Grid Illumination
Problem
There is a 2D grid of size n x n where each cell of this grid has a lamp that is initially turned off.
You are given a 2D array of lamp positions lamps, where lamps[i] = [rowi, coli] indicates that the lamp at grid[rowi][coli] is turned on. Even if the same lamp is listed more than once, it is turned on.
When a lamp is turned on, it illuminates its cell and all other cells in the same row, column, or diagonal.
You are also given another 2D array queries, where queries[j] = [rowj, colj]. For the jth query, determine whether grid[rowj][colj] is illuminated or not. After answering the jth query, turn off the lamp at
grid[rowj][colj] and its 8 adjacent lamps if they exist. A lamp is adjacent if its cell shares either a side or corner with grid[rowj][colj].
Return an array of integersans _,_whereans[j]should be1 if the cell in thejth query was illuminated, or0 if the lamp was not.
Examples
Example 1
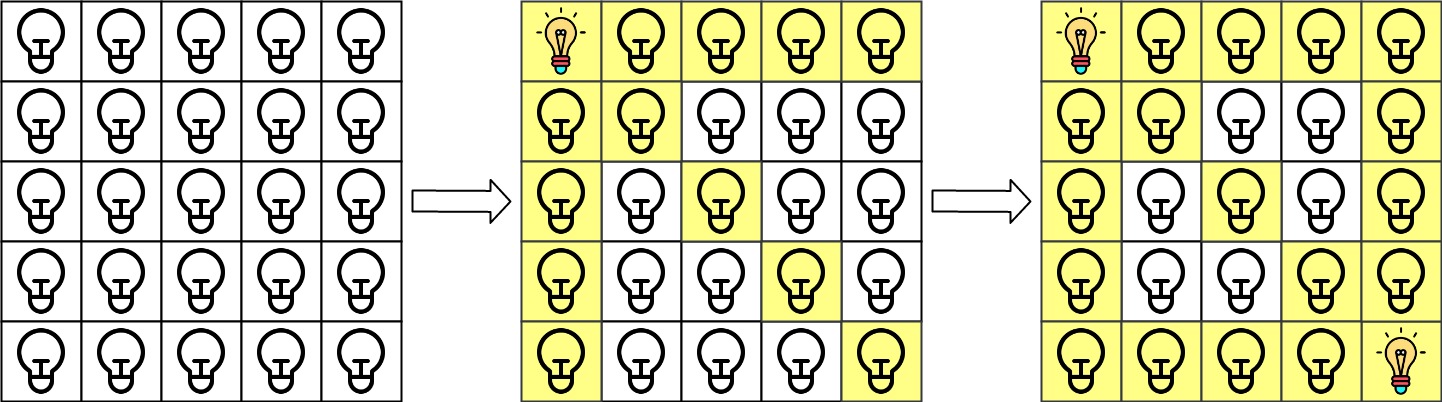
Input: n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[4,4]], queries = [[1,1],[1,0]]
Output: [1,0]
Explanation: We have the initial grid with all lamps turned off. In the above picture we see the grid after turning on the lamp at grid[0][0] then turning on the lamp at grid[4][4].
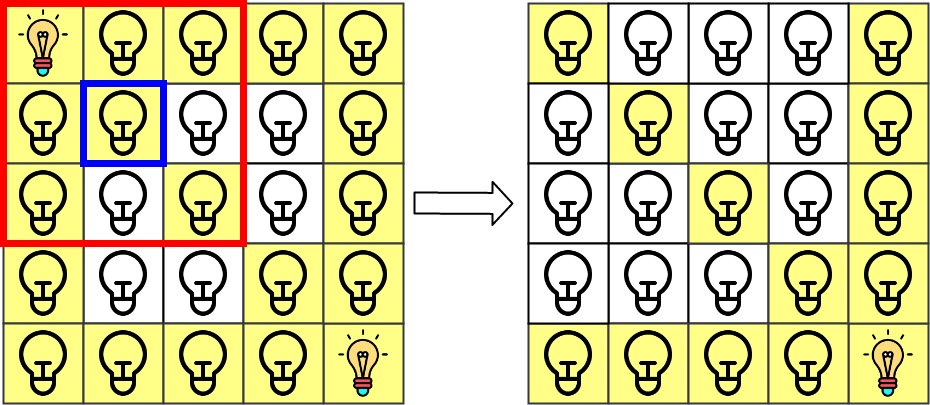
The 0th query asks if the lamp at grid[1][1] is illuminated or not (the blue square). It is illuminated, so set ans[0] = 1. Then, we turn off all lamps in the red square.
