Implement stack using queues
Problem
Implement a last-in-first-out (LIFO) stack using only two queues. The implemented stack should support all the functions of a normal stack (push, top, pop, and empty).
Implement the MyStack class:
void push(int x)Pushes element x to the top of the stack.int pop()Removes the element on the top of the stack and returns it.int top()Returns the element on the top of the stack.boolean empty()Returnstrueif the stack is empty,falseotherwise.
Notes:
- You must use only standard operations of a queue, which means that only
push to back,peek/pop from front,sizeandis emptyoperations are valid. - Depending on your language, the queue may not be supported natively. You may simulate a queue using a list or deque (double-ended queue) as long as you use only a queue's standard operations.
This problem is opposite of [Implement Queue using Stacks](implement-queue-using-stacks).
Follow up
Can you do it using 1 queue only?
Examples
Example 1:
Input:
["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"]
[[], [1], [2], [], [], []]
Output:
[null, null, null, 2, 2, false]
Explanation:
MyStack myStack = new MyStack();
myStack.push(1);
myStack.push(2);
myStack.top(); // return 2
myStack.pop(); // return 2
myStack.empty(); // return False
Solution
This problem can be solved by using two queues and later also with 1 Queue as well.
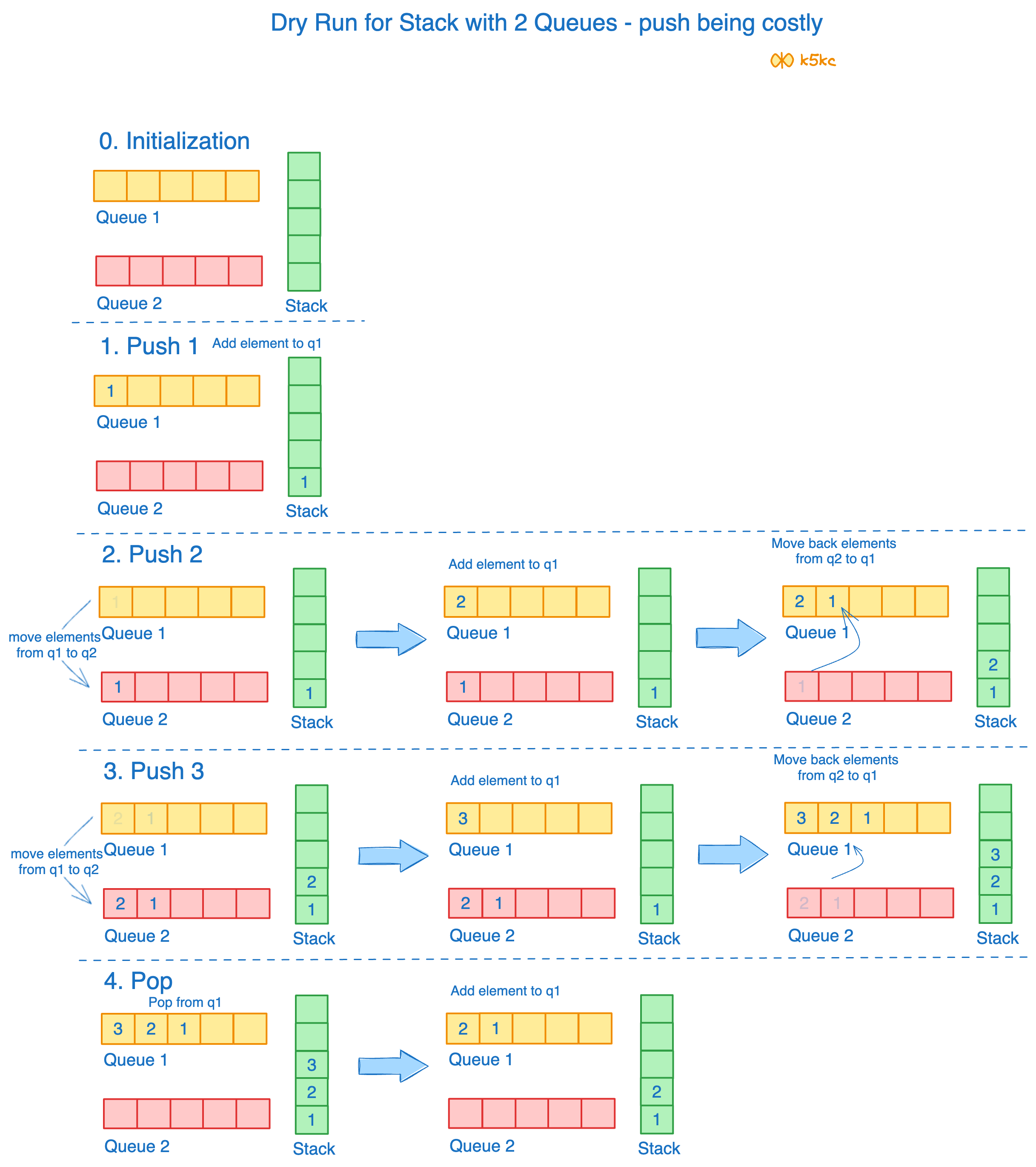
Method 1 - 2 Queues with copy (By Making Push Operation costly)
This method makes sure that newly entered element is always at the front of q1, so that pop operation just dequeues from q1. q2 is used to put every new element at front of q1.
