Longest Line of Consecutive One in Matrix
MediumUpdated: Aug 2, 2025
Practice on:
Problem
Given an m x n binary matrix mat, return the length of the longest line of consecutive one in the matrix.
The line could be horizontal, vertical, diagonal, or anti-diagonal.
Examples
Example 1:
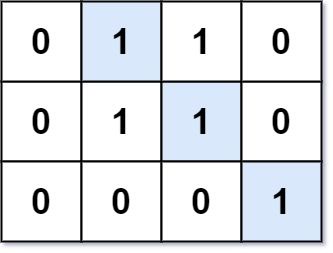
Input: mat = [[0,1,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,1]]
Output: 3
Example 2:
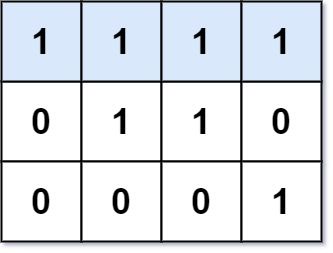
Input: mat = [[1,1,1,1],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,1]]
Output: 4
Constraints:
m == mat.lengthn == mat[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10^41 <= m * n <= 10^4mat[i][j]is either0or1.
Solution
Method 1 – Dynamic Programming for All Directions (1)
Intuition
To find the longest line of consecutive ones in all four directions (horizontal, vertical, diagonal, anti-diagonal), we use dynamic programming to keep track of the length of consecutive ones ending at each cell for each direction.
Approach
- Initialize a 3D dp array where
dp[i][j][d]stores the length of consecutive ones ending at cell (i, j) in direction d (0: horizontal, 1: vertical, 2: diagonal, 3: anti-diagonal). - For each cell in the matrix:
- If the cell is 1, update dp for all four directions based on previous cells.
- Update the answer with the maximum value found.
- Return the answer.
Code
C++
class Solution {
public:
int longestLine(vector<vector<int>>& mat) {
int m = mat.size(), n = mat[0].size(), ans = 0;
vector<vector<vector<int>>> dp(m, vector<vector<int>>(n, vector<int>(4)));
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1) {
dp[i][j][0] = (j > 0 ? dp[i][j-1][0] : 0) + 1; // horizontal
dp[i][j][1] = (i > 0 ? dp[i-1][j][1] : 0) + 1; // vertical
dp[i][j][2] = (i > 0 && j > 0 ? dp[i-1][j-1][2] : 0) + 1; // diagonal
dp[i][j][3] = (i > 0 && j+1 < n ? dp[i-1][j+1][3] : 0) + 1; // anti-diagonal
ans = max({ans, dp[i][j][0], dp[i][j][1], dp[i][j][2], dp[i][j][3]});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
Go
func longestLine(mat [][]int) int {
m, n := len(mat), len(mat[0])
dp := make([][][]int, m)
for i := range dp {
dp[i] = make([][]int, n)
for j := range dp[i] {
dp[i][j] = make([]int, 4)
}
}
ans := 0
for i := 0; i < m; i++ {
for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
if mat[i][j] == 1 {
dp[i][j][0] = 1
if j > 0 {
dp[i][j][0] += dp[i][j-1][0]
}
dp[i][j][1] = 1
if i > 0 {
dp[i][j][1] += dp[i-1][j][1]
}
dp[i][j][2] = 1
if i > 0 && j > 0 {
dp[i][j][2] += dp[i-1][j-1][2]
}
dp[i][j][3] = 1
if i > 0 && j+1 < n {
dp[i][j][3] += dp[i-1][j+1][3]
}
for d := 0; d < 4; d++ {
if dp[i][j][d] > ans {
ans = dp[i][j][d]
}
}
}
}
}
return ans
}
Java
class Solution {
public int longestLine(int[][] mat) {
int m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length, ans = 0;
int[][][] dp = new int[m][n][4];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1) {
