K Radius Subarray Averages
K Radius Subarray Averages Problem
Problem
You are given a 0-indexed array nums of n integers, and an integer k.
The k-radius average for a subarray of nums centered at some index i with the radius k is the average of all elements in nums between the indices i - k and i + k (inclusive). If there are less than k elements before or after the index i, then the k-radius average is -1.
Build and return an array avgs of length n where avgs[i] is the k-radius average for the subarray centered at index i.
The average of x elements is the sum of the x elements divided by x, using integer division. The integer division truncates toward zero, which means losing its fractional part.
- For example, the average of four elements
2,3,1, and5is(2 + 3 + 1 + 5) / 4 = 11 / 4 = 2.75, which truncates to2.
Examples
Example 1:
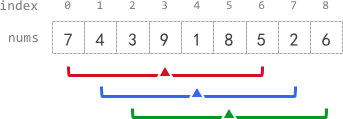
Input:
nums = [7,4,3,9,1,8,5,2,6], k = 3
Output:
[-1,-1,-1,5,4,4,-1,-1,-1]
Explanation:
- avg[0], avg[1], and avg[2] are -1 because there are less than k elements **before** each index.
- The sum of the subarray centered at index 3 with radius 3 is: 7 + 4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 = 37.
Using **integer division**, avg[3] = 37 / 7 = 5.
- For the subarray centered at index 4, avg[4] = (4 + 3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2) / 7 = 4.
- For the subarray centered at index 5, avg[5] = (3 + 9 + 1 + 8 + 5 + 2 + 6) / 7 = 4.
- avg[6], avg[7], and avg[8] are -1 because there are less than k elements **after** each index.
Example 2:
Input:
nums = [100000], k = 0
Output:
[100000]
Explanation:
- The sum of the subarray centered at index 0 with radius 0 is: 100000.
avg[0] = 100000 / 1 = 100000.
Example 3:
Input:
nums = [8], k = 100000
Output:
[-1]
Explanation:
- avg[0] is -1 because there are less than k elements before and after index 0.
Constraints:
n == nums.length1 <= n <= 1050 <= nums[i], k <= 105
Solution
Method 1 – Prefix Sum and Sliding Window
Intuition
To efficiently compute the average of every subarray of length 2k+1 centered at each index, we use a prefix sum array. This allows us to get the sum of any subarray in constant time. If there are not enough elements before or after an index, the answer is -1 for that index.
Approach
- Initialize an answer array with -1 for all positions.
- If
2k+1 > n, return the answer array (all -1). - Compute the prefix sum of the input array.
- For each index
ifromkton-k-1, compute the sum of the subarray fromi-ktoi+kusing the prefix sum. - Set the average at index
ias the integer division of the subarray sum by2k+1. - Return the answer array.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getAverages(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> ans(n, -1);
if (2 * k + 1 > n) return ans;
vector<long long> prefix(n + 1, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) prefix[i + 1] = prefix[i] + nums[i];
for (int i = k; i + k < n; ++i) {
long long sum = prefix[i + k + 1] - prefix[i - k];
ans[i] = sum / (2 * k + 1);
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func getAverages(nums []int, k int) []int {
n := len(nums)
ans := make([]int, n)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = -1
}
if 2*k+1 > n {
return ans
}
prefix := make([]int64, n+1)
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
prefix[i+1] = prefix[i] + int64(nums[i])
}
for i := k; i+k < n; i++ {
sum := prefix[i+k+1] - prefix[i-k]
ans[i] = int(sum / int64(2*k+1))
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int[] getAverages(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] ans = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(ans, -1);
if (2 * k + 1 > n) return ans;
long[] prefix = new long[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) prefix[i + 1] = prefix[i] + nums[i];
for (int i = k; i + k < n; i++) {
long sum = prefix[i + k + 1] - prefix[i - k];
ans[i] = (int)(sum / (2 * k + 1));
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun getAverages(nums: IntArray, k: Int): IntArray {
val n = nums.size
val ans = IntArray(n) { -1 }
if (2 * k + 1 > n) return ans
val prefix = LongArray(n + 1)
for (i in 0 until n) prefix[i + 1] = prefix[i] + nums[i]
for (i in k until n - k) {
val sum = prefix[i + k + 1] - prefix[i - k]
ans[i] = (sum / (2 * k + 1)).toInt()
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def getAverages(self, nums: list[int], k: int) -> list[int]:
n = len(nums)
ans = [-1] * n
if 2 * k + 1 > n:
return ans
prefix = [0]
for num in nums:
prefix.append(prefix[-1] + num)
for i in range(k, n - k):
s = prefix[i + k + 1] - prefix[i - k]
ans[i] = s // (2 * k + 1)
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn get_averages(nums: Vec<i32>, k: i32) -> Vec<i32> {
let n = nums.len();
let mut ans = vec![-1; n];
let k = k as usize;
if 2 * k + 1 > n {
return ans;
}
let mut prefix = vec![0i64; n + 1];
for i in 0..n {
prefix[i + 1] = prefix[i] + nums[i] as i64;
}
for i in k..n - k {
let sum = prefix[i + k + 1] - prefix[i - k];
ans[i] = (sum / (2 * k + 1) as i64) as i32;
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
getAverages(nums: number[], k: number): number[] {
const n = nums.length;
const ans = Array(n).fill(-1);
if (2 * k + 1 > n) return ans;
const prefix = [0];
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) prefix.push(prefix[prefix.length - 1] + nums[i]);
for (let i = k; i + k < n; i++) {
const sum = prefix[i + k + 1] - prefix[i - k];
ans[i] = Math.floor(sum / (2 * k + 1));
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), wherenis the length of the array, since prefix sums and window averages are computed in linear time. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the prefix sum array and answer array.