So, q1 is our main queue for pop, top and empty, but q2 is like a temp queue.
Pseudocode
Push
push(x)
1) One by one dequeue elements from q1 and enqueue to q2
2) Add x to q1
3) One by one move back elements from q2 to q1
Pop
pop()
1) Dequeue from q1
Code
Java
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> q2 = new LinkedList<>(); // tmp queue
public void push(int x) {
while(!q1.isEmpty()){
q2.offer(q1.poll());
}
q1.offer(x);
while(!q2.isEmpty()){
q1.offer(q2.poll());
}
}
public void pop() {
q1.poll();
}
public int top() {
return q1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty();
}
}
Complexity
Time Complexity:
- Push -
O(N) - Pop -
O(1) - Top -
O(1) - Stack Size -
O(1)
Dry Run
Suppose, we have to do following operations - push(1), push(2)
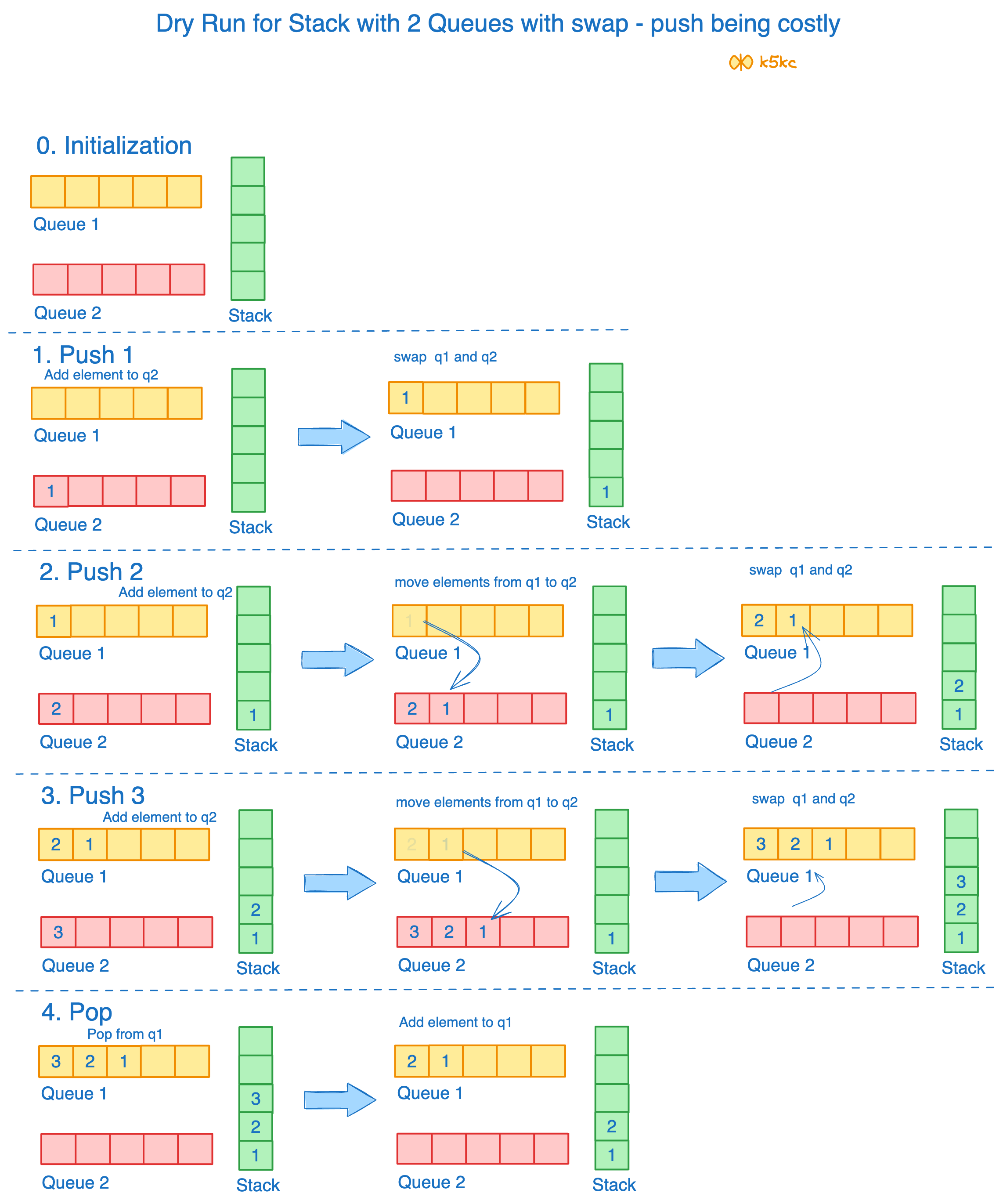
Method 2 - 2 Queues with swapping of queues (By Making Push Operation costly)
Pseudocode
Push
push(x)
1) Enqueue x to q2
2) One by one dequeue everything from q1 and enqueue to q2.
3) Swap the names of q1 and q2
// Swapping of names is done to avoid one more movement of all elements
// from q2 to q1.
Pop
pop()
1) DeQueue from q1
Code
Java
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> q2 = new LinkedList<>(); // tmp queue
public void push(int x) {
q2.offer(x);
while(!q1.isEmpty()){
q2.offer(q1.poll());
}
Queue<Integer> temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
}
public void pop() {
q1.poll();
}
public int top() {
return q1.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return q1.isEmpty();
}
}
Complexity
Time Complexity:
- Push -
O(N) - Pop -
O(1) - Top -
O(1) - Stack Size -
O(1)
Dry Run
