Letter Combinations of a Phone Number
Problem
Given a string containing digits from 2-9 inclusive, return all possible letter combinations that the number could represent. Return the answer in any order.
A mapping of digit to letters (just like on the telephone buttons) is given below. Note that 1 does not map to any letters.

Examples
Example 1:
Input: digits = "23"
Output: ["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd","ce","cf"]
Example 2:
Input: digits = ""
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: digits = "2"
Output: ["a","b","c"]
Solution
How do we solve this problem? Let’s quickly take our phone and look into the keypad. We will find –
0 --> {}
1 --> {}
2 --> {a,b,c}
3 --> {d,e,f}
4 --> {g,h,i}
5 --> {j,k,l}
6 --> {m,n,o}
7 --> {p,q,r,s}
8 --> {t,u,v}
9 --> {w,x,y,z}
Now if we press 2 there could be 3 possible values {a, b, c}. Then if we press 3 then the possible words would be all combination of 2 letters, one from 2–>{a, b, c} and other from 3->{d, e, f}. If we press down another number then the words formed will have first letter from 2-{a, b, c}, second number from 3->{d, e, f}, and 3rd letter from 4->{g, h, i}.
Does this look familiar? Yes, we solved this problem: [List Combinations - Generate unique combinations from list selecting 1 element from each](list-combinations-generate-unique-combinations-from-list-selecting-1-element-from-each)
Basically we run the algorithm with a list {L2, L3, L4} where
L2= {a, b, c}
L3= {d, e, f}
L4= {g, h, i}
So, given a sequence of n digits we will generate a list of lists using a precomputed map from digit to list of characters. Then we will call the permuteList.
Method 1 -DFS
This problem can be solves by a typical DFS algorithm. DFS problems are very similar and can be solved by using a simple recursion.
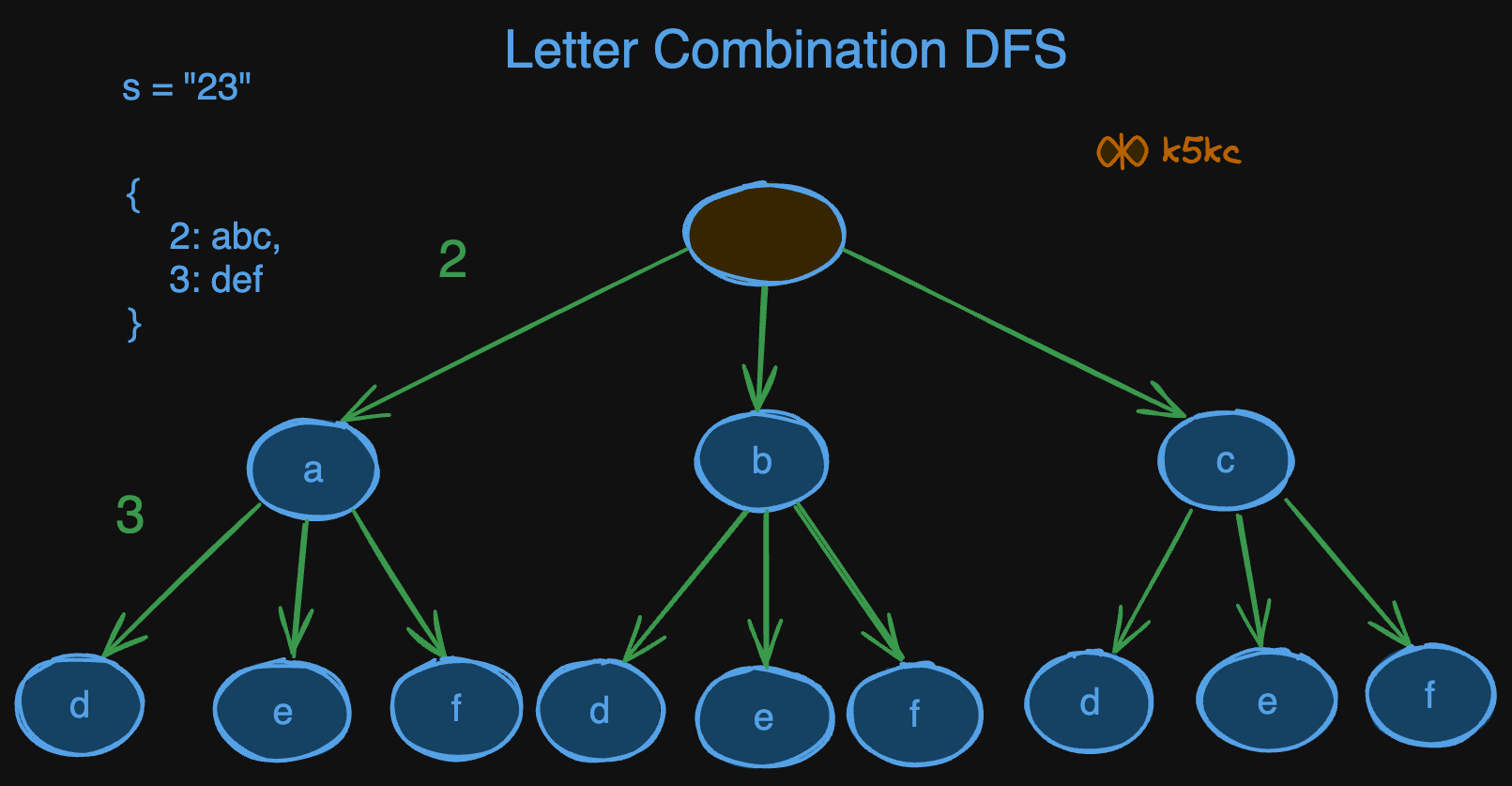
So, we will start with first index 0 in digits, then the next one, and so on.