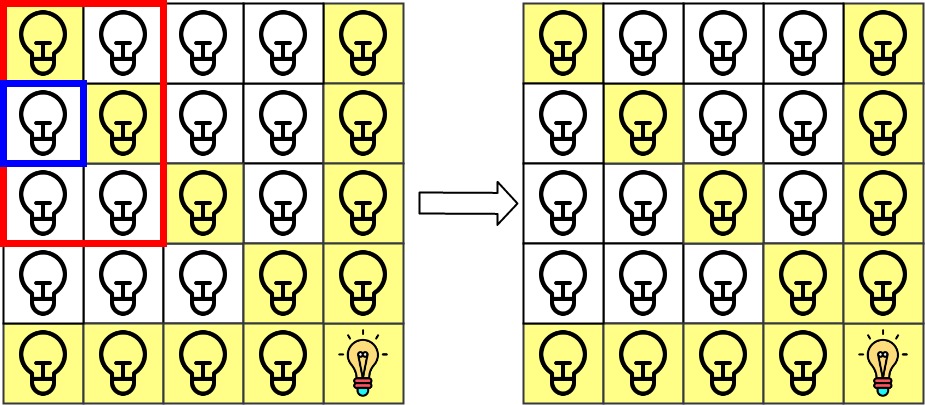
The 1st query asks if the lamp at grid[1][0] is illuminated or not (the blue square). It is not illuminated, so set ans[1] = 0. Then, we turn off all lamps in the red rectangle.
Example 2
Input: n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[4,4]], queries = [[1,1],[1,1]]
Output: [1,1]
Example 3
Input: n = 5, lamps = [[0,0],[0,4]], queries = [[0,4],[0,1],[1,4]]
Output: [1,1,0]
Constraints
1 <= n <= 10^90 <= lamps.length <= 200000 <= queries.length <= 20000lamps[i].length == 20 <= rowi, coli < nqueries[j].length == 20 <= rowj, colj < n
Solution
Method 1 – Hash Map Counting and Set for Lamps
Intuition
We need to efficiently check if a cell is illuminated by any lamp in its row, column, or diagonals, and quickly turn off lamps in a 3x3 area after each query. We can use hash maps to count the number of lamps affecting each row, column, and diagonal, and a set to track lamp positions.
Approach
- Use hash maps to count the number of lamps in each row, column, diagonal, and anti-diagonal.
- Use a set to store the positions of all currently on lamps.
- For each query:
- If the cell's row, column, diagonal, or anti-diagonal has a lamp, it is illuminated.
- After answering, turn off any lamp in the 3x3 area centered at the query cell, updating the hash maps and removing from the set.