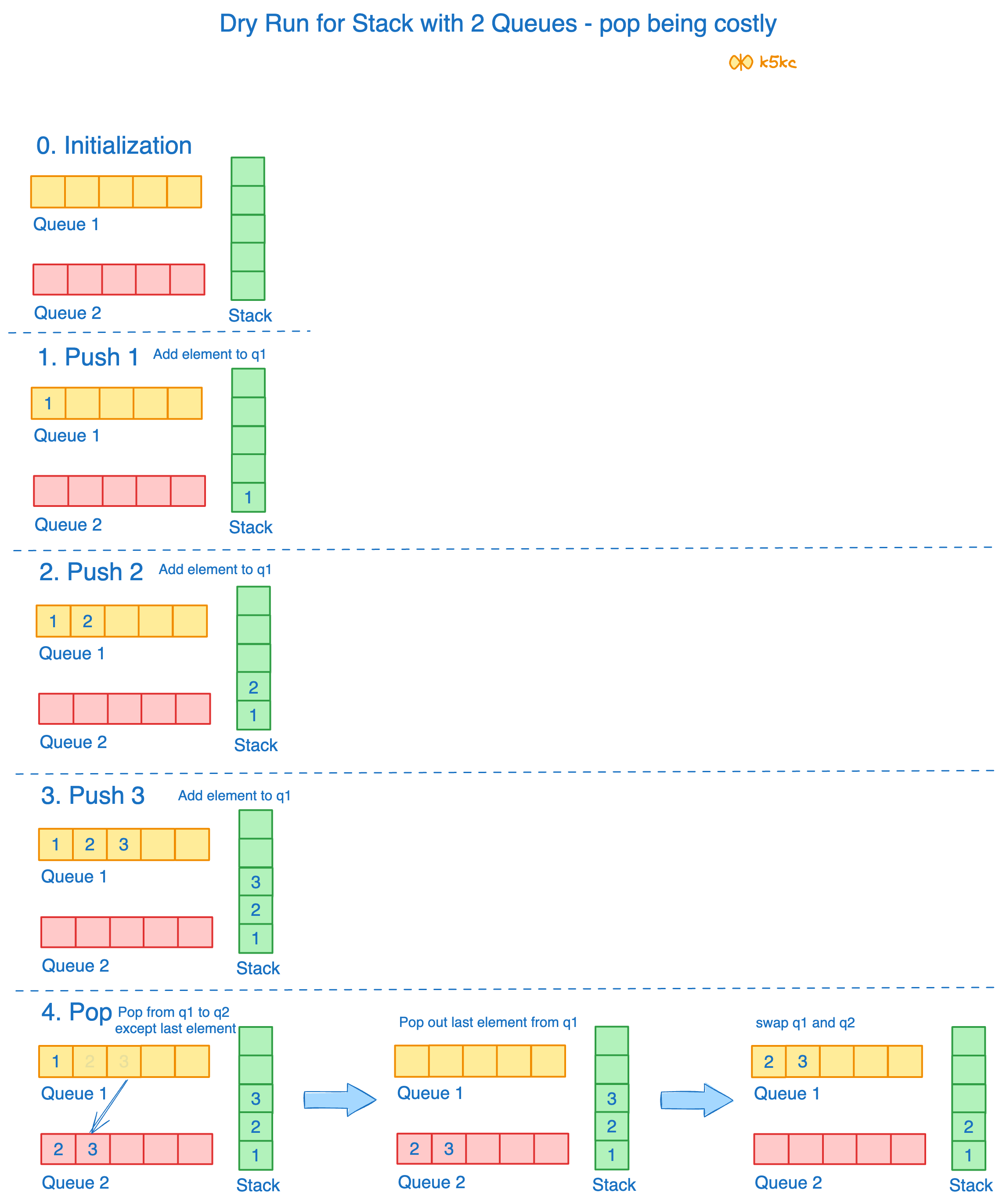
Method 3 - 2 Queues (By Making Pop Operation costly)
In push operation, the new element is always enqueued to q1. In pop() operation, if q2 is empty then all the elements except the last, are moved to q2. Finally the last element is dequeued from q1 and returned.
Pseudocode
push(x)
1) Enqueue x to q1
pop()
1) One by one dequeue everything except the last element from q1 and enqueue to q2.
2) Dequeue the last item of q1, the dequeued item is result, store it.
3) Swap the names of q1 and q2
4) Return the item stored in step 2
// Swapping of names is done to avoid one more movement of all elements from q2 to q1.
Code
Java
class MyStack {
Queue<Integer> q1, q2;
int currSize;
MyStack() {
q1 = new LinkedList<>();
q2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
void push(int x) {
q1.push(x);
currSize++;
}
void pop() {
if (q1.empty()){
return return;
}
// Leave one element in q1 and push rest to q2.
while (q2.size() != 1) {
q1.offer(q2.poll());
}
// Pop the only left element from q1
int num = q1.pop();
// swap the names of two queues
Queue<Integer> temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
}
int top() {
if (!q1.empty()) {
return q1.peek();
}
while (q2.size() != 1) {
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
// last pushed element
int topElement = q1.front();
// push last element to q2
q2.push(topElement);
// swap the two queues names
Queue<Integer> temp = q1;
q1 = q2;
q2 = temp;
return topElement;
}
int size() {
return currSize;
}
}
Complexity
Time Complexity:
- Push -
O(1) - Pop -
O(N) - Top -
O(N) - Stack Size -
O(1)
Dry Run
