Largest Submatrix With Rearrangements
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
You are given a binary matrix matrix of size m x n, and you are allowed to rearrange the columns of the matrix in any order.
Return the area of the largest submatrix withinmatrix _whereevery element of the submatrix is _1 after reordering the columns optimally.
Examples
Example 1
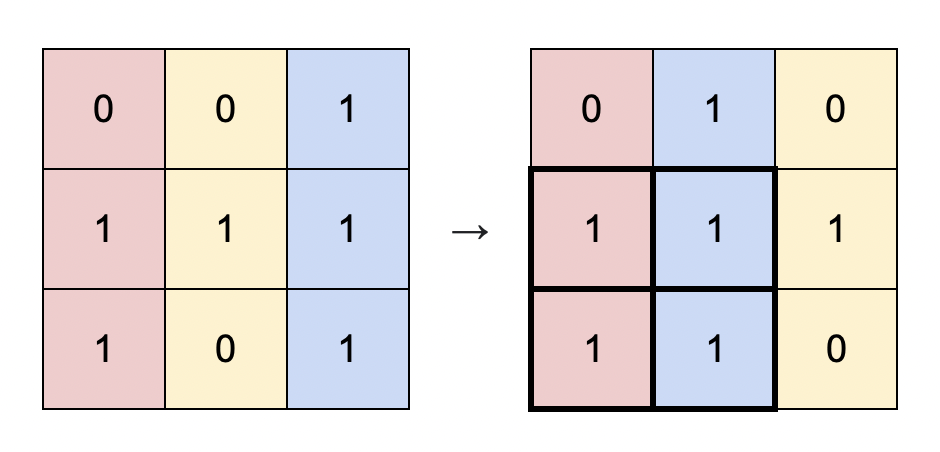
Input: matrix = [[0,0,1],[1,1,1],[1,0,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: You can rearrange the columns as shown above.
The largest submatrix of 1s, in bold, has an area of 4.
Example 2
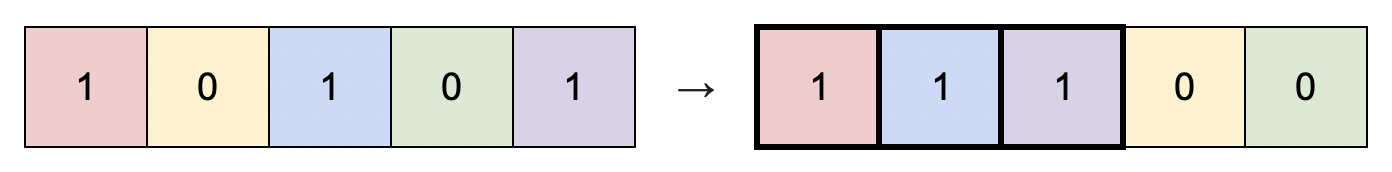
Input: matrix = [[1,0,1,0,1]]
Output: 3
Explanation: You can rearrange the columns as shown above.
The largest submatrix of 1s, in bold, has an area of 3.
Example 3
Input: matrix = [[1,1,0],[1,0,1]]
Output: 2
Explanation: Notice that you must rearrange entire columns, and there is no way to make a submatrix of 1s larger than an area of 2.
Constraints
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m * n <= 10^5matrix[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution
Method 1 – Histogram and Greedy Sorting
Intuition
For each row, treat the number of consecutive 1's above (including itself) as a histogram. By sorting each row's histogram in descending order, we can greedily maximize the area of a submatrix of 1's after rearranging columns.
Approach
- For each cell, compute the height of consecutive 1's above (including itself).
- For each row, sort the histogram heights in descending order.
- For each position in the sorted row, calculate the area as height * (index+1).
- Track and return the maximum area found.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int largestSubmatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
int m = matrix.size(), n = matrix[0].size(), ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (matrix[i][j]) matrix[i][j] += matrix[i-1][j];
for (auto& row : matrix) {
vector<int> h = row;
sort(h.rbegin(), h.rend());
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
ans = max(ans, h[j] * (j+1));
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func largestSubmatrix(matrix [][]int) int {
m, n := len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
ans := 0
for i := 1; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if matrix[i][j] == 1 {
matrix[i][j] += matrix[i-1][j]
}
}
}
for _, row := range matrix {
h := append([]int(nil), row...)
sort.Sort(sort.Reverse(sort.IntSlice(h)))
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if h[j]*(j+1) > ans { ans = h[j]*(j+1) }
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int largestSubmatrix(int[][] matrix) {
int m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length, ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (matrix[i][j] == 1) matrix[i][j] += matrix[i-1][j];
for (int[] row : matrix) {
int[] h = row.clone();
Arrays.sort(h);
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j)
ans = Math.max(ans, h[n-1-j] * (j+1));
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun largestSubmatrix(matrix: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = matrix.size
val n = matrix[0].size
var ans = 0
for (i in 1 until m)
for (j in 0 until n)
if (matrix[i][j] == 1) matrix[i][j] += matrix[i-1][j]
for (row in matrix) {
val h = row.copyOf()
h.sortDescending()
for (j in 0 until n)
ans = maxOf(ans, h[j] * (j+1))
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def largestSubmatrix(self, matrix: list[list[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(n):
if matrix[i][j]:
matrix[i][j] += matrix[i-1][j]
ans = 0
for row in matrix:
h = sorted(row, reverse=True)
for j, v in enumerate(h):
ans = max(ans, v * (j+1))
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn largest_submatrix(matrix: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = matrix.len();
let n = matrix[0].len();
let mut mat = matrix.clone();
for i in 1..m {
for j in 0..n {
if mat[i][j] != 0 {
mat[i][j] += mat[i-1][j];
}
}
}
let mut ans = 0;
for row in mat.iter_mut() {
row.sort_by(|a, b| b.cmp(a));
for (j, &v) in row.iter().enumerate() {
ans = ans.max(v * (j as i32 + 1));
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
largestSubmatrix(matrix: number[][]): number {
const m = matrix.length, n = matrix[0].length
for (let i = 1; i < m; ++i)
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j)
if (matrix[i][j]) matrix[i][j] += matrix[i-1][j]
let ans = 0
for (const row of matrix) {
const h = [...row].sort((a, b) => b - a)
for (let j = 0; j < n; ++j)
ans = Math.max(ans, h[j] * (j+1))
}
return ans
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(m*n*log n), where m and n are matrix dimensions. Each row is sorted. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for sorting each row.