- Return the results for all queries.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> gridIllumination(int n, vector<vector<int>>& lamps, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
unordered_map<int, int> row, col, diag, anti;
set<pair<int, int>> s;
for (auto& l : lamps) {
int x = l[0], y = l[1];
if (s.count({x, y})) continue;
s.insert({x, y});
row[x]++;
col[y]++;
diag[x - y]++;
anti[x + y]++;
}
vector<int> ans;
vector<pair<int, int>> dirs = {{0,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0},{1,1},{1,-1},{-1,1},{-1,-1}};
for (auto& q : queries) {
int x = q[0], y = q[1];
ans.push_back(row[x] || col[y] || diag[x - y] || anti[x + y] ? 1 : 0);
for (auto& d : dirs) {
int nx = x + d.first, ny = y + d.second;
if (s.count({nx, ny})) {
s.erase({nx, ny});
row[nx]--;
col[ny]--;
diag[nx - ny]--;
anti[nx + ny]--;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func gridIllumination(n int, lamps [][]int, queries [][]int) []int {
row, col, diag, anti := map[int]int{}, map[int]int{}, map[int]int{}, map[int]int{}
s := map[[2]int]bool{}
for _, l := range lamps {
x, y := l[0], l[1]
key := [2]int{x, y}
if s[key] { continue }
s[key] = true
row[x]++
col[y]++
diag[x-y]++
anti[x+y]++
}
dirs := [][2]int{{0,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0},{1,1},{1,-1},{-1,1},{-1,-1}}
ans := make([]int, len(queries))
for i, q := range queries {
x, y := q[0], q[1]
if row[x] > 0 || col[y] > 0 || diag[x-y] > 0 || anti[x+y] > 0 {
ans[i] = 1
}
for _, d := range dirs {
nx, ny := x+d[0], y+d[1]
key := [2]int{nx, ny}
if s[key] {
s[key] = false
row[nx]--
col[ny]--
diag[nx-ny]--
anti[nx+ny]--
}
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int[] gridIllumination(int n, int[][] lamps, int[][] queries) {
Map<Integer, Integer> row = new HashMap<>(), col = new HashMap<>(), diag = new HashMap<>(), anti = new HashMap<>();
Set<Long> s = new HashSet<>();
for (int[] l : lamps) {
int x = l[0], y = l[1];
long key = ((long)x << 32) | y;
if (s.contains(key)) continue;
s.add(key);
row.put(x, row.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1);
col.put(y, col.getOrDefault(y, 0) + 1);
diag.put(x - y, diag.getOrDefault(x - y, 0) + 1);
anti.put(x + y, anti.getOrDefault(x + y, 0) + 1);
}
int[] ans = new int[queries.length];
int[][] dirs = {{0,0},{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0},{1,1},{1,-1},{-1,1},{-1,-1}};
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; i++) {
int x = queries[i][0], y = queries[i][1];
if (row.getOrDefault(x,0) > 0 || col.getOrDefault(y,0) > 0 || diag.getOrDefault(x-y,0) > 0 || anti.getOrDefault(x+y,0) > 0) {
ans[i] = 1;
}
for (int[] d : dirs) {
int nx = x + d[0], ny = y + d[1];
long key = ((long)nx << 32) | ny;
if (s.contains(key)) {
s.remove(key);
row.put(nx, row.getOrDefault(nx,0)-1);
col.put(ny, col.getOrDefault(ny,0)-1);
diag.put(nx-ny, diag.getOrDefault(nx-ny,0)-1);
anti.put(nx+ny, anti.getOrDefault(nx+ny,0)-1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun gridIllumination(n: Int, lamps: Array<IntArray>, queries: Array<IntArray>): IntArray {
val row = mutableMapOf<Int, Int>()
val col = mutableMapOf<Int, Int>()
val diag = mutableMapOf<Int, Int>()
val anti = mutableMapOf<Int, Int>()
val s = mutableSetOf<Pair<Int, Int>>()
for (l in lamps) {
val (x, y) = l
if (s.contains(x to y)) continue
s.add(x to y)
row[x] = row.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1
col[y] = col.getOrDefault(y, 0) + 1
diag[x - y] = diag.getOrDefault(x - y, 0) + 1
anti[x + y] = anti.getOrDefault(x + y, 0) + 1
}
val dirs = listOf(0 to 0, 0 to 1, 0 to -1, 1 to 0, -1 to 0, 1 to 1, 1 to -1, -1 to 1, -1 to -1)
val ans = IntArray(queries.size)
for ((i, q) in queries.withIndex()) {
val (x, y) = q