Method 3 - Using Only 1 Queue 🏆
The idea is to keep newly inserted element always at front, keeping order of previous elements same. Below are complete steps.
Pseudocode
push(x)
1) Let size of q be l.
1) Enqueue x to q
2) One by one Dequeue l items from Queue and enqueue them.
pop()
1) DeQueue from q
Code
Java
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
public void push(int x) {
queue.add(x);
// this will add front element into
// rear of queue
for (int i=1; i<queue.size(); i++) {
queue.offer(queue.poll());
}
}
public void pop() {
queue.remove();
}
public int top() {
return queue.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
return queue.isEmpty();
}
}
Complexity
Time Complexity:
- Push -
O(N) - Pop -
O(1) - Top -
O(1) - Stack Size -
O(1)
Dry Run
push 1
-----
front
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
| 1 | | | | | | insert 1
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
push 2
-----
front
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
| 1 | 2 | | | | | insert 2
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
front
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
| 2 | 1 | | | | | remove and insert 1
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
push 3
-----
front
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
| 2 | 1 | 3 | | | | insert 3
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
front
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
| 1 | 3 | 2 | | | | remove and insert 2
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
front
+----+----+----+----+----+----+
| 3 | 2 | 1 | | | | remove and insert 1
+----+----+----+----+----+----+