0 && j + k < n; ++k) {
int sum = 0;
for (int d = 0; d < k; ++d) {
sum += grid[i - k + d][j + d];
sum += grid[i + k - d][j + d];
sum += grid[i - k + d][j - d];
sum += grid[i + k - d][j - d];
}
sum += grid[i][j - k];
sum += grid[i][j + k];
sum += grid[i - k][j];
sum += grid[i + k][j];
s.insert(sum);
}
}
}
vector<int> ans(s.rbegin(), s.rend());
if (ans.size() > 3) ans.resize(3);
return ans;
}
};
Go
type Solution struct{}
func (Solution) getBiggestThree(grid [][]int) []int {
m, n := len(grid), len(grid[0])
s := map[int]struct{}{}
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
s[grid[i][j]] = struct{}{}
for k := 1; i-k >= 0 && i+k < m && j-k >= 0 && j+k < n; k++ {
sum := 0
for d := 0; d < k; d++ {
sum += grid[i-k+d][j+d] + grid[i+k-d][j+d] + grid[i-k+d][j-d] + grid[i+k-d][j-d]
}
sum += grid[i][j-k] + grid[i][j+k] + grid[i-k][j] + grid[i+k][j]
s[sum] = struct{}{}
}
}
}
arr := make([]int, 0, len(s))
for v := range s { arr = append(arr, v) }
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(sort.IntSlice(arr)))
if len(arr) > 3 { arr = arr[:3] }
return arr
}
Java
class Solution {
public int[] getBiggestThree(int[][] grid) {
int m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
Set<Integer> s = new TreeSet<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
s.add(grid[i][j]);
for (int k = 1; i - k >= 0 && i + k < m && j - k >= 0 && j + k < n; k++) {
int sum = 0;
for (int d = 0; d < k; d++) {
sum += grid[i - k + d][j + d] + grid[i + k - d][j + d] + grid[i - k + d][j - d] + grid[i + k - d][j - d];
}
sum += grid[i][j - k] + grid[i][j + k] + grid[i - k][j] + grid[i + k][j];
s.add(sum);
}
}
}
int[] ans = s.stream().mapToInt(Integer::intValue).toArray();
return Arrays.copyOf(ans, Math.min(3, ans.length));
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun getBiggestThree(grid: Array<IntArray>): IntArray {
val m = grid.size
val n = grid[0].size
val s = sortedSetOf<Int>(compareByDescending { it })
for (i in 0 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
s.add(grid[i][j])
for (k in 1..minOf(i, m-1-i, j, n-1-j)) {
var sum = 0
for (d in 0 until k) {
sum += grid[i-k+d][j+d] + grid[i+k-d][j+d] + grid[i-k+d][j-d] + grid[i+k-d][j-d]
}
sum += grid[i][j-k] + grid[i][j+k] + grid[i-k][j] + grid[i+k][j]
s.add(sum)
}
}
}
return s.take(3).toIntArray()
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def getBiggestThree(self, grid: list[list[int]]) -> list[int]:
m, n = len(grid), len(grid[0])
s = set()
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
s.add(grid[i][j])
for k in range(1, min(i, m-1-i, j, n-1-j)+1):
total = 0
for d in range(k):
total += grid[i-k+d][j+d] + grid[i+k-d][j+d] + grid[i-k+d][j-d] + grid[i+k-d][j-d]
total += grid[i][j-k] + grid[i][j+k] + grid[i-k][j] + grid[i+k][j]
s.add(total)
return sorted(s, reverse=True)[:3]
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn get_biggest_three(grid: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let m = grid.len();
let n = grid[0].len();
let mut s = std::collections::BTreeSet::new();
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
s.insert(grid[i][j]);
for k in 1..=std::cmp::min(std::cmp::min(i, m-1-i), std::cmp::min(j, n-1-j)) {
let mut sum = 0;
for d in 0..k {
sum += grid[i-k+d][j+d] + grid[i+k-d][j+d] + grid[i-k+d][j-d] + grid[i+k-d][j-d];
}
sum += grid[i][j-k] + grid[i][j+k] + grid[i-k][j] + grid[i+k][j];
s.insert(sum);
}
}
}
s.iter().rev().take(3).cloned().collect()
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
getBiggestThree(grid: number[][]): number[] {
const m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length;
const s = new Set<number>();
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
s.add(grid[i][j]);
for (let k = 1; i - k >= 0 && i + k < m && j - k >= 0 && j + k < n; k++) {
let sum = 0;
for (let d = 0; d < k; d++) {
sum += grid[i - k + d][j + d] + grid[i + k - d][j + d] + grid[i - k + d][j - d] + grid[i + k - d][j - d];
}
sum += grid[i][j - k] + grid[i][j + k] + grid[i - k][j] + grid[i + k][j];
s.add(sum);
}
}
}
return Array.from(s).sort((a, b) => b - a).slice(0, 3);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m * n * min(m, n)), since for each cell, we try all possible rhombus sizes. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(m * n), for storing unique sums.