Kth Smallest Number in Multiplication Table
HardUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Nearly everyone has used the Multiplication Table. The multiplication table of size m x n is an integer matrix mat where mat[i][j] == i * j
(1-indexed).
Given three integers m, n, and k, return thekth smallest element in them x n multiplication table.
Examples
Example 1
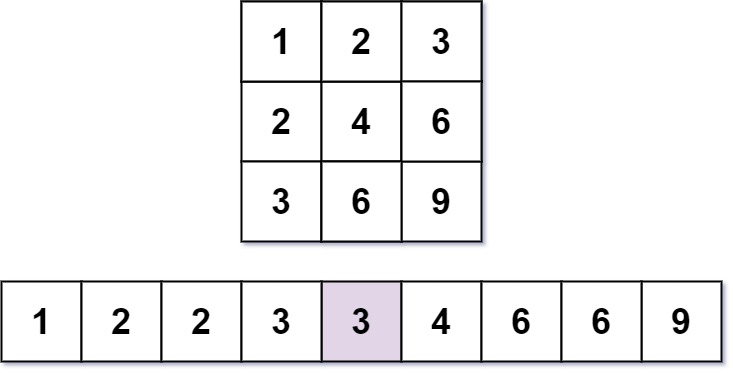
Input: m = 3, n = 3, k = 5
Output: 3
Explanation: The 5th smallest number is 3.
Example 2
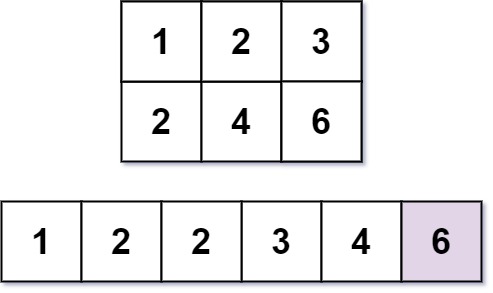
Input: m = 2, n = 3, k = 6
Output: 6
Explanation: The 6th smallest number is 6.
Constraints
1 <= m, n <= 3 * 10^41 <= k <= m * n
Solution
Method 1 – Binary Search on Value
Intuition
The multiplication table is sorted in each row and column. To find the k-th smallest number, we can use binary search on the value range. For a candidate value x, count how many numbers in the table are ≤ x. If the count is at least k, x could be the answer.
Approach
- Set left = 1, right = m * n (the largest value in the table).
- While left < right:
- Compute mid = (left + right) // 2.
- For each row i, count how many numbers ≤ mid (which is min(mid // i, n)).
- Sum the counts for all rows.
- If the count ≥ k, set right = mid; else, set left = mid + 1.
- Return left as the answer.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int findKthNumber(int m, int n, int k) {
int l = 1, r = m * n;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2, cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) cnt += min(mid / i, n);
if (cnt >= k) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
};
Go
func findKthNumber(m int, n int, k int) int {
l, r := 1, m*n
for l < r {
mid := (l + r) / 2
cnt := 0
for i := 1; i <= m; i++ {
cnt += min(mid/i, n)
}
if cnt >= k {
r = mid
} else {
l = mid + 1
}
}
return l
}
func min(a, b int) int { if a < b { return a }; return b }
Java
class Solution {
public int findKthNumber(int m, int n, int k) {
int l = 1, r = m * n;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (l + r) / 2, cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i) cnt += Math.min(mid / i, n);
if (cnt >= k) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun findKthNumber(m: Int, n: Int, k: Int): Int {
var l = 1
var r = m * n
while (l < r) {
val mid = (l + r) / 2
var cnt = 0
for (i in 1..m) cnt += minOf(mid / i, n)
if (cnt >= k) r = mid else l = mid + 1
}
return l
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def findKthNumber(self, m: int, n: int, k: int) -> int:
l, r = 1, m * n
while l < r:
mid = (l + r) // 2
cnt = sum(min(mid // i, n) for i in range(1, m+1))
if cnt >= k:
r = mid
else:
l = mid + 1
return l
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn find_kth_number(m: i32, n: i32, k: i32) -> i32 {
let (mut l, mut r) = (1, m * n);
while l < r {
let mid = (l + r) / 2;
let mut cnt = 0;
for i in 1..=m {
cnt += (mid / i).min(n);
}
if cnt >= k { r = mid; } else { l = mid + 1; }
}
l
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
findKthNumber(m: number, n: number, k: number): number {
let l = 1, r = m * n;
while (l < r) {
const mid = Math.floor((l + r) / 2);
let cnt = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= m; ++i) cnt += Math.min(Math.floor(mid / i), n);
if (cnt >= k) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return l;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m log(mn)), where m is the number of rows. Each binary search step checks all rows. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1), only a few variables are used.