Linked List Cycle 4 - Delete cycle
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Problem
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
Examples
Example 1
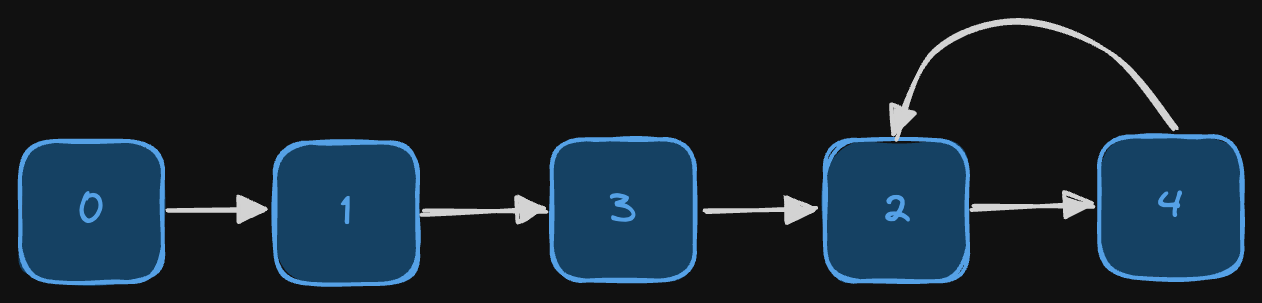
Input: head = [0, 1, 3, 2, 4]
output: [0, 1, 3, 2, 4]
Explanation: Cycle starts at node 2
Example 2
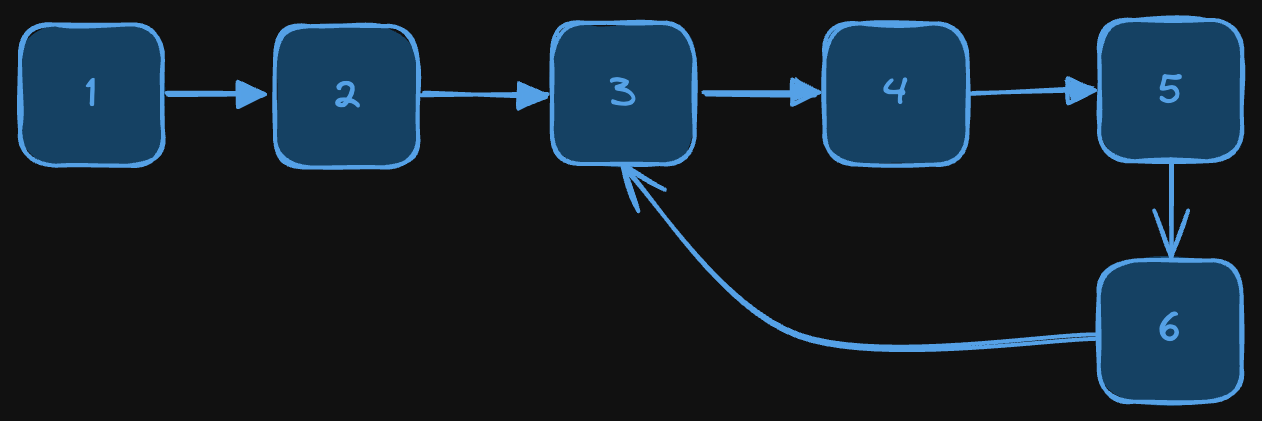
Input: head = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Explanation: Cycle starts at node 3
Solution
Method 1 - Using slow and fast pointer
The problem has 3 steps :
- Detect Cycle: Use Floyd’s Tortoise and Hare Algorithm to detect if a cycle exists. - [Linked List Cycle 1 - Detect Cycle](linked-list-cycle-1-detect-cycle)
- Find Cycle Entry Point: If a cycle is detected, use the pointers to find the start of the cycle. - [Linked List Cycle 2 - Find Start of a Cycle](linked-list-cycle-2-find-start-of-a-cycle)
- Remove Cycle: Modify the
nextpointer of the last node in the cycle to remove the cycle. Please go through 1 and 2 before continuing this post for better understanding.