Code
Java
Using String As Sub Ans
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
HashMap<Integer, String> digitsToCharMap = new HashMap<Integer, String> ();
digitsToCharMap.put(2, "abc");
digitsToCharMap.put(3, "def");
digitsToCharMap.put(4, "ghi");
digitsToCharMap.put(5, "jkl");
digitsToCharMap.put(6, "mno");
digitsToCharMap.put(7, "pqrs");
digitsToCharMap.put(8, "tuv");
digitsToCharMap.put(9, "wxyz");
digitsToCharMap.put(0, "");
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<String> ();
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0)
return result;
String currStr = new String();
backtrack(digits, 0, currStr, ans, digitsToCharMap);
return ans;
}
public void backtrack(String digits, int i, String currStr, List<String> result, Map<Integer, String> digitsToCharMap) {
if (digits.length() == currStr.size()) {
result.add(currStr);
return;
}
int currDigit = digits.charAt(i) - '0';
for (char c: digitsToCharMap.get(currDigit).toCharArray()){
backtrack(digits, i+1, currStr + c, result, digitsToCharMap);
}
}
Instead of digitsToCharMap we can also use digitsToCharArr and use index to get right combination:
// array
String[] mapping = {
"", "", "abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"
};
// combination:
String candidates = mapping[digits.charAt(index) - '0'];
Using StringBuilder
We can do few improvements in above code. WE can use StringBuilder instead of String for currStr. Also, we are storing integer as keys in digitsToCharMap. We have to do conversion again and again from char to integer. So, we can just keep it char.
Also, we can keep char array as value in the digitsToCharMap, to avoid conversions.
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
Map<Character, char[]> digitsToCharMap = new HashMap<Integer, String> ();
digitsToCharMap.put(2, "abc".toCharArray());
digitsToCharMap.put(3, "def".toCharArray());
digitsToCharMap.put(4, "ghi".toCharArray());
digitsToCharMap.put(5, "jkl".toCharArray());
digitsToCharMap.put(6, "mno".toCharArray());
digitsToCharMap.put(7, "pqrs".toCharArray());
digitsToCharMap.put(8, "tuv".toCharArray());
digitsToCharMap.put(9, "wxyz".toCharArray());
digitsToCharMap.put(0, "".toCharArray());
ArrayList<String> result = new ArrayList<String> ();
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0)
return result;
StringBuilder currStr = new StringBuilder();
backtrack(digits, 0, currStr, result, digitsToCharMap);
return result;
}
public void backtrack(String digits, int i, StringBuilder currStr, List<String> result, Map<Character, char[]> digitsToCharMap) {
if (digits.length() == currStr.size()) {
result.add(currStr.toString());
return;
}
int currDigit = digits.charAt(i) - '0';
for (char c: digitsToCharMap.get(currDigit).toCharArray()){
backtrack(digits, i+1, currStr.append(c), result, digitsToCharMap);
currStr.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
}
}
Using Char Array
If we use a char array to store each candidate, the code can be much more precise.
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
HashMap<Character, char[] > dict = new HashMap<Character, char[] > ();
dict.put('2', new char[] {
'a', 'b', 'c'
});
dict.put('3', new char[] {
'd', 'e', 'f'
});
dict.put('4', new char[] {
'g', 'h', 'i'
});
dict.put('5', new char[] {
'j', 'k', 'l'
});
dict.put('6', new char[] {
'm', 'n', 'o'
});
dict.put('7', new char[] {
'p', 'q', 'r', 's'
});
dict.put('8', new char[] {
't', 'u', 'v'
});
dict.put('9', new char[] {
'w', 'x', 'y', 'z'
});
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String> ();
if (digits == null || digits.length() == 0) {
return result;
}
char[] arr = new char[digits.length()];
helper(digits, 0, dict, result, arr);
return result;
}
private void helper(String digits, int index, HashMap<Character, char[] > dict, List<String> result, char[] arr) {
if (index == digits.length()) {
result.add(new String(arr));
return;
}
char number = digits.charAt(index);
char[] candidates = dict.get(number);
for (int i = 0; i<candidates.length; i++) {
arr[index] = candidates[i];
helper(digits, index + 1, dict, result, arr);
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n*4^n), As, we loop over n chars in stringdigits, so it will ben* X.Xwill come from cases for eg.9, it may map towxyzi.e. 4 chars, time complexity is4^n, hence overall time complexity. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n)assuming recursive stack.