Longest Cycle in a Directed Graph
Problem
You are given a directed graph of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1, where each node has at most one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented with a given 0-indexed array edges of size n, indicating that there is a directed edge from node i to node edges[i]. If there is no outgoing edge from node i, then edges[i] == -1.
Return the length of the longest cycle in the graph. If no cycle exists, return -1.
A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node.
Examples
Example 1:
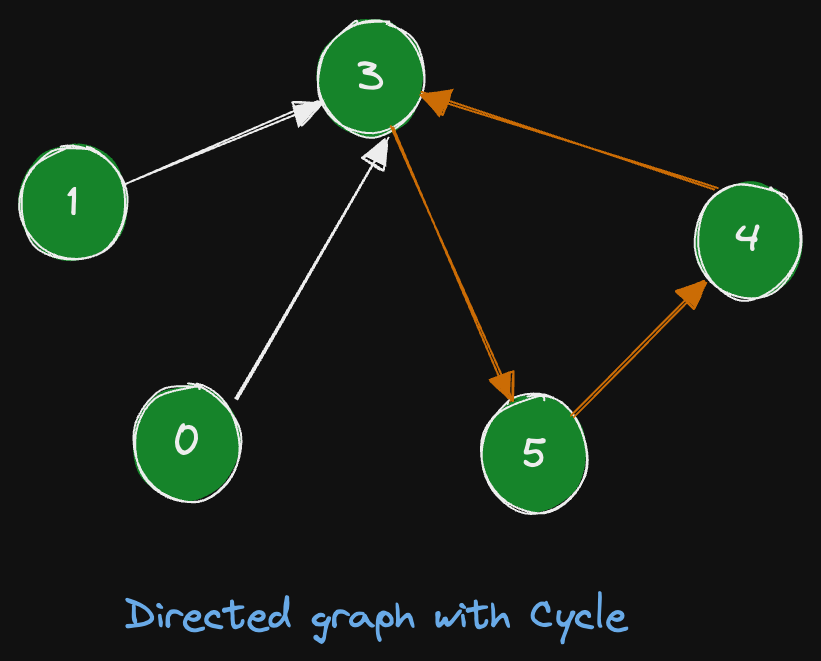
Input: edges = [3,3,4,2,3]
Output: 3
Explanation: The longest cycle in the graph is the cycle: 2 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2.
The length of this cycle is 3, so 3 is returned.
Example 2:
graph LR 0 --> 2 --> 3 --> 1
Input: edges = [2,-1,3,1]
Output: -1
Explanation: There are no cycles in this graph.
Solution
Method 1 – DFS with Visit Time Tracking
Intuition
The main idea is to use DFS to traverse the graph and track the visit time of each node during the current path. If we revisit a node that is already in the current path, we have found a cycle, and the cycle's length is the difference between the current time and the time when we first visited that node. By marking nodes as globally visited, we avoid redundant work.
Approach
- Iterate through each node in the graph.
- For each unvisited node, perform a DFS traversal:
- Use a map or array to record the time step when each node is first visited in the current path.
- If a node is revisited in the current path, calculate the cycle length.
- Mark nodes as globally visited to avoid reprocessing.
- Track the maximum cycle length found during all traversals.
- Return the maximum cycle length, or -1 if no cycle exists.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int longestCycle(vector<int>& edges) {
int n = edges.size(), ans = -1;
vector<bool> vis(n, false);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
int cur = i, dist = 0;
while (cur != -1) {
if (mp.count(cur)) {
ans = max(ans, dist - mp[cur]);
break;
}
if (vis[cur]) break;
vis[cur] = true;
mp[cur] = dist++;
cur = edges[cur];
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func longestCycle(edges []int) int {
n := len(edges)
vis := make([]bool, n)
ans := -1
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if vis[i] {
continue
}
mp := make(map[int]int)
cur, dist := i, 0
for cur != -1 {
if v, ok := mp[cur]; ok {
if dist-v > ans {
ans = dist - v
}
break
}
if vis[cur] {
break
}
vis[cur] = true
mp[cur] = dist
dist++
cur = edges[cur]
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int longestCycle(int[] edges) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[edges.length];
int ans = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
if (visited[i]) continue;
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int cur = i, dist = 0;
while (cur != -1) {
if (map.containsKey(cur)) {
ans = Math.max(ans, dist - map.get(cur));
break;
}
if (visited[cur]) break;
visited[cur] = true;
map.put(cur, dist++);
cur = edges[cur];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun longestCycle(edges: IntArray): Int {
val n = edges.size
val vis = BooleanArray(n)
var ans = -1
for (i in 0 until n) {
if (vis[i]) continue
val mp = mutableMapOf<Int, Int>()
var cur = i
var dist = 0
while (cur != -1) {
if (mp.containsKey(cur)) {
ans = maxOf(ans, dist - mp[cur]!!)
break
}
if (vis[cur]) break
vis[cur] = true
mp[cur] = dist++
cur = edges[cur]
}
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def longestCycle(self, edges: list[int]) -> int:
n = len(edges)
vis = [False] * n
ans = -1
for i in range(n):
if vis[i]:
continue
mp = dict()
cur, dist = i, 0
while cur != -1:
if cur in mp:
ans = max(ans, dist - mp[cur])
break
if vis[cur]:
break
vis[cur] = True
mp[cur] = dist
dist += 1
cur = edges[cur]
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn longest_cycle(edges: Vec<i32>) -> i32 {
let n = edges.len();
let mut vis = vec![false; n];
let mut ans = -1;
for i in 0..n {
if vis[i] { continue; }
let mut mp = std::collections::HashMap::new();
let mut cur = i;
let mut dist = 0;
while cur != usize::MAX && cur < n {
if let Some(&v) = mp.get(&cur) {
ans = ans.max(dist - v);
break;
}
if vis[cur] { break; }
vis[cur] = true;
mp.insert(cur, dist);
dist += 1;
let next = edges[cur];
if next == -1 {
cur = usize::MAX;
} else {
cur = next as usize;
}
}
}
ans as i32
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
longestCycle(edges: number[]): number {
const n = edges.length;
const vis = Array(n).fill(false);
let ans = -1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (vis[i]) continue;
const mp = new Map<number, number>();
let cur = i, dist = 0;
while (cur !== -1) {
if (mp.has(cur)) {
ans = Math.max(ans, dist - mp.get(cur)!);
break;
}
if (vis[cur]) break;
vis[cur] = true;
mp.set(cur, dist++);
cur = edges[cur];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(n), since each node is visited at most once in the global traversal, and each edge is followed at most once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(n), for the visited array and the local map for each traversal.