if (row.getOrDefault(x,0) > 0 || col.getOrDefault(y,0) > 0 || diag.getOrDefault(x-y,0) > 0 || anti.getOrDefault(x+y,0) > 0) {
ans[i] = 1
}
for ((dx, dy) in dirs) {
val nx = x + dx
val ny = y + dy
if (s.contains(nx to ny)) {
s.remove(nx to ny)
row[nx] = row.getOrDefault(nx,0)-1
col[ny] = col.getOrDefault(ny,0)-1
diag[nx-ny] = diag.getOrDefault(nx-ny,0)-1
anti[nx+ny] = anti.getOrDefault(nx+ny,0)-1
}
}
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def gridIllumination(self, n: int, lamps: list[list[int]], queries: list[list[int]]) -> list[int]:
from collections import defaultdict
row = defaultdict(int)
col = defaultdict(int)
diag = defaultdict(int)
anti = defaultdict(int)
s = set()
for x, y in lamps:
if (x, y) in s:
continue
s.add((x, y))
row[x] += 1
col[y] += 1
diag[x - y] += 1
anti[x + y] += 1
ans = []
dirs = [(0,0),(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0),(1,1),(1,-1),(-1,1),(-1,-1)]
for x, y in queries:
ans.append(1 if row[x] or col[y] or diag[x-y] or anti[x+y] else 0)
for dx, dy in dirs:
nx, ny = x + dx, y + dy
if (nx, ny) in s:
s.remove((nx, ny))
row[nx] -= 1
col[ny] -= 1
diag[nx-ny] -= 1
anti[nx+ny] -= 1
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn grid_illumination(n: i32, lamps: Vec<Vec<i32>>, queries: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
use std::collections::{HashMap, HashSet};
let mut row = HashMap::new();
let mut col = HashMap::new();
let mut diag = HashMap::new();
let mut anti = HashMap::new();
let mut s = HashSet::new();
for l in lamps.iter() {
let (x, y) = (l[0], l[1]);
if !s.insert((x, y)) { continue; }
*row.entry(x).or_insert(0) += 1;
*col.entry(y).or_insert(0) += 1;
*diag.entry(x - y).or_insert(0) += 1;
*anti.entry(x + y).or_insert(0) += 1;
}
let dirs = vec![(0,0),(0,1),(0,-1),(1,0),(-1,0),(1,1),(1,-1),(-1,1),(-1,-1)];
let mut ans = Vec::new();
for q in queries.iter() {
let (x, y) = (q[0], q[1]);
if row.get(&x).unwrap_or(&0) > &0 || col.get(&y).unwrap_or(&0) > &0 || diag.get(&(x-y)).unwrap_or(&0) > &0 || anti.get(&(x+y)).unwrap_or(&0) > &0 {
ans.push(1);
} else {
ans.push(0);
}
for (dx, dy) in &dirs {
let nx = x + dx;
let ny = y + dy;
if s.remove(&(nx, ny)) {
*row.entry(nx).or_insert(0) -= 1;
*col.entry(ny).or_insert(0) -= 1;
*diag.entry(nx-ny).or_insert(0) -= 1;
*anti.entry(nx+ny).or_insert(0) -= 1;
}
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
gridIllumination(n: number, lamps: number[][], queries: number[][]): number[] {
const row = new Map<number, number>(), col = new Map<number, number>(), diag = new Map<number, number>(), anti = new Map<number, number>();
const s = new Set<string>();
for (const [x, y] of lamps) {
const key = `${x},${y}`;
if (s.has(key)) continue;
s.add(key);
row.set(x, (row.get(x) || 0) + 1);
col.set(y, (col.get(y) || 0) + 1);
diag.set(x - y, (diag.get(x - y) || 0) + 1);
anti.set(x + y, (anti.get(x + y) || 0) + 1);
}
const dirs = [[0,0],[0,1],[0,-1],[1,0],[-1,0],[1,1],[1,-1],[-1,1],[-1,-1]];
const ans: number[] = [];
for (const [x, y] of queries) {
ans.push(row.get(x) || col.get(y) || diag.get(x-y) || anti.get(x+y) ? 1 : 0);
for (const [dx, dy] of dirs) {
const nx = x + dx, ny = y + dy, key = `${nx},${ny}`;
if (s.has(key)) {
s.delete(key);
row.set(nx, (row.get(nx) || 0) - 1);
col.set(ny, (col.get(ny) || 0) - 1);
diag.set(nx-ny, (diag.get(nx-ny) || 0) - 1);
anti.set(nx+ny, (anti.get(nx+ny) || 0) - 1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(L + Q)— WhereLis the number of lamps andQis the number of queries. Each lamp and query is processed in constant time due to hash maps and set operations. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(L + Q)— For hash maps and set to store lamp and illumination state.