dp[i][j][0] = (j > 0 ? dp[i][j-1][0] : 0) + 1;
dp[i][j][1] = (i > 0 ? dp[i-1][j][1] : 0) + 1;
dp[i][j][2] = (i > 0 && j > 0 ? dp[i-1][j-1][2] : 0) + 1;
dp[i][j][3] = (i > 0 && j+1 < n ? dp[i-1][j+1][3] : 0) + 1;
for (int d = 0; d < 4; d++) ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][j][d]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Kotlin
class Solution {
fun longestLine(mat: Array<IntArray>): Int {
val m = mat.size
val n = mat[0].size
val dp = Array(m) { Array(n) { IntArray(4) } }
var ans = 0
for (i in 0 until m) {
for (j in 0 until n) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1) {
dp[i][j][0] = if (j > 0) dp[i][j-1][0] + 1 else 1
dp[i][j][1] = if (i > 0) dp[i-1][j][1] + 1 else 1
dp[i][j][2] = if (i > 0 && j > 0) dp[i-1][j-1][2] + 1 else 1
dp[i][j][3] = if (i > 0 && j+1 < n) dp[i-1][j+1][3] + 1 else 1
for (d in 0..3) ans = maxOf(ans, dp[i][j][d])
}
}
}
return ans
}
}
Python
class Solution:
def longestLine(self, mat: list[list[int]]) -> int:
m, n = len(mat), len(mat[0])
dp = [[[0]*4 for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]
ans = 0
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if mat[i][j] == 1:
dp[i][j][0] = (dp[i][j-1][0] if j > 0 else 0) + 1
dp[i][j][1] = (dp[i-1][j][1] if i > 0 else 0) + 1
dp[i][j][2] = (dp[i-1][j-1][2] if i > 0 and j > 0 else 0) + 1
dp[i][j][3] = (dp[i-1][j+1][3] if i > 0 and j+1 < n else 0) + 1
ans = max(ans, dp[i][j][0], dp[i][j][1], dp[i][j][2], dp[i][j][3])
return ans
Rust
impl Solution {
pub fn longest_line(mat: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let m = mat.len();
let n = mat[0].len();
let mut dp = vec![vec![vec![0; 4]; n]; m];
let mut ans = 0;
for i in 0..m {
for j in 0..n {
if mat[i][j] == 1 {
dp[i][j][0] = if j > 0 { dp[i][j-1][0] } else { 0 } + 1;
dp[i][j][1] = if i > 0 { dp[i-1][j][1] } else { 0 } + 1;
dp[i][j][2] = if i > 0 && j > 0 { dp[i-1][j-1][2] } else { 0 } + 1;
dp[i][j][3] = if i > 0 && j+1 < n { dp[i-1][j+1][3] } else { 0 } + 1;
ans = ans.max(dp[i][j][0].max(dp[i][j][1]).max(dp[i][j][2]).max(dp[i][j][3]));
}
}
}
ans
}
}
TypeScript
class Solution {
longestLine(mat: number[][]): number {
const m = mat.length, n = mat[0].length;
const dp = Array.from({length: m}, () => Array.from({length: n}, () => Array(4).fill(0)));
let ans = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] === 1) {
dp[i][j][0] = (j > 0 ? dp[i][j-1][0] : 0) + 1;
dp[i][j][1] = (i > 0 ? dp[i-1][j][1] : 0) + 1;
dp[i][j][2] = (i > 0 && j > 0 ? dp[i-1][j-1][2] : 0) + 1;
dp[i][j][3] = (i > 0 && j+1 < n ? dp[i-1][j+1][3] : 0) + 1;
ans = Math.max(ans, dp[i][j][0], dp[i][j][1], dp[i][j][2], dp[i][j][3]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
Complexity
- ⏰ Time complexity:
O(mn), where m and n are the dimensions of the matrix. We scan each cell once. - 🧺 Space complexity:
O(mn), for the dp array.