Code
Java
public class Solution {
public void removeCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
// Step 1: Detect cycle using Floyd’s Tortoise and Hare Algorithm
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (slow == fast) { // Cycle detected
breakCycle(head, slow);
return;
}
}
}
private void breakCycle(ListNode head, ListNode meetingPoint) {
ListNode start = head;
ListNode cycleNode = meetingPoint;
// Step 2: Find the entry point of the cycle
while (start != cycleNode) {
start = start.next;
cycleNode = cycleNode.next;
}
// Step 3: Find the last node in the cycle and break the cycle
ListNode lastNode = cycleNode;
while (lastNode.next != cycleNode) {
lastNode = lastNode.next;
}
lastNode.next = null; // Remove the cycle
}
// Helper function to create a cycle for testing
public void createCycle(ListNode head, int pos) {
if (pos == -1)
return;
ListNode tail = head, cycleEntry = null;
int index = 0;
while (tail.next != null) {
if (index == pos) {
cycleEntry = tail;
}
tail = tail.next;
index++;
}
tail.next = cycleEntry; // Create the cycle
}
// Helper function to print the linked list
public void printLinkedList(ListNode head) {
ListNode current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.val + " -> ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("None");
}
// Helper function to create a linked list from an array
public ListNode createLinkedList(int[] arr) {
if (arr.length == 0)
return null;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode current = dummy;
for (int value : arr) {
current.next = new ListNode(value);
current = current.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
int[] arr1 = {3, 2, 0, -4};
ListNode head1 = solution.createLinkedList(arr1);
solution.createCycle(head1, 1);
System.out.println("Linked List with Cycle:");
solution.printLinkedList(
head1); // This will print indefinitely if there is a cycle
solution.removeCycle(head1);
System.out.println("Linked List after removing Cycle:");
solution.printLinkedList(head1);
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def removeCycle(self, head: ListNode) -> None:
slow, fast = head, head
# Step 1: Detect cycle using Floyd’s Tortoise and Hare Algorithm
while fast and fast.next:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next.next
if slow == fast: # Cycle detected
self.breakCycle(head, slow)
return
def breakCycle(self, head: ListNode, meetingPoint: ListNode) -> None:
start, cycleNode = head, meetingPoint
# Step 2: Find the entry point of the cycle
while start != cycleNode:
start = start.next
cycleNode = cycleNode.next
# Step 3: Find the last node in the cycle and break the cycle
lastNode = cycleNode
while lastNode.next != cycleNode:
lastNode = lastNode.next
lastNode.next = None # Remove the cycle
# Helper function to create a cycle for testing
def create_cycle(head: ListNode, pos: int) -> None:
if pos == -1:
return
tail, cycleEntry = head, None
index = 0
while tail.next:
if index == pos:
cycleEntry = tail
tail = tail.next
index += 1
if cycleEntry:
tail.next = cycleEntry # Create the cycle
# Helper function to print the linked list
def print_linked_list(head: ListNode) -> None:
current = head
visited = set()
while current:
if current in visited:
print(f"{current.val}(cycle starts here) -> ", end="")
break
print(f"{current.val} -> ", end="")
visited.add(current)
current = current.next
print("None")
# Helper function to create a linked list from an array
def create_linked_list(arr) -> ListNode:
if not arr:
return None
dummy = ListNode(0)
current = dummy
for val in arr:
current.next = ListNode(val)
current = current.next
return dummy.next
# Example usage
arr1 = [3, 2, 0, -4]
head1 = create_linked_list(arr1)
create_cycle(head1, 1)
print("Linked List with Cycle:")
print_linked_list(head1) # This will print indefinitely if there is a cycle
solution = Solution()
solution.removeCycle(head1)
print("Linked List after removing Cycle:")
print_linked_list(head1)
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n)wherenis the number of nodes in the linked list- Cycle Detection:
O(n), wherenis the number of nodes in the linked list. - Finding Cycle Entry Point:
O(n), as in the worst case, you may need to traverse almost all nodes. - Removing Cycle:
O(n), as it involves another traversal to find the last node in the cycle.
- Cycle Detection:
- 🧺 Space complexity:
O(1), as we are using a constant amount of extra space for pointers.